2.10 Notes Concavity and the Second Derivative Test
advertisement

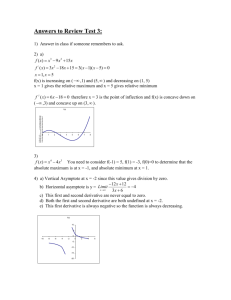
2.10 Concavity and the Second Derivative Test 0 +1 +2 -1 -2 +3 Concave Down a -3 b y=f(x) *** If the first derivative is decreasing on an interval a, b then the original function f(x) is concave down on a, b . Concave Up -3 +3 -2 +2 -1 a +1 0 y=f(x) b *** If the first derivative is increasing on an interval Example 1: a, b then f(x) is concave up on a, b . f x x3 3x2 1 Let Find intervals on which f(x) is concave up and concave down. f ' x 3x 2 6 x f '' x 6 x 6 x 1 (Possible point of Inflection (PPOI); might be a place where the original function’s concavity changes.) ,1 1, Test # 0 2 sign f'' -- + Conclusions About F Concave Down POI at Concave Up 1, 1 *(Remember that the Y value for the POI comes from 1, f 1 ) We did this problem in 4.3 using the first derivative to find where we had a relative max or min. 4.3: f ' x 3x 2 6 x 3x x 2 , 0 0, 2 2, Test # -1 1 3 Sign f’ + - + Conclusions About f Increasing Decreasing Increasing Relative Max at Relative min at 2, 3 0,1 Dec Concave Down Inc Concave Down (POI) Inc Concave Up Dec Concave Up ************************************************************************************************************ Example 2: Find the X value of the POI: f x xe x , 2 2, f ' x x e x 1 e x 1 Test # 0 3 f ' x e x xe x Sign f” -- + f '' x e x 1 e x xe x POI at (2, f(2)) = 2, 2e 2, e2 2 2 f '' x e x e x xe x f '' x xe x 2e x f '' x e x x 2 x2 PPOI Example 3: f x x4 f ' x 4 x3 f '' x 12x2 PPOI at x=0 , 0 0, Test # -1 1 Sign f” + + Conclusions: NO POI!!! No sign change! Example 4: 5 g x sin x On the interval x 2 2 g ' x cos x g '' x sin x PPOI at x 0, , 2 Test # Sign g’’ ,0 2 4 + 0, , 2 2 3 2 5 2 , 2 9 4 -- + -- POI at x=0, Review: π, 2π 2.9 I. f ' x tells us when f x is increasing and decreasing. II. First derivative test; used to find relative mins and relative maxes. ( ) ( ) ( ) Test# Sign of f’ + - + rel max, rel min 2.10 I. f '' x tells us when f x is concave up and concave down. (find PPOI) ( ) ( ) ( ) Test # Sign of f”’ + POI, No POI II. The second derivative test is used to find relative mins and relative maxes. Find the critical numbers from f’ Evaluate c1 , c2 , c3 f '' c1 rel min at c1 , f c1 f '' c2 rel max at c2 , f c2 f '' c3 0 undefined = test failed!! Example: 1. Locate the relative mins and maxes for f ( x) x 4 2 x 2 using the second derivative test. f ' x 4 x3 4 x 4 x x 2 1 4 x x 1 x 1 x 1, 0, 1 f '' x 12x2 4 Sign of f '' 0 rel max at 0,0 *remember that the “y” value comes from ( f '' 1 rel min at 1, 1 f '' 1 rel min at 1, 1 Redo example one using first derivative test to compare and contrast the differences: f x x4 2x2 f ' x 4x 4x 3 4 x x 2 1 , 1 1,0 0,1 1, test # -2 -0.5 0.5 sign f’ - + - 4 x x 1 x 1 x 1, 0, 1 2. rel min rel max 2 + rel min f x x3 5x2 3x k Find the value of k for which f has 11 as its relative minimum. Work: f ' x 3x2 10 x 3 0 3x 1 x 3 1 x x3 3 f '' x 6x 10 1 f '' 3 f '' 3 rel min f 3 11 3 3 5 3 3 3 k 11 2 k 20 , f(0))