Section 3.4 * Concavity and the Second Derivative Test
advertisement

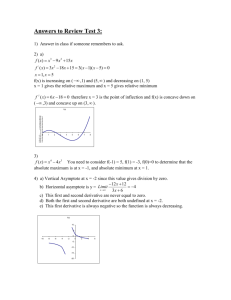
Section 3.4 – Concavity and the Second Derivative Test The Second Derivative and the Function The first derivative tells us where a function is increasing or decreasing. But how can we tell the manner in which a function is increasing or decreasing? For example, if f '(x) = 3x2 +3 then f(x) is always increasing because f '(x) is always positive. But which graph below represents f(x)? Concavity If the graph of a function f lies above all of its tangents on an interval I, then it is said to be concave up (cupped upward) on I. If the graph of a function f lies below all of its tangents on an interval I, then it is said to be concave down (cupped downward) on I. CONCAVE DOWN CONCAVE UP Test for Concavity a) If f ''(x) > 0 for all x in I, then the graph of f is concave upward on I. b) If f ''(x) < 0 for all x in I, then the graph of f is concave downward on I. Slopes are CONCAVE UP decreasing. Slopes are CONCAVE DOWN increasing. Procedure for Finding Intervals on which a Function is Concave Up or Concave Down If f is a continuous function on an open interval (a,b). To find the open intervals on which f is concave up or concave down: 1. Find the critical numbers of f ' and values of x that make f '' undefined in (a,b). 2. These numbers divide the x-axis into intervals. Test the sign (+ or –) of the second derivative inside each of these intervals. 3. If f '' (x) > 0 in an interval, then f is concave up in that same interval. If f ''(x) < 0 in an interval, then f is concave down in that same interval. Find where the first derivative is increasing and decreasing. Example 1 Use the graph of f '(x) below to determine when f is concave up and concave down. f is concave down when the derivative is decreasing. A critical point for the first derivative (f''=0) Concave Up: (1, ∞) f ' (x) x f is concave up when the derivative is increasing. Concave Down:(-∞,1) Example 2 3 Find where the graph f x x 3x 1 is concave up and Domain of f: where it is concave down. All Reals Find the critical numbers of f ' Find the first derivative. nd derivative Find where the 2 x dxd x 3 3x 1 is 0 or undefined Find the second derivative. ' x 3x 2 3 0 6x f ' f f '' x dxd 3 x 2 3 x0 f '' x 6 x Find the sign of the second derivative on Answer the question each interval. f '' x The function is concave 0 x 1 x 1 down on (-∞,0) because f '' 1 6 f ''<0 and is concave up on f '' 1 6 (0,∞) because f ''>0 The Change in Concavity If a graph changes from concave upward to concave downward (or vice versa), then there must be a point where the change of concavity occurs. This point is referred to as an inflection point. CONCAVE DOWN CONCAVE UP Inflection Points A point P on a curve is called an inflection point if the graph is concave up on one side of P and concave down on the other side. In calculus terms, (if f is continuous on an interval that contains c) c is an inflection point if f '' changes from positive to negative or vice versa at c. Thus, f '' (c) must equal 0 or be undefined. Example Determine the points of inflection of f t t 6 t . Domain of f: Find the critical numbers of f ' All Reals 3 Find the derivative. f ' t t f ' t 2 3 185t 13 3 6 t 6 t NOTE: 6 is not an inflection point since the 2nd derivative does not change sign. 1 3 6 t Find where the 2nd derivative is 0 or undefined 23 Find the second derivative. f '' t 3 6 t 13 2 5 185t 9 6 t 23 3 31 6 t 2 3 0 10t 72 10t 72 The 2nd t 7.2 derivative is f '' t 9106tt 724 3 undefined at t=6. Find the sign of the second derivative on each interval. Find the value of the function: f '' x f 7.2 8.131 6 7.2 x5 x7 x 8 f '' 5 2.44 f '' 8 0.35 Answer the question f '' 7 0.22 Example: Answer The point of Inflection is (7.2,8.131) because the second derivative changes from negative to positive values at this point. White Board Challenge Find where the inflection point(s) are for f 2 if f ''(x) = 4cos x – 2 on [0,π]. Justify. x 34 or 4 because the second derivative changes from negative to positive at these points. How the concavity is connected to Relative Minimum and Maximum When a critical point is a relative maximum, what are the characteristics of the function? The function is concave downward at B. When a critical point is a relative minimum, what are the characteristics of the function? The function is concave upward at C. D f(x) B A C x The Second Derivative Test Let f be a function such that f '(c) = 0 (a critical number of a continuous function f(x) ) and the second derivative exists on an interval containing c. (a) If f ''(c) < 0, there is a relative maximum at x = c. f(x) Relative Maximum f '(c) = 0 f ''(c) < 0 c x The Second Derivative Test Let f be a function such that f '(c) = 0 (a critical number of a continuous function f(x) ) and the second derivative exists on an interval containing c. (b) If f ''(c) > 0, there is a relative minimum at x = c. f(x) f '(c) = 0 f ''(c) > 0 Relative Minimum c x The Second Derivative Test Let f be a function such that f '(c) = 0 (a critical number of a continuous function f(x) ) and the second derivative exists on an interval containing c. (c) If f ''(c) = 0, then the second-derivative test fails (either a maximum, or a minimum, or neither may occur). Here is a common example of neither a minimum or maximum f(x) f '(c) = 0 f ''(c) = 0 c x When the SecondDerivative Test fails, the critical point can often be classified using the FirstDerivative Test. Example 1 5 3 Domain of f: Find the relative extrema of f x 3x 5x 2 . All Reals Find the critical numbers Apply the 2nd Find the first derivative. Find where the derivative is 0 or undefined Derivative Test f ' x dxd 3x5 5 x 3 2 4 2 3 0 15 x 15 x f '' x 60 x 30 x 4 2 2 2 f ' x 15x 15x 0 15 x x 1 f '' 0 0 FAIL 2 0 15x x 1 x 1 x 0, 1, 1 Apply the 1st Derivative Test where the 2nd Derivative Test Fails. -1 x 0.5 f ' 0.5 2.8125 0 1 f ' x x 0.5 f ' 0.5 2.8125 No sign change means x=0 is not a relative extrema. f '' 1 30 MIN f '' 1 30 MAX Find the value of the function: f 1 0 f 1 4 Answer the question Example 1: Answer The function has a relative maximum of 4 at x = -1 because the second derivative is negative at this point. The function has a relative minimum 0 at x = 1 because the second derivative is positive at this point. Example 2 The Second Derivative Test is less popular than the First Derivative Test for two reasons: the Second Derivative Test does not always work and a question often requires a student to find where a function is increasing/decreasing before asking for the relative min/max (Thus, the sign chart for the First Derivative Test is done already). Yet, the AP Test will have questions, like the one below, specifically about the Second Derivative Test: Example: If the function f has a horizontal tangent line at x = 4 and f ''(4) = 3, what is true about f(4)? f 4 is a relative minimum