American Revolution
advertisement

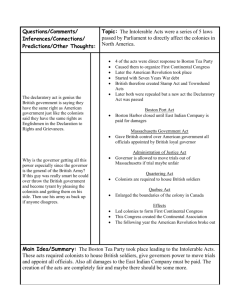
Road to the American Revolution Learning Target • Britain’s victory over France in the imperial struggle for North America led to new conflicts among the British government, the North American colonists and the American Indians culminating in the creation of a new nation, the United States. French & Indian War • The French & Indian War had represented a change in relations with England for the American colonists. In all previous colonial wars, England had required the colonists to fight the war for themselves. French & Indian War • In the French & Indian War, for the first time, English soldiers were sent to fight side by side with colonial soldiers & militia. • From the colonial point of view, this changes things. Proclamation Line of 1763 • The French & Indian War had opened up a great deal of Western Land, but England would not allow the Colonists to settle any of it. • The English knew someone had to help pay for that war, but how… Taxes 1763: The Proclamation of 1763 1764: The Sugar Act 1764: The Currency Act 1765:The Stamp Act 1765: The Quartering Act of 1765 1765: Virginia Stamp Act Regulations 1766: The Declaratory Acts 1767: The Townshend Acts 1768: Boston Non-Importation Agreement 1770: The Boston Massacre 1772: The Gaspee Affair 1773: The Tea Act 1773: The Boston Tea Party 1774: The Boston Port Act 1774: Administration of Justice Act 1774: Massachusetts Government Act 1774: The Quartering Act of 1774 1774: The Quebec Act • In response to the Proclamation of 1763 & taxes… • In response to the Proclamation of 1763 & taxes… Taxes • King George placed Lord Greenville in charge of raising revenue from the colonies. • The first tax Greenville came up with to hit the colonies was the Sugar Tax. • A tax placed on molasses from the Caribbean. Sugar Tax • The plan was to drive up the cost of Caribbean molasses and make English molasses (that was taxed) cheaper to buy. Sugar Tax • But the colonists decided it was even cheaper to just smuggle in molasses from the Caribbean and avoid the tax altogether. • By the way, the tax the English wanted the colonists to pay on one gallon of English molasses (to pay for a war to eliminate the French threat in the Ohio Valley)… • From England’s point of view, the taxes were perfectly reasonable. • The French & Indian War had been fought for the benefit of the colonists, to protect them from the threat the French forts in the Ohio Valley represented. • The English decided that since the war had been fought for the colonists, they should help pay for it. • But the colonists… Tax Burden Colonies Public Debt: England Public Debt: Tax Burden Colonies Public Debt: £2.6 million England Public Debt: £140 million Tax Burden Colonies Public Debt: England Public Debt: £2.6 million £140 million Interest: Interest £104,000 / year £ 5,000,000 / year Tax Burden Colonies Public Debt: England Public Debt: £2.6 million £140 million Interest: Interest £104,000 / year Per Person debt: 18 schillings / person £ 5,000,000 / year Per Person debt: £18 / person Sugar Tax • The English were stunned by the colonial reaction to the Sugar Tax. • They knew they were already paying more in taxes! • But the King had a problem, he had told the colonists to do something and they were refusing to do it. • He could not let them get away with that! Vice Admiralty Courts were set up to deal with people who broke the Sugar Tax. • There were no juries, offenders were dealt with by a judge appointed by the King. • In the wake of the Sugar Tax came the rallying cry throughout the colonies: “No taxation without representation” Stamp Tax • Greenville then came up with the Stamp Tax. – A tax on legal and other documents. – Had already been in place in the colonies and had not been a problem. Stamp Tax • In England, a Stamp Tax raised £100,000 / year • Greenville wanted to raise £60,000 / year from the colonists. • Greenville was fired and replaced by a man named Charles Townshend. • He simply added more taxes to the colonists. Paper Glass Tea Taxes • The colonists decided not to buy any of the taxed items. They either smuggled it in, or did without – – but they would not pay those taxes! Taxes • People living in England got upset at this. The colonists would not pay their share of the French & Indian War. The the costs were being shifted back to England. • Since Parliament was responsible for collecting the taxes, people in England turned their attention to Parliament to make the colonists pay. Parliament • Parliament is an elected body. They did what the voters wanted and they wanted more taxes, fines & penalties for nonpayment of taxes by the colonists. Parliament • Only men living in England could vote for members of Parliament. – Not the colonists! • In order to ensure these new taxes are being paid, England sent more troops over to enforce them. Boston Massacre • In Boston, there were 4,000 British troops to strictly enforce the tax laws. – They looked down on the colonists because they weren’t what they considered to be “real Englishmen”. Boston Massacre • On March 5, 1770 a crowd gathered at the Customs House in Boston to protest taxes and the treatment they saw as unfair by British soldiers. Boston Massacre • British soldiers who had been stationed there fired into the crowd, this was the Boston Massacre. Boston Massacre • In response to the Boston Massacre, two things happened: – British troops all moved from Boston, to an island in Boston Harbor. – All taxes repealed on colonial imports except the tax on tea! Boston Tea Party • The colonists drank tea like Seattleites drink coffee today. Boston Tea Party • To avoid paying tax on tea, the colonists simply smuggled it in. – Up to 90% of the tea consumed in the colonies was smuggled and untaxed. Boston Tea Party The Intolerable Acts • The Intolerable Acts were laws that were really punishments that King George III put on the colonies. because he wanted to punish them for the Boston Tea Party. The Intolerable Acts • The Boston Port Bill closed Boston Harbor to everything but British ships. • The Quartering Act The colonists had to house and feed the British troops. If the colonists didn't do this, they could be shot. • The Administration of Justice Act British Officials could not be tried in colonial courts for crimes. The Intolerable Acts • • Massachusetts Government Act The British Governor was in charge of all the town meetings in Boston. There would no more self-government in Boston. • • The Quebec Act Extended the Canadian borders to cut off the western colonies of Connecticut, Massachusetts and Virginia. First Continental Congress • September 1774, 55 delegates from 12 colonies (not Georgia) met and decided to work together to do anything short of war to help Boston. First Continental Congress • Came up with a plan to resist the Intolerable Acts. – They would not import English goods, or export goods to England. – Mostly important because it was the first time the colonies came together to act together as one. Boston • England decided the main problem in the colonies was in Boston. • So they focused their attention there. Boston • General Gage, the British official in charge of Boston realized that the situation was much more serious than it appeared. Boston • Gage called for a repeal of the Intolerable Acts, or 20,000 more troops to keep things under control. Boston • However, the Intolerable Acts stayed and he got 3,500 more troops. • This didn’t help him at all. Not enough men to help and more than enough to make people of Boston even more upset. Lexington & Concord Olive Branch Petition • The colonies tried one more time to avoid war with The Olive Branch Petition. – Appealed to the King directly to remove the Intolerable Acts and they would avoid war. Second Continental Congress • Became the first American government Second Continental Congress – They took all state militias and combined them into one American Army. Second Continental Congress – Named George Washington as commanding general of the American Army Second Continental Congress – Printed American currency. Second Continental Congress – Established a method to deal with foreign countries. • The two sides were now set…