Sedimentary Rocks
advertisement

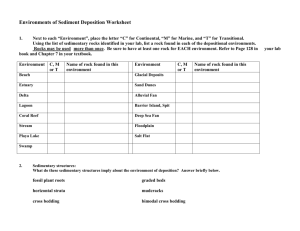
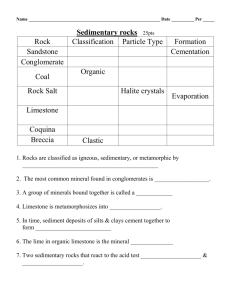
Earth Science Notes SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Objectives I can… • Explain what Sedimentary Rocks are • Explain the processes that create sediments and sedimentary rocks • Classify Sedimentary Rocks. • Tell the geological history of an area based on the bedding patterns Sedimentary Rocks • Rocks formed from sediments • Sedimentary rocks often form as layers on the bottom of a body of water. Sedimentary Rock Formation • Sediments are loose materials like small rocks, minerals, and organic debris. • Weathering and erosion produce sediments – Weathering – the breaking down of rocks into bits via chemical and mechanical means. – Erosion – the moving of these small bits of rock to a new location where they are deposited. Sedimentary Rock Formation • Weathering and Erosion Sedimentary Rock Formation • Sedimentary rocks form from other rocks • These rocks are compacted and cemented together. – Compaction – sediments stick together due to pressure – Cementation – minerals are deposited between pieces of sediment – holding it together. • Lithification the process by which sediments can undergo chemical and physical processes to become sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary Rock Formation • Compaction and Cementation Sedimentary Rock Formation • Sedimentary rocks display certain characteristics that allows draw conclusions about the history of landforms and rock formations. • One such feature bedding. This is the result of sediment settling out in large flat areas. Sedimentary Rock Formation • STRATIFICATION refers to the way sediment layers are stacked over each other, and can occur on the scale of hundreds of meters. It is a fundamental feature of sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary Rock Features Types of Bedding • Graded Bedding – size of the sediments become large the farther down you go in a rock layer – form when a steep pile of sediment on the sea floor (or lake floor) suddenly slumps into a canyon or off a steep edge. Sedimentary Rock Features Types of Bedding • Cross-Bedding – forms when sand is transported as sand-dune like bodies, in which sediment is moved up and eroded along a gentle up-current slope, and redeposited (avalanching) on the downcurrent slope. Sedimentary Rock Features • RIPPLE MARKS are produced by flowing water or wave action. Ancient ripples on a sandstone surface. Ripples are symmetrical and show "tuning-fork" branches. This indicates to a geologist that the sandstones were deposited in an environment with wave action (nearshore). Sedimentary Rock Features • Sedimentary rocks may contain “signs” of life. Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Clastic (Detrital) Sedimentary Rocks: sedimentary rocks made from broken bits of other rocks • Ex: Conglomerate – large sediments, rounded rocks • These types of rocks have rounded sediments because they were near wind and water • EX: Breccia – large sediments, sediments have sharp angles • These types of rocks have jagged sediments because they were not near wind and water Detrital Sedimentary Rocks Conglomerate Breccia Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Chemical Sedimentary Rocks: sedimentary rocks that form when dissolved minerals come out of solution. • Often founds along seas or lakeshores. • This type of rock is the only form of sedimentary rock that did not form from preexisting rocks. – Ex: Limestone (CaCO3) – forms when calcium carbonate comes out of a solution. • Limestone is deposited on bottom of lakes and seas. – Ex: Rock salt – forms when the evaporation of water occurs, leaving behind the salt Chemical Sedimentary Rocks Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Organic (Biochemical) Sedimentary Rocks: sedimentary rocks made of once living things • This type of rock will form when clams, corals, snails, and mussels die and let their shells accumulate on the ocean floor. – Ex: Chalk – made from the shells of organisms. – Ex: Coal – formed from the decay and compaction of plant materials. Organic Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Summary • What makes a rock Sedimentary? • Formation of Sedimentary Rocks • Classification of Sedimentary Rocks – Detrital / Chemical / Organics