8-3 REACTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Objectives:
The students will be able to:
1. explain the biochemical processes that a plant uses in photosynthesis
2. explain the role ADP-ATP cycle has within the chloroplast of the cell
3. explain the light reactions
4. explain the steps of photophosphorylation and the Calvin Cycle
http://www.science.siu.edu/plant-biology/PLB117/JPEGs%20CD/0076.JPG
Remember from
CH. 2?
Enzymes for PHOTOSYNTHESIS are
in the ________________
CHLOROPLASTS
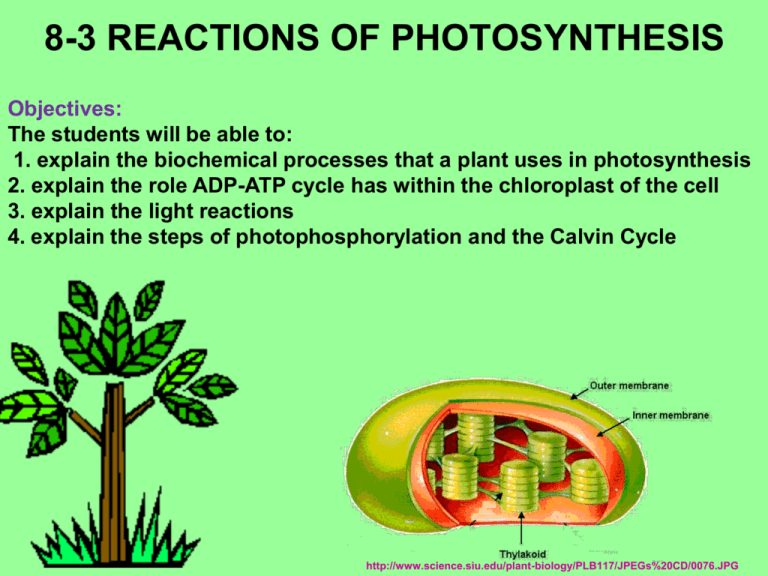
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HAPPENS IN
CHLOROPLASTS
THYLAKOIDS
= sac-like
photosynthetic
membranes
inside chloroplast
GRANUM (pl. grana)
= stack of thylakoids
Many grana exist in chloroplast.
Chloroplast Spaces
THYLAKOID
SPACE
STROMA
Gel-filled
space inside
chloroplast,
between
grana
Gel-filled space
Inside the
thylakoid
sac
cytoplasm
Gel-filled space OUTSIDE
chloroplast but inside the cell
membrane
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HAPPENS IN
CHLOROPLASTS
Proteins that are part of the thylakoid
membranes organize
Light absorbing PIGMENTS
________________________________
into
clusters called _____________________
PHOTOSYSTEMS (PS)
Inside a Chloroplast
Proteins in the thylakoid membrane organize
chlorophyll and other pigments into clusters called
photosystems, which are the light-collecting units
of the chloroplast.
Photosystems
Chloroplast
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Electron Carriers
When electrons in chlorophyll absorb sunlight, the
electrons gain a great deal of energy.
Cells use electron carriers to transport these highenergy electrons from chlorophyll to other
molecules.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW
In thylakoid
membranes
In stroma
Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions
require light.
The light-dependent reactions
produce oxygen gas and
convert ADP and NADP+ into
the energy carriers ATP and
NADPH.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Photosynthesis begins when chlorophyll pigments in
photosystem II (PSII) absorb light, increasing their
energy level.
Photosystem II
Light-Dependent Reactions
These high-energy electrons become unstable and
are passed from PSII chlorophyll to the electron
transport chain.
Photosystem II
High-energy
electron
Electron
carriers
Light-Dependent Reactions
PSII enzymes in the thylakoid membrane also break
water molecules into:
Photosystem II
2H2O
High-energy
electron
Electron
carriers
Light-Dependent Reactions
– hydrogen ions H+
– oxygen atoms
– energized electrons
Photosystem II
+
O2
2H2O
High-energy
electron
Electron
carriers
Light-Dependent Reactions
The energized electrons from water replace the
high-energy electrons that chlorophyll lost to the
electron transport chain.
