Electronic Communications
advertisement

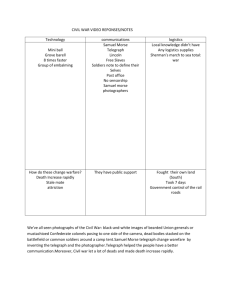
Lesson 6 Electronic Communications Samuel Morse 1791-1872 Samuel Morse is best known as the inventor of the telegraph in 1835, Samuel Morse proved that signals could be transmitted by wire. He used pulses of current to deflect an electromagnet. And on May 1, 1844, the first news was dispatched by electric telegraph. Until 1877, all rapid long-distance communication depended upon the telegraph. That year, a rival technology developed that would again change the face of communication….. In 1840 he patented a new code that used combinations of dots and dashes to represent all 26 letters in the alphabet and numbers from 1 to 10. It was named Morse Code The original Morse telegraph printed code on tape. However, as the operation developed into sending by key and receiving by ear. A trained Morse operator could transmit 40 to 50 words per minute. http://www.connectedearth.com/Playit/morsecodeandsemaphore/index.htm LESSON NOTES The word "telegraph" is derived from Greek and means "to write far"; so it is a very exact word, for to write far is precisely what we do when we send a telegram. The word today, used as a noun, denotes the system of wires with stations and operators and messengers, girdling the earth and reaching into every civilized community, whereby news is carried swiftly by electricity. But the word was coined long before it was discovered that intelligence could be communicated by electricity. It denoted at first a system of semaphores, or tall poles with movable arms, and other signaling apparatus, set within sight of one another. While a professor of arts and design at New York University in 1835, Samuel Morse proved that signals could be transmitted by wire. He used pulses of current to deflect an electromagnet, which moved a marker to produce written codes on a strip of paper the invention of Morse Code. The following year, the device was modified to emboss the paper with dots and dashes. He gave a public demonstration in 1838, but it was not until five years later that Congress (reflecting public apathy) funded $30,000 to construct an experimental telegraph line from Washington to Baltimore, a distance of 40 miles. In 1837 Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail had an electromagnetic telegraph that would turn presses of a key at one end into movements of a lever or paper punch at the other. They could send and record short and long pulses along the line - but without any way of turning those into letters and numbers. They needed a code and together worked to develop it. He developed a 'language' that translated letters of the alphabet and numerals into individual code 'symbols' that could travel down the same wire one after the other and be printed out at the receiving end; these formed the basis of Morse Code. In 1844, he sent his first public message, which read: 'What hath God wrought!' The subsequent development of a sounder device meant that his dots and dashes could be 'read' by ear as well as visually on paper. The arrival of the electric telegraph in 1837 created a new reality: messages transmitted very quickly and reliably over distances farther than a man could see. As the networks grew the distances became greater and greater, linking towns, then countries and finally continents. Within 30 years the telegraph had transformed business, commerce, government and society. But the impact on ordinary lives was subtler. Reuters was created by founder Paul Reuter in 1851 to deliver news and information, specialising in financial data, using the fastest available means, ranging from pigeon post to express trains.The company rose to prominence by making use of the telegraph system, particularly bringing news into London via the Dover-Calais submarine telegraph cable. The company sealed its reputation by being the first to deliver the news of Abraham Lincoln's assassination.Since then Reuters has developed a reputation of being first with the news. This was consistently proved with notable 'scoops', which included the details of the Armistice agreement that ended the First World War in 1918, Khrushchev denouncing Stalin in 1956, and both the construction and the fall of the Berlin Wall. Reuters has also pioneered new technology to deliver stories rapidly including the use of computers, video screens, television, wireless and the Internet. Samuel Morse Samuel Finley Breese Morse, (1791-1872), was a famous American inventor and painter. Morse graduated from Yale in 1810 and went on to study painting in England. In 1815, he took up portrait painting and was quite successful in this field. Morse helped to found the National Academy of Design and served as its first president. In 1827, Morse became interested in electricity. In 1832, he began a 12-year period perfecting his version of an electric telegraph, for which he subsequently received the first patent for this type of device. Electric Telegraph The telegraph was the first device to send messages using electricity. Telegraph messages were sent by tapping out a special code for each letter of the message with a telegraph key. The telegraph changed the dots and dashes of this code into electrical impulses and transmitted them over telegraph wires. A telegraph receiver on the other end of the wire converted the electrical impulses to dots and dashes on a paper tape. Later, this code became universal and is now known as Morse Code. Before electric telegraphy, most messages that traveled long distances were entrusted to messengers who memorized them or carried them in writing. These messages could be delivered no faster than the fastest horse. In the United States, the Morse telegraph was successful for a number of reasons, including its simple operation and its relatively low cost. By 1851, the country had over 50 telegraph companies though most telegraph business was controlled by the Magnetic Telegraph Company, which held the Morse patents.