Leaf morphology
advertisement

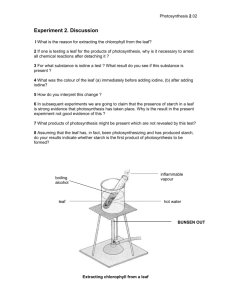
PLANT MORPHOLOGY PLANTS ARE AUTOTROPHIC by Maria Koprowska Objectives, students will be able to: 1. describe a typical plant and leaf morphology 2. explain the relationship between leaf morphology and its function 3. define what photosynthesis is 4. interpret photosynthesis as an essential vital process Key question 1: Why are plant parts organized in systems? Each part of a plant is a specialized organ that has a different function. All parts together cooperate with each other and make up a system. Plant structure Most plants consist/składać się of two main parts: 1. that grows above the ground - shoot system/pęd stem/łodyga, node/węzeł, bud/pączek leaves/liście, fruit/owoc, flower/kwiat) 2. that grows underground - root system/korzeń 3. (primary root/korzeń główny, secondary root/korzeń boczny) 1 Key question 2: Do all leaves look the same? No, they come in various shapes/różne kształty and sizes, but most often they have the same structural elements. Leaf morphology Leaf is a specialized organ that is meant for food production. It is the most important site of the process of photosynthesis. Most leaves consist of two main parts: a leaf blade and petiole. However, we can point out more leaf features according to which we can group them into different categories. tip-wierzchołek, blade-blaszka liściowa, base-nasada blaszki, petiole-ogonek, stipules-przylistek, bud-pąk, midrib-nerw główny, margin-brzeg, lateral vein-nerw boczny Leaves come as simple leaves/liście pojedyncze or compound leaves/ liście złożone and they differ/różnią się according to their: blade shape, blade division/ podział blaszki, shape of the margin/kształt brzegu, shape of the tip/ kształt wierzchołka, shape of the base/kształt nasady liścia, presence or absence of the petiole/obecność bądź brak ogonka (sessile leaf/liść siedzący, bezogonkowy), vein system/venation/unerwienie. Examples: 2 Key question 3: Why are leaves not the shape of a football? Leaves are the main organs of photosynthesis. It means they need to absorb as much light as they can but they also need carbon dioxide from the environment to diffuse easily. Therefore, leaves are usually not round like a ball but flat like paper sheet. Leaf morphological features and their function 1. Petiole connects the leaf blade with the plant stem. Thanks to petioles flexible movement/płynny ruch, plants are able to regulate the surface/powierzchnia of sunlight absorption/pochłanianie during the day. Leaves are the powerhouse of a plant. 2. Vascular tissue/tkanka przewodząca which is inside a petiole and leaf blade is meant for in and out food and water transport. Vascular tissue branches out/rozgałęziać się to provide/zapewnić required/potrzebny chemical substances for each cell in the leaf. 3. Flat and thin leaf blades are meant to increase/zwiększyć sunlight exposure/naświetlenie and enable/umożliwić efficient gas exchange between the leaf tissues and the environment. 4. Green leaf color is due to the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. There are also other photosynthetic pigments in leaves e.g. yellow, orange or red which become visible/widoczny in the fall as a result of chlorophyll degradation/rozkład. During photosynthesis, different lengths/długość of sun radiation/promieniowanie is absorbed/pochłaniać by different types of pigment similarly as it is in algae. In some plants, that grow in shade, chloroplasts accumulate/gromadzić się very close to the surface to increase light absorption. This also makes the color of leaves deep dark. 3 Key question 4: Why is photosynthesis one of the wonders of life? It provides the basic source of energy, which is glucose, needed for all vital functions/funkcje życiowe of all living organisms. Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is conversion/przemiana of inorganic compounds/związki nieorganiczne: carbon dioxide CO₂ and water H₂o into organic compounds/związki organiczne which are sugars, e.g. C₆H₁₂O₆ in the presence of energy from the sun. 4 During photosynthesis, sun energy is absorbed/pochłaniać by chlorophyll located in chloroplasts. The energy splits water molecule/rozpad cząsteczki wody into hydrogen/wodór and oxygen/tlen. Further, atoms of hydrogen and molecules of carbon dioxide/dwutlenek węgla undergo a series of complex/skomplikowany chemical reactions which take place in chloroplasts. The final product of the reaction is glucose and oxygen as a byproduct/produkt uboczny which comes from water molecule. Leaves release/uwalniać the oxygen to the environment through stomata /aparaty szparkowe. Key question 5: What products of photosynthesis, as a heterotrophic consumer, could you not live without? Students answer for themselves. Benefits of photosynthesis Sun energy, in the process of photosynthesis, is converted into chemical energy and stored in the molecules of glucose and other organic compounds. Glucose will be used by a plant as a : 1. energy material, needed for carrying all vital functions (cellular respiration/oddychanie komórkowe, ATP production) 2. storage material/ materiał zapasowy, like starch/skrobia, fat and proteins/białka. These organic compounds are stored/przechowywać in fruit and seeds. Plants can convert/zamienić them back into glucose when needed. 3. building material, cellulose/celuloza which is the component/składnik of cell wall and other chemicals needed for growth. Plants are autotrophic/samożywny organisms that are the first link of the food chain/łańcuch pokarmowy in nature. Plants are able to accumulate sun energy in organic molecules. That is why they are called producers. All other organisms which depend on plants are called consumers. 5 Hoping you have had fun learning Bibliografia Wykorzystane w lekcji obrazki zostały pobrane ze stron: 1. http://www.shiachildren.com/english/information/plants/6.php 2.http://generalhorticulture.tamu.edu/h202/labs/lab2/leafm.html 3. http://kids.britannica.com/elementary/art-89144/Leaves-come-in-many-different-shapes 4.http://biology4isc.weebly.com/3-photosynthesis-and-transport-of-solutes.html 5.http://theawkwardyeti.com/tag/photosynthesis/ 6.http://www.geography.hunter.cuny.edu/~tbw/soils.veg/lecture.outlines/ecology.chap.6/ecology.c hap.6.htm 7.http://www.squizzes.com/food-chain-fun/ 6