Lecture 1: Life Cycle Models
advertisement

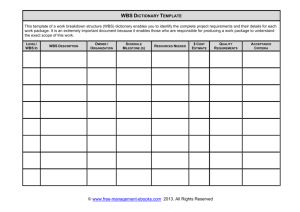
Lecture 3.1: Project Planning: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) [SEF Ch 9] Dr. John MacCarthy UMBC CMSC 615 Fall, 2006 1 Agenda WBS Overview Levels and Types of WBSs WBS Examples System of Systems Program WBS System Program WBS Subsystem/Subcontract WBS Software Program WBS WBS Dictionary Work Packages Cost/Control Accounts WBS Conclusions 2 Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Overview [1] References: Systems Engineering Fundamentals, Chapter 9 MIL-HDBK-881A (30 July 2005), DoD Handbook Work Breakdown Structures for Defense Materiel Items Purpose: Defines the total system Provides the framework for planning, prioritizing, managing and tracking all work done on a project Definition: A logical decomposition of project products and activities to work packages. “A means of organizing system development activities based on system and product decompositions.” - SEF Products Activities Work Packages Provides the framework for Cost Estimating and cost reporting (i.e., the Cost Structure) Resource allocation Status Reporting Performance Measurement Managing program risk 3 Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Overview [2] Characteristics: Hierarchical Numbering System Multi-Level Product-Oriented Structure: Table (Spreadsheet) Org Chart (Graphic) Outline (Text) Products and services required to develop, produce, and support the end items Based on Life Cycle The first three (end product) WBS levels are organized as: Based on the System (Physical) Architecture Enabling Products/Services: Formats: End Products: the prime mission product(s) Level 1: Overall System Level 2: Major Element (or Segment) Level 3: Subordinate Components (or Prime Items) Levels 4+ continue the decomposition to the CI level 4 Types of WBS Program WBS Contract WBS High-Level (First 3 levels) Provides Program Structure Generally developed/controlled by Customer (Government) Detailed (Levels 4+) Provides framework for Contract Work Packages and Costing Generally developed by Contractor Generally follows Program WBS Each WBS ALWAYS includes a WBS Dictionary WBS Dictionary: A Description of each element of the WBS, it identifies: Key deliverables (by CLIN) allocated to that element Key activities Key milestones/events Organization responsible for the element Subcontract WBS Detailed (Level 4+) Provides framework for Subcontract Work Packages and Costing Generally developed by Subcontractor Generally follows Contract WBS 5 WBS Development Developed by Systems Engineering-led IPT SE generally provides structure for: Program Control IPT/ suborganization participation Levels 1-3 of all WBS based on MIL-HDBK-881 Levels 4+ of the End Product and Systems Engineering portions of the WBS Develop Project Management portion of WBS Develop other parts of WBS as appropriate Oversee entire WBS development since it serves as framework for project control and management (costing, resourcing, reporting, risk, etc.) Design/Development IPT participation (development of End Product portion of WBS) T&E IPT participation (development of T&E portion of WBS) Other IPT/ suborganization participation (to ensure all work activities are properly represented) By the book, Systems Engineering generally leads WBS development, since the WBS should be based on the system (physical) architecture In reality, Program Control often develops the WBS with SE support 6 WBS Best Practices Use MIL-HDBK-881A as GUIDANCE: Start by following 881A to the extent possible: Reduces “Why did you …” questions Forces consideration of most potential sources of cost (50+ years of experience) Provides structure that has proven successful for 50+ years Generally a WBS will be tailored to meet program needs There is no “perfect” WBS Focus on Products and Services, not Activities First Element should reflect the System Architecture “End Products” Contractor WBSs should follow the Program WBSs to the extent possible Generally Subcontract WBS(s) should fit seamlessly into the Contract WBS Decompose to product-oriented (or event-oriented) work packages, to the extent possible. Examples include: WBSs should be “Product Oriented,” not “Activity Oriented” Specific Requirements Documents Design Packages Specific Studies or Classes of Studies Specific Technical Reviews Training Documentation Some work packages will have to be LOE activities, but minimize these. Examples include: Management Configuration Management IPT Integration 7 WBS Levels (PMP Element) (Level 0 System of Systems) Level 1 Overall