Levers - CPO Science
advertisement

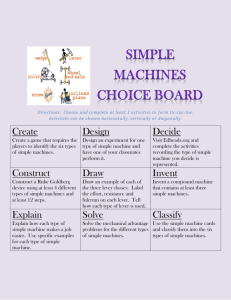
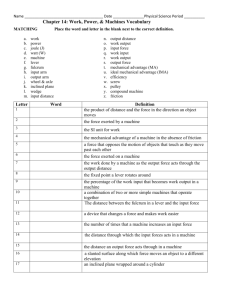
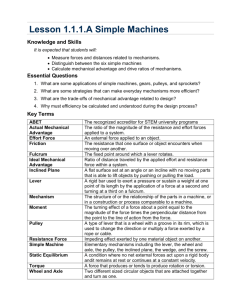
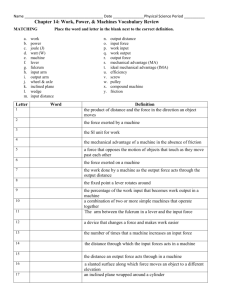
Key Questions: What is a newton? How does a lever work? What is the relationship between force and distance in a simple machine? What factors balance a lever? Performance Objectives Describe how a lever works. Identify the relationship between force and distance on a lever. Apply the concept of mechanical advantage to levers. Lever Assembly SAFETY NOTE: WATCH for FALLING weights on bare toes or sandals or table tops! DO not place the fulcrum higher than hole 3 of stand! FORCES Forces have two important properties: strength (magnitude) and direction. In the English system of units, the strength of a force is measured in pounds. When you measure your own weight in pounds, you are measuring the force of gravity acting on your body. The NEWTON In the metric system, the strength of a force is measured in newtons (N). A quarter-pound hamburger has a weight of about 1 newton (1 lb = 4.448 N). Zero the Spring Scale In the metric system, the strength of a force is measured in newtons (N). Gravity and weight The force of gravity on an object is called weight. Mass and weight are not the same thing! Gravity and weight A 10-kilogram rock has a mass of 10 kilograms no matter where it is in the universe. A 10-kilogram rock’s weight however, can vary greatly depending on where it is. Simple Machines A simple machine is an unpowered mechanical device, such as a lever. Simple machines change the magnitude or direction of forces Introducing… The Lever A lever includes a stiff structure (the lever) that rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum. fulcrum Anatomy of the lever Fulcrum – point around which the lever rotates Input Force – Force exerted ON the lever Output Force – Force exerted BY the lever CPO Lever – First Class All The Way Here we have a first class lever. The fulcrum is between the input and output. Can you get two weights to balance? Levers in Equilibrium Hang your weights like shown here. Does the lever balance? What variables can be changed to balance a lever? Four Variables in a Lever Amount of Input Force Amount of Output Force Length of Input Arm Length of Output Arm Lever Challenge Hang weights from the lever and get it to balance. Use only 3 strings, one string per position and string MUST have weight. Do 4 trials and record how many weights to hang and where you hang them. Lever Challenge Lever Concept Hang 1 weight 10 cm from the fulcrum. Where does the output force need to be to oppose our input force? 1 1 Basic Lever Investigation If we move the input force 10 cm, how much more do we need to add for the same output force? Try it... 1 Basic Lever Investigation If we move the input force 10 more cm, how much more do we need to add for the same output force? Add two masses at 20 cm. 1 Mathematical Rule for Balancing the Lever What mathematical relationship can you find that will balance the lever every time? Put your rule in terms of input and output and forces and distances. What if there is more than one location on either side of the lever? What is the Relationship? Input Force x Length of Input Arm = Output Force x Length of Output Arm Force x Distance = Force x Distance # of Weights x Distance = # of Weights x Distance What if there several groups of weights ? Sum of Input = Sum of Output (F1 x D1) + (F2 x D2) = (F3 x D3) + (F4 x D4) TOY Engineers Allow time for students to brainstorm possible design ideas and to plan how they will construct their toys. Once students have built their toys, let them share their creations with the class. Outcomes Use science Think scientifically Communicate technical ideas Teach all students Be science conscious NOT science phobic What questions do you have about the CPO Levers?