Mussel Collection & Dissection
advertisement

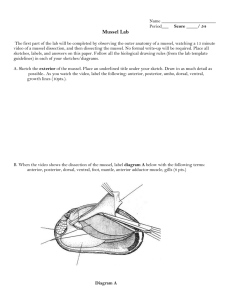
Mussel Collection & Dissection http://hmsc.oregonstate.edu/projects/rocky/blue_mussels.jpg Mytilus ecology M. trossulus M. galloprovinicialis Native to the North Pacific (originally) Native to the Considered tolerant of: Considered tolerant of: Lower salinity Large tidal fluctuation Colder waters Mediterranean Sea Higher salinity Small tidal fluctuation Warmer waters Reference: Braby & Somero, 2005, Marine Biology External morphological differences M. trossulus Photo by Dr. YM Yakovlev M. galloprovincialis Photo from Ulster Museum M. californianus Photo from McDaniel University Bay mussel California mussel Hatchet shape Smooth texture Periostracum* intact *Thin chitinous covering that protects the shell Elongate shape Ribbed texture Periostracum eroded Random sampling Mussels are collected at intervals along a transect line The intervals are drawn from a list of random numbers 0 cm 500 cm 100 cm 170 cm 380 cm Mussel collection 500 cm 0 cm Quick Quiz Why do we use random sampling? a. So our data will accurately represent the actual population b. Because it’s a convenient way to collect specimens c. So we can be consistent with previous researchers d. All of the above Quick Quiz Why do we use random sampling? a. So our data will accurately represent the actual population b. Because it’s a convenient way to collect specimens c. So we can be consistent with previous researchers d. All of the above Quick Quiz What is the proper way to transport marine mussels? a. In ethanol so they will be preserved quickly b. In freshwater to facilitate cleaning c. In seawater so they will stay alive d. In a plastic bag on ice Quick Quiz What is the proper way to transport marine mussels? a. In ethanol so they will be preserved quickly b. In freshwater to facilitate cleaning c. In seawater so they will stay alive d. In a plastic bag on ice Quick Quiz If the mussels will be sacrificed, why must they be kept alive after collection? a. It is the humane thing to do b. To keep DNA intact c. To allow cells to finish dividing d. To make dissection easier Quick Quiz If the mussels will be sacrificed, why must they be kept alive after collection? a. It is the humane thing to do b. To keep DNA intact c. To allow cells to finish dividing d. To make dissection easier Mussel Dissection Mussel Dissection Posterior adductor muscle (shell closers) Dorsal Hinge Excurrent Siphon Incurrent Siphon Anterior Posterior Byssus Ventral Mussel Dissection Mantle edge (secretes shell and is sensory) Incurrent and excurrent siphons Mantle surface (containing outgrowth of gonad) Hinge Mussel Dissection Mantle has now been lifted, but nothing is cut away Mantle edge Cut adductor muscle Gonad (proliferates into mantle which is otherwise thin and translucent) Gill surface Oral palp (one of two pairs) Mussel Dissection Right gill (filaments separated) Visceral mass Left gill Byssus Foot Palp Mussel Dissection Foot retractors Hinge Tiny anterior adductor muscle (shell closer) Posterior adductor muscle (shell closer) Mantle attachment scar Mussel Dissection Muscle scars on shell distinguish Bay from California mussels Posterior adductor & retractor muscles shortened, wide (Bay) Anterior adductor muscle centered (California) Posterior adductor & retractor muscles elongate, thin (California) Anterior adductor muscle on ventral edge (Bay) Tissue for extraction We use gill tissue for DNA extractions because… Cell density is high Connective tissue content is low Mucus content is low Therefore tissue breaks down easily and contains lots of DNA Gill Physiology Gills are used for respiration and sieving of food particles (e.g. phytoplankton) Siphons move water in and out Small particles are passed by the gills to the mouth region Palps transfer food from gill into the mouth H2O Out H2O In Food Quick Quiz Mussel gill tissue is optimal for DNA extraction for all of the following reasons EXCEPT: a. low mucus content b. high cell density c. proximity to digestive tissue d. low connective tissue content Quick Quiz Mussel gill tissue is optimal for DNA extraction for all of the following reasons EXCEPT: a. low mucus content b. high cell density c. proximity to digestive tissue d. low connective tissue content Quick Quiz Why do we measure the size of the mussels? a. It’s a good thing to do b. To see if different sexes are different sizes c. To see if animals on docks are bigger d. To see if there are correlations with species Quick Quiz Why do we measure the size of the mussels? a. It’s a good thing to do b. To see if different sexes are different sizes c. To see if animals on docks are bigger d. To see if there are correlations with species Mussel dissection Cut posterior adductor muscle and open valves of mussel Locate gill and cut off one rice grain worth of tissue Place gill tissue in tube and begin DNA extraction Continue dissection and identification of internal body parts Identify gender of mussel Use muscle scar to confirm not M. californianus END Resources Mussel Collection Handout Mussel Dissection Handout Ecological gradients and mussels paper Diversity of The Invertebrates: A Laboratory Manual Pacific Coast Version. by James W. Nybakken. William C. Brown Publications. 1995. Light’s Manual: Intertidal Invertebrates of the Central California Coast. Smith & Carlton, eds. University of California Press. 1975. Living Invertebrates. by Pearse, Pearse, Buchsbaum, & Buchsbaum. Boxwood Press. 1987. California State Chemistry Standards Grade 8 6c. Living organisms have many different kinds of molecules California State Biology Standards Grade 7 5a. Plants and animals have levels of organization for structure and function 5b. Organ systems function because of the contribution of individual organs, tissues, and cells Grades 9-12 9. As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the [human] body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment California State Investigation and Experimentation Standards Grades 7, 9-12 a/b. Select and use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect data, analyze relationships, and display data Grade 8 a. Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to test a hypothesis National Standards Grades 6-12 Content Standard A: Science as Inquiry Content Standard C: Life Science Content Standard E: Science and Technology