Big Question:
advertisement

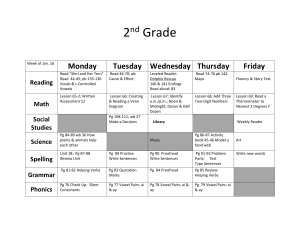
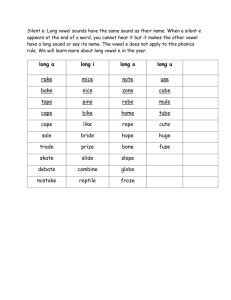
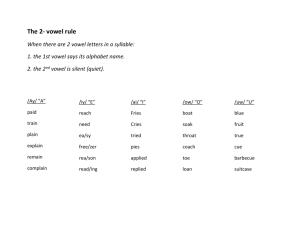
How do we learn the value of money? Author: Tololwa M. Mollel Illustrator: E.B. Lewis Genre: Realistic Fiction Timer proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder arranged bundles dangerously errands excitedly steady unwrapped wobbled More Words to Know astonishment confident scoffed fragrance lures wares Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Question of the Day How could working teach you about money? Build Concepts Character and Setting Story Structure Build Background Vocabulary Fluency: Appropriate Phrasing Compound Sentences Vowel Sounds in out and toy Selling Food Fluency: Model Listen as I read “Village Market.” Notice how I use punctuation as a signal for pauses and expressing phrasing. Be ready to answer questions after I finish. Who are the characters in the poem? How does the author describe the setting of the poem? What to Sell Selling Food Actions Senses Turn to page 116. What do you KNOW? What would you WANT What have you to find out? LEARNED? After we read our story, we will add what we learned in the last column. Word Meaning Chart Word arranged bundled dangerously errands excitedly steady unwrapped wobbled Meaning Sentence arranged - put things in a certain order bundles – things tied or wrapped together dangerously – not safely errands – short trips that you take to do something excitedly – with strong, lively feelings steady – firmly fixed unwrapped – opened wobbled – moved unsteadily from side to side; shook astonishment – great surprise; sudden wonder; amazement confident – firmly believing; certain; sure scoffed – made fun of something to show you do not believe or respect it fragrance – a sweet smell lures – to attract someone or something by offering something desirable wares – things for sale Next slide Grammar: are you proud of your knew bike Are you proud of your new bike? we sold peachs and they sold beans We sold peaches, and they sold beans. I wanted to buy everything, but I clutched my coins tightly in my pocket. The sentence is a compound sentence. Two simple sentences have been combined with a comma and the word but. A simple sentence has one subject and one predicate. A compound sentence contains two simple sentences joined by a comma and a word such as and, but, or or. Simple Sentence: The boy helped his mother. Simple Sentence: His mother bought him a bicycle. Compound Sentence: The boy helped his mother, and his mother bought him a bicycle. The two parts of a compound sentence have ideas that make sense together. A comma goes after the first sentences before the word and, but, or or. The family had a farm. simple sentence The boy planted beans, and his mom planted pumpkins. compound sentence The family ate bananas and spinach. simple sentence The spinach tasted good, but the bananas tasted better. compound sentence The boy picked the crops, and his father sold them. compound sentence A wheelbarrow carries crops but it is hard to push. A wheelbarrow carries crops, but it is hard to push. You can pick peas or you can gather sweet potatoes. You can pick peas, or you can gather sweet potatoes. It rains in spring and the crops grow quickly. It rains in spring, and the crops grow quickly. Coffee grows on trees and pumpkins grow on vines. Coffee grows on trees, and pumpkins grow on vines. Farming is hard work but the family enjoys it. Farming is hard work, but the family enjoys it. Spelling: proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder Question of the Day What are some of the ways that writers help the reader learn about the character and the setting of their stories? Vowel Diphthongs Word Structure Character and Setting Story Structure Realism and Fantasy Develop Vocabulary Fluency: Echo Reading Compound Sentences Vowel Sounds in out and toy Open-Air Markets Turn to page 118. Pages 120 - 127 Fluency: Turn to page 125. As I read, notice how I pause at commas. Now we will practice together doing three echo readings of page 125. Grammar: he saved his money and it was a large amount He saved his money, and it was a large amount. the boys new bicycle costs alot The boy’s new bicycle costs a lot. A compound sentences contains two sentences joined by a comma and a word such as and, but, or or. The two sentences that are joined make sense together. Spelling: proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder Question of the Day How are Saruni and the other characters in “My Rows and Piles of Coins” similar to or different from people you know? Character and Setting Story Structure Word Structure Realism and Fantasy Develop Vocabulary Fluency: Appropriate Phrasing Compound Sentences Vowel Sounds in out and toy Geography/Cultures Pages 128 – 135 Fluency: Turn to page 134. As I read, notice how I pause at commas and how you read chunks of words between commas. Now we will practice together doing three echo readings of page 134. Grammar: dad teached him to ride a bike in an our Dad taught him to ride a bike in an hour. can he ride it good now Can he ride it well now? Compound sentences can add variety to writing. A compound sentence provides a change from a series