Photosystem II
+
2H2O
High-energy
electron
O2
Light-Dependent Reactions
As plants remove electrons from water, oxygen is
left behind and is released into the air.
Photosystem II
+
O2
2H2O
High-energy
electron
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Light-Dependent Reactions
The hydrogen ions left behind when water is
broken apart by PSII enzymes, end up in the inner
thylakoid space.
Photosystem II
+
O2
2H2O
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Light-Dependent Reactions
High-energy electrons move through the electron
transport chain from photosystem II to
photosystem I.
Photosystem II
+
O2
2H2O
ETC
Photosystem I
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Light-Dependent Reactions
Pigments in photosystem I use energy from
light to re-energize the electrons.
+
O2
2H2O
Photosystem I
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADP+ then picks up these high-energy
electrons, along with some H+ ions, and becomes
NADPH. NADPH is released in the stroma.
+
O2
2H2O
2 NADP+
2
2
NADPH
Light-Dependent Reactions
Soon, inside the thylakoid space there’s a high concentration
of H+ which can be used by the ATPase as a concentration
gradient to make ATP. HOW???
+
O2
2H2O
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
Light-Dependent Reactions
H+ ions cannot cross the membrane directly.
ATP synthase
+
O2
2H2O
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
Light-Dependent Reactions
The cell membrane contains a protein called ATP
synthase that allows H+ ions to pass through it
ATP synthase
+
O2
2H2O
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
Light-Dependent Reactions
As H+ ions pass through ATP synthase, the
protein rotates.
ATP synthase
+
O2
2H2O
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
Light-Dependent Reactions
As it rotates, ATP synthase binds ADP and a
phosphate group together to produce ATP.
ATP synthase
+
O2
2H2O
ADP
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
Because of this system, light-dependent reactions
produce not only high-energy carrier NADPH, but
ATP as well. ATP is also released in the stroma.
ATP synthase
+
O2
2H2O
ADP
2 NADP+
2
2
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
NADPH
LIVING THINGS NEED ENERGY
CARRIERS
Molecule that carries
ATP
= _______
Molecule that carries
HIGH ENERGY ELECTRONS
NADPH
= ___________
Images by Riedell
Frying pan image from: BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006
HIGH ENERGY ELECTRONS
require a special carrier, too
___________
NADPH is one
of the carriers that
cells use to transport
high energy electrons.
+
2
e
H
________ + _____ + _____
→
____________
_______= nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Light &
Water
Light-Dependent
Reaction
ATP
NADPH
Light-Independent
Reactions
Oxygen
LIGHT-DEPENDENT
REACTIONS
INSIDE THYLAKOID SPACE
ATP SYNTHASE
↓
PHOTOSYSTEM II
Thylakoid
membrane
↓
↓
ELECTRON TRANSPORT
SYSTEM
PHOTOSYSTEM I
ATP
NADPH
OUTSIDE THYLAKOID IN STROMA
WHY DOES PHOTOSYSTEM II
COME BEFORE PHOTOSYSTEM I?
PSII was discovered and named 1st
PHOTOSYSTEM II
↓
↓
PHOTOSYSTEM I
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS
LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTIONS
LIGHT
Require ______________
Molecules are part of ________________
thylakoid membranes
Made up of __________________
PHOTOSYSTEMS II & I
connected by ______________________
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
ATP SYNTHASE
& ___________________
Uses light energy for the following processes:
ATP
ADP + P → _______
NADPH
NADP+ + 2e- + 2H + → _________
H20 molecules and
PSII breaks apart ______
releases _____________
oxygen
The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH from the lightdependent reactions to produce high-energy
sugars.
Because the Calvin cycle does not require light, these
reactions are also called the light-independent or dark
reactions.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Six carbon dioxide molecules enter the cycle from
the atmosphere and combine with six 5-carbon
The Calvin Cycle
molecules.
