Response to Intervention (IDEA 2004)…How to make it work in
advertisement

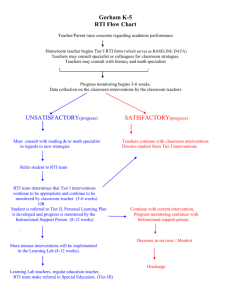
CARS + RtI How to Make it Work in a Shrinking Economy Oakhurst Elementary Presenter - Gail Lancaster –Associate Faculty National University/Fresno Campus Resource Specialist/Oakhurst Elementary glancaster@nu.edu H.R. 1350 (IDEA 2004) IN GENERAL- Notwithstanding section 607b, when determining whether a child has a specific learning disability as defined in section 602, a local educational agency shall not be required to take into consideration whether a child has a severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability in oral expression, listening comprehension, written expression, basic reading skill, reading comprehension, mathematical calculation, or mathematical reasoning. IDEA 1997 v. IDEA 2004 IDEA 1997 – Student has SLD if: Student failed to achieve commensurate with age and ability if provided appropriate teaching experiences AND - IEP team found SEVERE DISCREPANCY between achievement and intellectual ability IDEA 2004 – No longer required to find severe discrepancy IEP team may use a process that determines if the child responds to a SCIENTIFIC RESEARCHED BASED INTERVENTION Problems with the Discrepancy Model Critics have described the model as a wait to fail model. Students must be at least 2 years behind before receiving help. Easier to catch students up at an earlier age but they would not qualify. By the time they qualify emotional damage and self concept issues are harder to get rid of. Teacher Qualifications Department of Ed encourages RtI Disconnect between CCTC and Dept of Ed. Fully qualified: if doing Tier III should have M/M credential (RSP certificate) and Multiple subject. How will this discrepancy be resolved? Multi Tiered Model of Service Delivery Tier 1 - Universal Interventions Tier 2 - Selected Interventions Tier 3 - Intensive Interventions Tier 4(?) – Special Ed services. 3 tiered model Tier 3: Intensive, Individual Interventions (5%) •Individual Students •Assessment-based •High Intensity •Of longer duration Tier 2: Targeted Group Interventions (15%) •Some students (at-risk) •High efficiency •Rapid response Tier 1: Universal Interventions (80%) •All students •Preventive, proactive 1-5% 1-5% 5-10% 80-90% 5-10% Students 80-90% OES RtI Began the process January 06’ because we wanted to take a proactive stance. We wanted to make the model work for us and for students. The team embraced the chance to work with students and to develop this model before the state mandated how it should look. Team formed Principal, School Psychologist, Resource Specialist, Reading Specialist OES RTI Model weekly for 6 months. Visited other Reading Labs Did significant amount of research and reading on RtI /followed the research Looked at various researched based reading programs Researched DIBELS assessment program Brought in presenters from various programs Began to set the stage for staff buy in/ presented ideas to staff in Spring Contacted State Diagnostic Center for assistance/ became one of their projects RESEARCH ISSUES What worked? – Strong leadership – Collaborative team effort – Using data to drive instruction – Having a small school – Bottom-up approach versus top-down You need to answer these questions What is your vision? What are your goals and objectives? How can you make this work? How can you work smarter not harder? How can you make it easier for staff? How can you get staff to buy in? How would your model be different? What are your resources? How much would this cost? Could you do it within your current resources? What researched programs do you think would work? What would you do next? What questions do you need to get answered before you begin? 5 minutes – please share with a partner Building Teacher Buy In Everything presented to the staff must be well planned Use team building skills to help pull staff together before model is presented Approach this in several ways: – “You’ve said this is a problem here is one way we are trying to address it” – Acknowledgement of frustration at working with low level readers and making little progress. Teacher Buy in Cont. Prior to presenting to whole staff – choose “positive” leader to present ideas to and work out more issues Presented DIBELS with the idea of taking other assessments off their plates/or other tests Gave teachers freedom during lab time to do differentiation, platoon groupings etc. (Big ideas of Reading) Acknowledged their professionalism in the choices they made in the class but monitor that Tier I students have interventions in regular ed .classroom. Periodically check with your staff on the following: – Is this working? – What do you need to make it work better? – What questions do you have? Everything must be collaborative and well planned! Tier 1 Program (Primary Prevention; General Education; Universal core instructional program) During the Tier I pull-out program, focus in on the “BIG IDEAS” of reading instruction: •Phonemic Awareness •Alphabetical Principal •Accuracy and fluency reading to connected text •Vocabulary development •Reading Comprehension What this can look like: •Actively engaged students working in small groups receiving differentiation of instruction; fluidity within the groups •Teachers providing explicit and systematic instruction •Center activities focusing on various skills development •Activities like Readers Theater and Literature Circles Tier I Materials Teachers have the freedom to use their professional judgment in providing differentiated instruction – – – – – – – – – Open Court: Re-teach Open Court: ELD component Hampton Brown SRA Readers Theater Literature Circles Partner Reading Teacher directed grouping Team teaching Tier II More intense instruction Biweekly progress monitoring Small groups More individualized Tier II Materials Selected Lexia: primary reading/ CD Rom, -(phonemic awareness and phonics) Rewards: Intermediate level, -(multisyllabic decoding) Read Naturally: tapes and CD Rom, -(fluency) Drops in the Bucket/Frog Games -(language skills) After School Achievers Reading Club - (reading strategies/language skills/comprehension) Hampton Brown: (language Development for EL’s) Guided Reading Book Sets Tier III Most intensive instruction Weekly progress monitoring Programs are individualized and adjusted as needed Usually preliminary to a referral Tier III Materials Orton Gillingham/Zoophonics Steck Vaughn Power up (intermediate CD Rom/online) Read Naturally Edmark reading (CD) Some students/Language focus Referral Maintain tracking sheets when students switch levels Put tracking sheets in reg ed cum Can now use tracking sheets to establish interventions No longer need a discrepancy School Psych Report Answers the following questions: – Does xxx qualify for special education based on the criteria set forth under Federal RtI guidelines? Data must be collected to establish a pattern. OAKHURST ELEMENTARY OAKHURST Screening for Program Placement Worksheet Interventions = entry field School Name: Oakhurst Elementary School District Name: Bass Lake Joint Union Elementary District Teacher/Test Gr 4 / Oakhurst Elementary School Bass Lake Joint Union Gr 4 / Fluency Intervention Programs Star AR Decoding Intervention Programs San Indicate if Special Education Student ELL CELDT 07' SE EL 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 19 20 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 ELL CELDT 09' ELL CELDT 08' CST EnglishLanguage Arts Score Year: 2007 CST EnglishLanguage Arts Score Year: 2007 EI EI I I EI I I EI I A A EA 2008 score 300 SE Post 2008 score \ 139 64 57 104 122 78 80 B PRO BB FBB B BB PRO PRO 334 367 267 251 327 282 387 367 B PRO BB B B BB \ B 300 383 285 307 314 285 \ 318 103 95 97 PR0 PRO B 354 362 317 B B B 307 326 330 114 112 126 PRO BB B 376 285 342 PRO BB B 361 285 338 EA I SE SE I EA 102 122 126 100 113 140 B Pro Pro \ PRO B 306 381 381 \ 362 334 B Pro Pro PRO B B 318 381 375 366 307 300 85 96 33 62 71 BB B BB \ BB 278 323 274 \ 289 BB BB FBB BB BB 281 270 242 285 262 88 163 53 38 89 68 107 67 74 93 66 70 133 59 88 89 97 81 90 105 89 118 109 110 93 63 65 83 26 63 62 Target 105 CWPM Target 118 CWMP Passage/ Grade Level 50 4 109 160 69 74 104 92 134 83 106 114 93 96 171 79 111 124 141 91 97 109 102 153 103 130 95 78 82 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 45 79 86 Test Pre Date test Date test given given: Test May 09' Aubg 08' Jan 09' Target 93 CWPM 340 EA 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 May 08 ORF Target 3rd 110 Student Grade Level Examp Jane Doe le Pseudoword Decoding Dibles Grade 4 6 Student Name Diego Quick 136 111 Target 118 CWPM Inst Passage Grade Level CW post test Date test given: May 09' Inst Passage Grade Level CW 0 4 8 2 2 4 2 10 9 9 10 4 10 2 10 3 9 3 10 4 4 4 3 1 2 9 10 8 10 10 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 19 20 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 5 6 2 30 31 32 34 (Highest Unit Complet ed) Date test given: Pre Test Post Test Date test given: Date test given: Aug 08' May 09' Aug 08' Grade Level grade level Grade Level of Passage Grade Level of Passage A D 0 6 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 19 20 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 5 6 2 31 32 33 34 3.3 5.7 2.5 2.1 3 2.5 4.5 4.6 3.6 4,7 4.9 2.5 5.8 3.1 3.9 3.6 3.4 4.4 3.2 6.6 3.6 4.8 5 4.6 4.6 2.3 3.8 3.8 1.5 2.3 2.8 3.1 1.3 Pre Test Date test given: Jan 09' 4.4 4 2.5 2.4 4.8 3.3 4.1 5.4 3.9 5.6 4.1 3.8 6.6 4.5 5.1 4.3 4.5 4.4 3.6 5.1 4.6 5.6 4.5 3.5 5.7 2.6 2.7 3 May 09' Differences between HS and Elementary RTI Elementary RTI framework does not necessarily translate into high school RTI Purpose of high school RTI drives framework components High school RTI serves different needs High School RTI Many schools are struggling Research not as well defined Multiple implementation issue – Communication/between staff – Changing roles/gen ed. staff need to make changes to way core content is delivered – Movement between tiers – Assessment