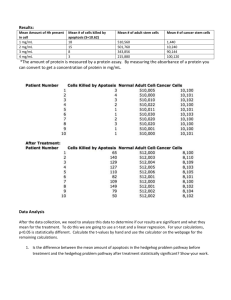
Using the capital return data and a debt-to
advertisement

1. Using the capital return data and a debt-to-capital estimation, what is the estimated return for a company with a d-to-c of 30? a. b. c. d. 2. In the three variable estimate of Capital Returns, the expected return to capital for an Energy company is a. b. c. d. 3. -2.4 18 16 Dependent upon its debt-to-capital ratio and so is not possible to determine without further assumptions. Using the three-variable estimate of the Capital Return data, if the F-statistic of this model equaled 20, then a. b. c. d. 4. 12.5 15.5 16.2 17.2 The R2 of the model would equal 39.5%. The SSE of the model would be 3665. The Standard Error of the regression would decrease. There is insufficient information to solve the problem. Using the four-variable estimate of the Capital Return data, if the SSE of this model was 6000, then a. Since more than 90% (6000/6648) of the variation is unexplained, then for any value of alpha less than 10%, the model is statistically insignificant. b. The model is statistically insignificant at the 5% level, but is statistically significant at the 1% level. c. The model is statistically insignificant at the 5% level and at the 1% level. d. The model is statistically significant at the 5% level but not at the 1% level. 5. Using the results from the Capital Return estimation, the model including all six variables compared to the model with only two variables, using a partial F-test a. Is not statistically significantly more explanatory at the 5% level but is at the 1% level. b. Is not statistically significantly more explanatory at the 1% level but is at the 5% level. c. Is not statistically significantly more explanatory at the 5% level or at the 1% level. d. Is statistically significantly more explanatory at the 5% level and at the 1% level. 6. Using the capital return data and a margin estimation, the hypothesis that the margin has no effect on capital return … a. b. c. d. 7. The maximum return in the capital return data is 42.2 for a company with a debt-tocapital ratio of 7.4. Using the debt-to-capital estimation of the returns, what would a revised return have to drop to in order for this company’s return not to be an outlier at the 5% level? a. b. c. d. 8. can not be true since the best estimate is 0.063. is certainly true since the best estimate is 0.063. can be rejected for any practical level of statistical certainty. can not be rejected for any practical level of statistical certainty. 30 35 Impossible to determine with the materials provided. The standard t-statistic shows that this new return would certainly be an outlier for any practical value of alpha, including 5%. Using the capital return data, if a linear regression is constructed of sales as a function of debt-to-capital, then the intercept of the resulting estimate is: a. b. c. d. About 3%. About 30. Not statistically significant for most of the data points. Statistically significant. 9. Using a two variable estimation of salary, if the values of the model remained the same except that the sample size was 100, then a. b. c. d. 10. The R2 and adjusted-R2 would remain unchanged. The R2 would increase and the adjusted-R2 would decrease. The R2 would decrease and the adjusted-R2 would increase. The R2 would remain unchanged and the adjusted-R2 would increase. Using a six-variable estimate of Salary, if the SSE of this model was 25,000,000,000, then a. Since more than 80% of the variation is unexplained, then for any value of alpha less than 20%, the model is statistically insignificant. b. The model is statistically insignificant at the 5% level, but is statistically significant at the 1% level. c. The model is statistically insignificant at the 5% level and at the 1% level. d. The model is statistically significant at the 5% level but not at the 1% level. 11. Using a three-variable estimate of Salary, if the F-statistic of this model equaled 20, then a. b. c. d. 12. The R2 of the model would equal 56%. The SSE of the model would be 1145588974. The Standard Error of the regression would decrease. There is insufficient information to solve the problem. Using the existing categorical analysis of the Salary data, the average annual value for having any graduate degree is approximately: a. b. c. d. Impossible to determine. $10,000 $20,000 $50,000 13. Using a four-variable (Executive, Alpha, Prior, Education) estimation of Salary, the average salary for a non-executive female employee with a Bachelors’ degree and 10 years of Prior and Alpha experience is approximately: a. b. c. d. 14. Using a five-variable Salary model (Alpha, Prior, Executive, Education, and Educ4), what is the expected annual salary for a newly hired Female Executive with a Master’s degree who has 5 years of prior experience? a. b. c. d. 15. $60,000 $70,000 $80,000 $90,000 For a three-variable regression model with a sample size of 50 and an R2 of 80%, then the value of the F-statistic: a. b. c. d. 16. $35,000 $40,000 $50,000 $60,000 Cannot be determined without knowing the various sum-of-squares of the model. Is less than or equal to 50. Is more than 50 but less than or equal to 100. Is more than 100. If the R2 is 50% for a 6-variable model based upon a sample size of 100, then the adjusted-R2 of the model is: a. b. c. d. 47% 50% 53% Dependent upon the t-statistics of the model. 17. In order to estimate the VIFs for the five variable model of Salary the number of additional regressions required is: a. b. c. d. 18. If the correlation coefficient is statistically significant at the 5% level for a sample of size 100 for variables X and Y that have standard deviations of 10 and 20, then the sample covariance of the variables must be: a. b. c. d. 19. Greater than 40. Less than 40. Greater than 40 and Less than 40. Greater than 40 or Less than -40. If DELL and IBM have a sample covariance of 100 and DELL’s average stock price is $50, IBM’s average stock price is $90.88, IBM’s standard deviation is $14.87, then using a linear regression of IBM’s price to estimate DELL’s price, what is DELL’s stock price when IBM’s price is $100? a. b. c. d. 20. 2 3 4 5 Less than $45. Between $45 and $50. Greater than $50 but less than $55. Greater than $55. If the F-statistic of a 4-variable regression model is 4.60, then the regression model is statistically significant at the 1% level: a. If the sample size is more than 25. b. At no level of the sample size. c. Impossible to determine since the degrees of freedom for the numerator/denominator are unknown. d. For any sample size of four or greater since the 1% t-statistic with 3 degrees-offreedom is approximately 4.54.