RuBisCo enzyme facilitates
CO2 fixation.
CO2 Enters the Cycle
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
The result is twelve 3-carbon molecules, which are
then converted into higher-energy forms.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
The Calvin Cycle
The energy for this conversion comes from ATP and
high-energy electrons from NADPH.
Energy Input
12
12 ADP
12
NADPH
12 NADP+
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
The Calvin Cycle
Two of twelve 3-carbon molecules are removed
from the cycle.
Energy Input
12
12 ADP
12
NADPH
12 NADP+
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
The Calvin Cycle
The two 3C molecules are used to produce glucose
6C molecules.
12
12 ADP
12
NADPH
12 NADP+
6-Carbon sugar
produced
Sugars and other compounds
The Calvin Cycle
The 10 remaining 3-carbon molecules are converted
back into six 5-carbon molecules, which are used to
begin the next cycle.
12
12 ADP
6 ADP
12
NADPH
6
12 NADP+
5-Carbon Molecules
Regenerated
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Sugars and other compounds
Calvin Cycle
CO2 Enters the Cycle
Rubisco enzyme
Energy input
from light reactions
5-Carbon
Molecules
Regenerated
Two 3-Carbon Sugars are produced initially;
a 6-Carbon glucose sugar is assembled from them
Sugars and other compounds
CALVIN CYCLE
LIGHT INDEPENDENT
(also called _________________________)
or DARK REACTIONS
DOES NOT require ____________
LIGHT
____________
Happens in _________
STROMA between thylakoids
NADPH donates _______________
Hydrogen + electrons
ATP donates _________________
ENERGY
CO2 donates ______________
Carbon & oxygen
to make __________
GLUCOSE
http://www.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookCHEM2.html
Photosynthesis songs
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ww33L
0lD37I
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yrQzE
w9xY5k
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
AMOUNT
OF WATER
____________________
Water is needed by PSII in light reactions, so
slow or stop
a shortage of water can ________________
photosynthesis. Desert plants that live in
dry conditions have
adaptations for drought and
high temperatures.
waxy coating on their
leaves to prevent water loss.
In addition, they only use PSI
light reactions which don’t
use water.
Factors that Affect
Photosynthesis
TEMPERATURE
Photosynthesis enzymes function
best between 0° C - 35° C
At temperatures above or below
this range, photosynthesis will
slow or stop
Conifers in winter may carry out
photosynthesis only occasionally
LIGHT INTENSITY and WAVELENGTH
________________________________________
More light and also presence of the red and blue
wavelengths increase rate of photosynthesis up
to a certain level until plant reaches its maximum
rate of photosynthesis.
CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION
• If temp is too high, stomata close and CO2
concentration in the leaves becomes too low;
in this case, the RuBisCo enzyme will use as
a substrate oxygen instead of CO2, along
with ATP and NADPH products of light
reactions, depleting and degrading the plant
even more in a process called
PHOTORESPIRATION
__________________________.
Desert
plants avoid this process by concentrating
the CO2 before it gets to RuBisCo.
THE BIG PICTURE
PHOTOSYNTHESIS provides
OXYGEN
the _____________
we breathe
and the __________
sugars
heterotrophs (like us)
consume to survive
Carbon
WATER
dioxide + ____________
_____________
Sugars
Oxygen
_______________ + ____________
Photosynthesis self quiz
• http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/
U2Photosynthesis.htm
Concept Map
Section 8-3
Photosynthesis
includes
use
to produce
Go to
Section:
takes place in
take place in
of
uses
to produce
Concept Map
Section 8-3
Photosynthesis
includes
Lightdependent
reactions
Calvin cycle
use
take place in
PSI, PSII, ETC,
ATPase, H2O,
Light energy
Thylakoid
membranes
to produce
ATP
NADPH
Go to
Section:
O2
takes place in
Stroma
uses
ATP
NADPH
CO2
of
to produce
Chloroplasts
High-energy
sugars
How well do you understand
photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Play this game and find out!
• https://www.quia.com/rr/34827.html