Unique Features of High School RTI Staff Roles • Who provides the additional interventions? How to do you plan to support this new role for staff? • How do special education and/or behavioral specialists support the framework? • If RTI is implemented in more than one content area, how will you support content teachers into becoming more than “teachers of content?” Long Beach HS District Assessment: Test all incoming 9th graders at end of 8th grade. – Use CST, course grades, and assessments in Language! curriculum. Decisions are not based on a single data point. All incoming 9th graders receive core literacy instruction. Curriculum Structure Students ½ a year to two years behind receive the core literacy program as well as an additional literacy workshop course. – Materials scaffold the core literacy program. More than 2 years behind – Double block of language arts that consists of intensive English Lang arts program or an after school reading program. – Curriculum: Language! and Lindamood Bell – Monitored though “cluster tests” HS research suggestions Research is limited Ideas for assessment – Group Reading Assessment and Diagnostic Evaluation (GRADE) – Woodcock Reading Mastery Tests Revised – Research going on using Strategies Intervention Model Junior High Model Ranchos Middle School Golden Valley Unified School District Madera County RMS Assessment Use CST and CELDT as screening tools Students are placed into reading strategies classes and further testing is continued San Diego quick is used to measure word in isolation decoding Scholastics 3-minute fluency is used to measure oral reading fluency Reading Specialist does most of the individual assessments Performs these assessments during lunch, prep period and class time. District use to hire a substitute to help in order to finish assessments, now uses PEP/Tutorial time Who Gets Assessed? Students scoring as Basic (below 325 CST) Below Basic and Far Below Basic. Teacher or Parent Concerns can trigger an assessment. Students scoring below a 2.0 GPA. Students placed in an intervention class receive additional testing. Students scoring on grade level are then moved out of intervention class. Need to score 120 WPM Logistics Students grouped by grade level or ELD label but not on data Students stay for a year, can be moved at semester Have begun screening 6th graders, prior to coming to Jr. High Interventions for 7th and 8th graders delivered in a double block period combining the intervention with the core Language Arts Instruction Interventions Rewards 6-Minute Solution (ORF) Read Naturally Pilot Site for Reading Plus (on computer) Modifications due to Cost Interventions will be cut from 4 periods a day to 3 Specialist shared between two sites Lone Star Elementary Grade level interventions Multiple Tiers – Tier 1: monitoring – Tier 2: SOAR –Students Out and Reading – Tier 2+: ART2 (At Risk Tier 2) monitored weekly – Tier III: IEP students and failed progress in Tier 2+ LS Identification Tier III: IEPs; failed progress in Tier2+ Tier 2+; CST FBB/BB and lowest DIBLES Intensive Tier 2: B/BB/FBB; DIBLES strategic and intensive Tier 1: English Learners, CST P*/A (3 – 6) DIBLES Benchmark (K – 2) LS Tier I Assessment – CELDT – AR STAR – Read Naturally – Rewards Delivery – Gen Ed classroom/ small group instruction Monitor – DIBLES monthly, AR STAR monthly, Unit Assessments LS Tier 2+/2 Assessment – Quick phonics screener – Phonics for Reading – Rewards – Literature Connection/complete Delivery – 4 days a week 30 min time blocks Monitor – Tier 2+ weekly DIBLES, Biweekly program progress – Tier 2 Monthly DIBLES, AR STAR M, Program Progress LS Tier III Assessment – EL- IPT listening/speaking – Test used in other Tiers Delivery – Small group (3 - 4) Monitor – Weekly DIBLES – Biweekly program monitor – IEP Quarterly Check Assessment Dibels Pseudoword AR- Decoding (GL WIAT) STAR Color coded tracking sheet for ease of selection Learn to trust data!!! Check with reg ed teachers Planning Instructional Groupings Team process Relied heavily on Dibels data – Must determine most important indicator Analyzed other diagnostic measures Analyzed STAR CST testing levels Increase in decoding (9 months of Tier II and Tier III labs used WIAT GL Pseudoword decoding scores – includes spec ed students) Grade 2 10.2 months Grade 3 9.8 Grade 4 8.8 Grade 5 7.9 Over all average 9 months Schedule Cont. 8:10 – 8:55 – 9:40 – 10:40 – 11:25 – 8:50 9:35 10:20 11:20 12:10 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th What We Learned! Both Reg ed teachers and Core team had to learn to trust the data Don’t put too many students in lab – Leave openings for students who just moved to your school. – Don’t transition students too soon. Let long term memory kick in. Don’t refer a child unless they have had a full year in Tier III For More Information National High School Centerwww.betterhighschools.org National Center on RTIwww.rti4success.org Center on Instructionwww.centeroninstruction.org RTI Wire www.jimwrightonline.com