of choppy simples sentences. Spelling: proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder Question of the Day What are some different ways you might save money? Long Vowel Digraphs Web Site/ Text Features Reading Across Texts Fluency: Echo Reading Compound Sentences Vowel Sounds in out and toy Save Money Pages 138 – 141 Fluency: Turn to page 134. We will echo read this page aloud three times, using appropriate phrasing. Grammar: i tried to cary a box on my bike. But it was too heavy. I tried to carry a box on my bike, but it was too heavy. cant you put it on you’re bike Can’t you put it on your bike? Test Tip: You may be asked to identify a compound sentence. A compound sentence combines two sentences. Each combined sentence has a subject and a predicate. Not a Compound Sentence: Tim and Mary rode their bikes. Not a Compound Sentence: Sam talked and laughed. Compound Sentence: Tim rode his bike, and Sam talked. Spelling: proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder Question of the Day How could working teach you about money? Build Concept Vocabulary Character and Setting Word Structure Book Report Compound Sentences Vowel Sounds in out and toy Graphs Selling Food A character is a person who takes part in the events of a story Writers tell some things about characters. You can also figure out about characters by their words and actions. The setting is when and where a story takes place. A writer may tell you the setting, or you may figure out the setting from details. A simile is a comparison of two unlike things that are alike in some ways. A simile uses like or as (“her eyes shone like diamonds”) or a comparative adjective and than (“Jay was happier than the sunniest day”). Look for the clue words like, as, or than. A simile should not be taken literally; it is a figure of speech used to show a comparison. You can use word structure to determine the meaning of unfamiliar words with prefixes or suffixes. List any unknown words you find as you read “My Rows and Piles of Coins.” Create a chart showing the unknown word and its definition based on the base word and its prefix or suffix. Then use a dictionary to confirm meanings. Word Base + prefix or suffix Meaning Prefixes and suffixes such as dis-, -ly, and –ful change the meaning of the base word. With a partner use reference sources to make a list of words with prefixes and suffixes. Then create a chart showing the base word, its prefix or suffix, and the meaning of the word. Word Base Word Prefix or suffix Meaning Grammar: tom made a choyce and he was happy with it Tom made a choice, and he was happy with it. toyes and games is expensive Toys and games are expensive. Spelling: proud shower hour amount voyage choice avoid thousand prowl employ bounce poison annoy appoint broil however mountain coward turmoil chowder Two vowels together can stand for the long sound of the first vowel, but there is another possibility. Sometimes two vowels together stand for a new sound. Each vowel contributes to the new sound. The vowel dipthongs oi and oy stand for /oi/. The vowel dipthongs ou and ow often stand for /ou/. join Which letters in join are vowels? What vowel sound o you hear in join? round Which letters in round are vowels? What vowel sound do you hear in round? boy Which letters in boy are vowels? What vowel sound do you hear in boy? cow Which letters in cow are vowels? What vowel sound do you hear in cow? royal rebound aloud tower avoid Detroit frowning destroy Our neighbors have been playing noisy music for an hour. Do you want to hang around at my house? How loyal are you to your friends? We studied the long vowel digraphs ee, ea, ai, ay, oa, and ow. Read the sentence to yourself. Raise your hand when you know which words have long vowel digraphs. The birds don’t seem to be afraid of the scarecrow. seem, afraid, scarecrow Which digraph spells long e? ee Which digraph spells long a? ai Which digraph spells long o? ow Draw a neat map that shows rural roads and busy highways. neat, shows, roads, highways Which digraph spells long e? ea Which digraphs spells long o? ow, oa Which digraph spells long a? ay neatness bungalow anyway restrain subway railroad outgrow freedom betray degree peachy below If you don’t brush your teeth, they will decay. Emma’s birthday is on Sunday. My goal is to read a book a week. I know my dog will wag her tail when I come home. What kind of information might you find in a graph? Describe different kinds of graphs you have seen. A pictograph uses pictures to show amounts. The titles and labels tell what the information is about. The key tells what each pictures stands for. A picture might stand for 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, or even 100 objects. A circle graph (also called a pie graph) is shaped like a circle. The entire circle stands for a whole. Each section circle graph is part of the whole. If a section is large, it stands for a large part of the whole. A small section stands for a small part of the whole. The sections are labeled with words and numbers. The numbers show what part of the whole each section is. Spelling City: Spelling Words Vocabulary Words More Vocabulary Words Story test ◦ Classroom webpage, ◦ Reading Test AR ◦ Other Reading Quizzes ◦ Quiz #