Quinn Assesment Key
advertisement

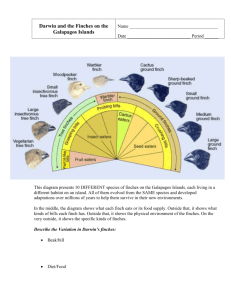
Fill in the Blank 1. A GENE POOL consist of all genes, including all the different alleles, that are present in a population. BL:Knowledge Objective: define gene pool 2. A situation in which allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population is known as the FOUNDER EFFECT. BL: Knowledge Objective: define founder effect 3. The HARDY-WEINBERG principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. BL: Knowledge Objective: define Hardy-Weinberg 4. Random change is allele frequency is called GENETIC DRIFT. BL: Knowledge Objective: define and explain why genetic drift is more prominent in smaller populations Multiple Choice 5. When two species are capable of interbreeding but have different courtship and mating techniques this is a type of? a. Behavioral Isolation b. Temporal Isolation c. Geographic Isolation d. Climatic Isolation BL: Application Objective: Compare and contrast behavioral, geographic, and temporal isolation 6. A difference in beak size of finches comes from adaptations stemming from varying? a. Climates b. Seed sizes c. Habitats d. Weather patterns BL: Analysis Objective: predict what will happen to traits under certain environmental factors 7. A group of finches have moved from Island A and have been reproducing on Island B for 100 years. A finch, caught in a storm, has ended back up on Island A. Will he likely be able to reproduce with the finches on Island A? a. Yes b. No BL: Application Objective: compare and contrast behavioral, geographic, and temporal isolation 8. A monogenic trait has how many alleles? a. One b. Two c. Three d. Four BL: knowledge Objective: compare and contrast mono and polygenic traits, providing examples 9. According to the above graph, a Widow’s Peak is most likely a _____________ trait. a. Dominant b. Recessive c. Unable to determine without further information d. Co-dominant BL: comprehension Objective: determine dominant and recessive traits from a graph Use the above pie graph for the next two questions. 10. The relative frequency of the dominant white allele is? a. 90% b. 35% c. 57.5% d. 42.5% BL: application Objective: calculate relative frequency of a population 11. The relative frequency of the recessive black allele is? a. 10% b. 57.5% c. 65% d. 42.5% BL: application Objective: calculate relative frequency of a population 12. On a remote island there is a species of frogs that come in the color green and brown. Normally the island is a lush green color causing brown frogs to be more susceptible to predators . After a severe drought most of the trees have been left dead and withered. What can be predicted to happen to the frogs? a. The populations will remain the same b. Both populations will decrease c. The brown frog population will increase while the green frog population will decrease d. The brown frog population will decrease more while the green frog population will increase more BL: analysis Objective: predict what will happen to traits under certain environmental factors Use the above table to answer the following ___ questions. 13. This bird’s beak is used to monopolize fruit as a food source. a. Large Tree Finch b. Sharp-billed Ground Finch c. Cactus Finch d. Vegetarian Finch BL: application Objective: Identify by sight 5 different finches beaks and match them to the food source they monopolize 14. This bird’s beak is used to monopolize large seeds as a food source. a. Vegetarian Finch b. Cactus Finch c. Large ground Finch d. Warbler Finch BL: application Objective: Identify by sight 5 different finches beaks and match them to the food source they monopolize 15. This bird’s beak is used to monopolize insects as a food source. a. Small Ground Finch b. Woodpecker Finch c. Vegetarian Finch d. Cactus Finch BL: application Objective: Identify by sight 5 different finches beaks and match them to the food source they monopolize 16. A population of squirrels ended up on two different sides of a crevice after a sudden earthquake. The rift is too deep and far to cross. 100 years pass as the rift slowly closes and the species reunite but cannot breed. This is an example of? a. Temporal Isolation b. Geographic Isolation c. Behavioral Isolation d. Climatic Isolation BL: comprehension Objective: compare and contrast behavioral, geographic, and temporal isolation 17. Ten individuals are stranded on an abandoned island. The trait for blue eyes started at 50%. After 3 generations the trait has dwindled to 5%. This is an example of? a. Temporal Isolation b. Genetic Drift c. Random Mating d. Dominant Trait BL: comprehension Objective: define and explain why genetic drift is prominent in smaller populations 18. An example of a polygenic trait is? a. Height b. Widow’s Peak c. Tongue Rolling d. Eye color BL: knowledge Objective: compare and contrast poly and monogenic traits providing examples For the following question either give an example of a factor which goes against the HardyWeinberg principle or give the Hardy-Weinberg Principle which the factor is going against. 19. Random Mating – Courtship rituals BL: knowledge Objective: five examples as to why the 5 factors rarely, if ever, happen in nature 20. Island recently discovered by a small population of individuals- large populations BL: knowledge Objective: list the 5 factors that would cause gene frequencies to remain the same 21. Immigration – No movement in or out of the population BL: knowledge Objective: : list the 5 factors that would cause gene frequencies to remain the same 22. No mutation – frame shift BL: knowledge Objective: five examples as to why the 5 factors rarely, if ever, happen in nature 23. No natural selection – wild breeding BL: knowledge Objective: five examples as to why the 5 factors rarely, if ever, happen in nature Short answers 24. Pick two of the beak types and explain how the shape helps it adapt to the food source it is exploiting. a. Woodpecker Finch beak – long and thin, allows brid to easily drill through wood/out layer of plants and skewered insects living in side b. Large Ground Finch beak – large and sturdy, allows for the bird to easily crack the shells of nuts BL: analysis Objective: Analyze why the different beak configurations helped the finches to monopolize a particular food source 25. What is temporal isolation and give an example. a. When species reproduce at different times of the year b. Orchids – different species release pollen on specific, non overlapping days BL: comprehension Objective: compare and contrast temporal, behavioral and geographic isolation, giving examples 26. Why is genetic drift is more effective on a smaller population? a. Since the allele frequencies are so small, genetic drift works more effectively on smaller populations. The random chance of one trait dominating, or dying out, increases as variability decreases. BL: comprehension Objective: define and explain why genetic drift is more prominent in smaller populations Essay In your opinion, which type of isolation has the greatest effect on the change of populations? A personal question, that, as long as accurate scientific support is given in addition to a linear thought process shown, will be given full credit. BL: evaluation Objective: compare and contrast behavioral, geographic, and temporal isolation Objectives List Define gene pool Calculate relative frequency of a population Determine dominant and recess traits from a graph Compare and contrast poly and monogenic traits, providing examples as well Predict what will happen to traits under certain environmental factors Define and explain why genetic drift is more prominent in smaller populations Define founder effect and give examples List the 5 factors that would cause gene frequencies to remain the same Define the Hardy-Weinberg principle Give an example as to why the 5 factors rarely, if ever, happen in nature Compare and contrast behavioral, geographic, and temporal isolation Identify by sight 5 different finches beaks and match them to the food source they monopolize Analyze why the different beak configurations helped the finches to monopolize the various food sources