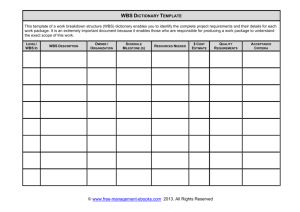
(WBS).
advertisement

The American University in Cairo Engineering Department Mechanical Engineering Unit MENG 446 : Management of Engineering Projects Dr. L.K. Gaafar Joseph Kamal Mohamed El Daour Mohamed El Fatih Sherif Masoud Youssef Youssef Work Breakdown Structure Outline Introduction Origin of WBS Definition WBS Structure Developing WBS WBS Role Applying WBS Project Coding System WBS Rules Conclusion Introduction During the course of any project, numerous activities must be completed by several individuals or organizations. A key strategy of effective planning is to partition the project into manageable chunks that can be individually planned, estimated, and controlled. Such division is done through the development of a work breakdown structure (WBS). The work breakdown structure is a graphical tool that displays the project’s statement of work. Origin of WBS The WBS approach of the US Department of Defense’s Cost/schedule Control System Criteria (C/CSC) or ‘C.Spec.’ was established as far back as the late 1960s. Using WBS was limited in the 1970s and 80s because of its close association with the relatively complex C.Spec. total system. In the 1990s WBS was gaining more widespread adoption in private industry. Many Project management software packages today are incorporating WBS as integral to their use. Definition A work breakdown structure, according to the Project Management Institute, is a product-oriented “family tree” or hierarchal listing that allows the total scope of the project to be organized and defined. WBS starts with a single box at the top that represents the whole project which is then partitioned into its components with lower level boxes. WBS Structure LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3 LEVEL 4 The Project Example Developing WBS 1. Identify the major project elements (usually the project deliverables plus project management functions). 2. Decide if adequate cost and duration estimates can be developed for each element at this level. If so, go to step 4. 3. Subdivide each element into smaller components that can be identified in terms of tangible, verifiable results. These components should reflect how the project will be accomplished. 4. Verify the decomposition by determining if all lower-level items are necessary and sufficient for completion of the item decomposed. Each item should be clearly and completely definable by a brief scope statement. WBS Role Partitions the major project deliverables into smaller components to improve the accuracy of cost estimates. Provides a mechanism for collecting and organizing actual costs. Provides a mechanism for time, cost, and performance tracking. Allows establishing responsibility assignments for each element. WBS Role (Cont.) The WBS allows: Program description as the summation of sub divided elements. Linking Objectives to company resources in a logical manner. Schedules and status-reporting procedures. Network construction and control planning. Applying WBS The work sequence affects the WBS and the WBS affects the work sequence. Size of the WBS reflects the time the project manager needs to spend to coordinate the elements. As the size increases, communication requirements grow. Therefore a project should not be decomposed into any larger set of elements than is necessary to deliver a quality project in a timely manner. Each item in the WBS is generally assigned a unique identification code to facilitate this process. Project Coding System Project coding system is used to structure the project, identify the cost accounts, WBS elements, and establish their relationships. Coding simply involves using a multi-digit number, or assembly of numbers and letters, each of which, or a combination of which, has a meaning or significance. Each code number uniquely identifies a cost account, WBS element, and their parent-child relationship in the WBS. Example Program: New Plant construction and Start-up 01-00-00 Project1: Analytical Study Task1: Marketing/Production Study Task 2:Cost Effectiveness Analysis 01-01-00 01-01-01 01-01-02 Project 2: Design and layout Task 1: Production Processing Sketches Task 2: production Processing Blueprints 01-02-00 01-02-01 01-02-02 Project 3: Installation Task 1: Fabrication Task 2: Set Up Task 3: Testing and Run 01-03-00 01-03-01 01-03-02 01-03-03 Project 4: Program Support Task 1: Management Task 2: Purchasing Raw Materials 01-04-00 01-04-01 01-04-02 WBS Rules Elements should reflect the number of subcontracts. Both the WBS and work description should be easy to understand. All schedules should follow the WBS. No attempt should be made to subdivide work arbitrarily to the lowest possible level. The lowest level of work should not end up having a ridiculous cost in comparison to other efforts. WBS Rules (Cont.) The WBS should remain flexible to accommodate scope-ofeffort changes. Elements should identify discrete and tangible milestones. Activity element levels should reflect a trust in certain groups to perform their responsibilities. Most lowest-control-level elements should range from 0.5% to 2.5% of the total project budget. Conclusion The WBS diagram can be developed by hand. For large projects, when there are dozens of activities that need to be identified, developing the WBS is done using a software. WBS is a very valuable tool for managers because it helps them plan and control their projects. When developing a WBS, a set of rules should be followed to guarantee reaping its maximum benefits For instance, managers should avoid planning unnecessary activities so they do not waste money and time on them. Thank You Ready for Your Questions