System Level 2 System PMP(s) Level 3 Subsystem PMPs Level 4 Component PMPs Level 5+ CI/SCSI 8 Generic System of Systems WBS WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 1 XYZ System of Systems (SOS) 1 1 System of Systems Prime Mission Product (PMP) 1 1 1 System 1 1 1 1 1 System 1 Prime Mission Product 1 1 1 2 System 1 Program Management & Systems Engineering 1 1 1 3 System 1 Engineering 1 1 1 4 System 1 Test and Evaluation 1 1 1 5 Initial Spares/Repair Parts 1 1 2 System 2 1 1 3 System 3 1 1… … 1 1N System N 1 2 System of Systems Program Management & Systems Engineering 1 2 1 Program Management 1 2 1 1 Management 1 2 1 2 Program Planning & Control (WBS, Cost, Schedule) 1 2 1 3 Program Operations & Logistics (incl. HR & Security) 1 2 1 4 Programmatic Baseline Management & Reviews 1 2 1 5 Risk Management 1 2 2 Systems Engineering 1 2 2 1 SE Management & Planning 1 2 2 2 Architecture 1 2 2 3 Requirements 1 2 2 4 Analysis 1 2 2 5 Modeling & Simulation 1 2 2 6 Technical Baseline Management & Reviews 1 2 2 7 Cross IPT Integration 1 2 2 8 Specialty Engineering (incl. IA, RAM, ILS, etc.) 1 2 3 Acquisition Logistics 1 2 4 Configuration Management 1 2 5 Quality Assurance 1 3 System of Systems Test and Evaluation 1 3 1 SOS DT&E 1 3 2 SOS OT&E 1 3 3 SOS Mock-ups/System Integration Labs (SILs) 1 3 4 SOS T&E Support 1 3 5 SOS Test Facilities 1 4 Initial Spares/Repair Parts System Level WBS is provide in following Slide Note: Design & Prototype Development are all considered part of the PMP WBS Elements Note: This basic structure is followed at lower levels. Note Program Management & Systems Engineering WBS Elements. These also appear in lower-level System and Subsystem WBSs Note “Product-Oriented” structure of first WBS Element & Activity Oriented structure of following Elements 9 Generic System WBS Note: Structure of System PM & SE is same as SoS structure. WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 1 System 1 (HW) 1 1 System 1 Prime Mission Products (PMPs) 1 1 1 Subsystem 1 (HW eg.) 1 1 1 1 Subsystem 1 Components (CSCIs & Builds) 1 1 1 2 Subsystem 1 Integration 1 1 1 3 Subsystem 1 Systems Engineering 1 1 1 4 Subsystem 1 T&E 1 1 1 5 Subsystem 1 Training 1 1 1 6 Subsystem 1 Data 1 1 1 7 Subsystem 1 Training 1 1 1 8 Subsystem 1 Data 1 1 1 9 Subsystem 1 Peculiar Support Equipment 1 1 1 10 Subsystem 1 Common Support Equipment 1 1 1 11 Initial Subsystem 1Spares and Repair Parts 1 1 2 Subsystem 2 (SW eg.) 1 1 3 Subsystem 3 1 1 … … 1 1 N Subsystem N 1 1 N+1 Communications Subsystem (HW & SW) 1 1 N+1 1 Radio System 1 1 N+1 2 Data Link 1 1 N+1 3 Comm System SW 1 1 N+1 4 Comm System HW 1 1 N+1 2 Communications Integration Assembly & Checkout 1 1 N+2 System Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout Detailed HW and SW Subsystem Level WBSs are provide in later Slides. Note: Design & Prototype Development are all considered part of the PMP WBS Elements. End Products Enabling Products 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 7 8 9 10 Program Management & Systems Engineering System Test and Evaluation 1 Development Test & Evaluation (DT&E) 2 Operational Test & Evaluation (OT&E) 3 Mock-ups & System Integration Labs (SILs) 4 T&E Support 5 Test Facilities Training 1 Equipment 2 Services 3 Facilities Data 1 Technical Publications 2 Engineering Data 3 Management Data 4 Support Data 5 Data Repository Peculiar Support Equipment 1 Test and Measurement Equipment 2 Support & Handling Equipment Common Support Equipment Operations/Site Activation Industrial Facilities Initial System Spares & Repair Parts Note “Product-Oriented” structure of first WBS Element & Activity Oriented structure of following Elements Note: This basic structure is followed at lower levels. 10 Aircraft System WBS: Spreadsheet Format [1] WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 1 Aircraft System 1 1 Aircraft Prime Mission Products (PMPs) 1 1 1 Airframe 1 1 2 Propulsion 1 1 3 Communications/Identification 1 1 3 1 Radio System 1 1 3 2 Data Link 1 1 3 3 Comm System SW 1 1 4 Navigation Guidance 1 1 5 Fire Control/Radar 1 1 5 1 Receiver 1 1 5 2 Transmitter 1 1 5 3 Radar Applications SW 1 1 5 4 Radar Systems Software 1 1 5 5 Radar Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout 1 1 6 Automatic Flight Control 1 1 7 Central Computer 1 1 8 Electronic Warfare 1 1 9 Weapon Delivery System 1 1 10 Armament 1 2 Program Management & Systems Engineering (See SoS) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 7 8 9 10 System Test and Evaluation 1 Development Test & Evaluation (DT&E) 2 Operational Test & Evaluation (OT&E) 3 Mock-ups & System Integration Labs (SILs) 4 T&E Support 5 Test Facilities Training 1 Equipment 2 Services 3 Facilities Data 1 Technical Publications 2 Engineering Data 3 Management Data 4 Support Data 5 Data Repository Peculiar Support Equipment 1 Test and Measurement Equipment 2 Support & Handling Equipment Common Support Equipment Operations/Site Activation Industrial Facilities Initial System Spares & Repair Parts 11 Aircraft System WBS: Graphic Format [2] 12 Subsystem/Subcontract WBS Generic Subcontract WBS WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 1 Subsystem 1 1 1 Subsystem 1 Prime Mission Products (PMPs) 1 1 1 1 Component (CI/CSCI) 1 1 1 1 2 Component (CI/CSCI) 2 1 1 1 … … 1 1 1 N Component (CI/CSCI) N 1 1 1 N+1 Component Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout 1 2 Platform Integration 1 3 Subsystem Program Management & Systems Engineering 1 4 Subsystem Test and Evaluation 1 5 Subsystem Training 1 6 Subsystem Data 1 7 Subsystem Peculiar Support Equipment 1 7 Subsystem Common Support Equipment 1 8 Subsystem Operations/Site Activation 1 9 Initial Subsystem Spares & Repair Parts Radar Subsystem WBS WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 1 System 1 1 Fire Contro/Radar Subsystem 1 1 1 FC/Radar Prime Mission Products (PMPs) 1 1 1 1 Receiver 1 1 1 2 Transmitter 1 1 1 3 Radar Applications SW 1 1 1 4 Radar Systems Software 1 1 1 5 FC/Radar Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout 1 1 2 Platform Integration 1 1 3 Subsystem Program Management & Systems Engineering 1 1 4 Subsystem Test and Evaluation 1 1 5 Subsystem Training 1 1 6 Subsystem Data 1 1 7 Subsystem Peculiar Support Equipment 1 1 7 Subsystem Common Support Equipment 1 1 8 Subsystem Operations/Site Activation 1 1 9 Initial Subsystem Spares & Repair Parts 13 Generic Software Program WBS Structure WBS LEVEL 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 System (SW) 1 1 System 1 Prime Mission Product (PMP) 1 1 1 Subsystems (Hardware) 1 1 1 1 Subsystem (CI) 1 1 1 1… … 1 1 1 M Subsystem (CI) M 1 1 2 Application SW 1 1 2 1 Build 1 1 1 2 1 1 CSCI 1 1 1 2 1 2 CSCI 2 1 1 2 1 … 1 1 2 1 N CSCI N 1 1 2 1 N+1 App SW Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout 1 1 2 2 Build 2 1 1 2… .. 1 1 2 L Build L 1 1 3 System S/W 1 1 4 (HW/SW) Integration, Assembly, Test and Checkout 1 2 Platform Integration 1 3 Program Management & Systems Engineering 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8 8 9 10 11 System Test and Evaluation 1 Development Test & Evaluation (DT&E) 2 Operational Test & Evaluation (OT&E) 3 Mock-ups & System Integration Labs (SILs) 4 T&E Support 5 Test Facilities Training 1 Equipment 2 Services 3 Facilities Data 1 Technical Publications 2 Engineering Data 3 Management Data 4 Support Data 5 Data Repository Peculiar Support Equipment 1 Test and Measurement Equipment 2 Support & Handling Equipment Common Support Equipment 1 Test and Measurement Equipment 2 Support & Handling Equipment Operations/Site Activation Industrial Facilities Initial System Spares & Repair Parts 14 WBS Element/WBS Dictionary WBS Level WBS Number (1.X.Y) Name of Element Description of Element Scope of Element Major Activities/Tasks Major Artifacts Major Subelements Major Deliverables (CLIN reference) Cost Description SOW References 15 Work Packages Purpose: Provides a description of the work that is to be assigned to a given organization from a given WBS element Contents: Use: Basis Basis Basis Basis for for for for assigning work prioritizing work costing work scheduling work Rules of thumb: All activities are led by a single organization May include work from other organizations Value ~$200 K WBS Reference Work Package Title Work Package Number Assigned Organization Type of Activity Earned Value Level of Effort Work Package Description Work Package Basis of Estimate (BOE) Work Package Schedule 16 Work Package Descriptions Contents: List of Artifacts to be developed List of Tasks to be performed Description of Tasks and Artifacts Purpose of Tasks and Artifacts Key Output Dependencies Key Input Dependencies Principal and/or Intermediate Milestones for Earned Value Reporting 17 Typical SE Services and Products Some Typical Services: Systems Engineering Management System Architecting Requirements Generation Configuration Management Systems Analysis Modeling and Simulation Validation and Verification Support Reviews and Audits This is a partial list. Services and Products provided by SE vary from project to project. Some Typical Products: Work Packages Plans Systems Engineering Plan Risk Management Plan Configuration Management Plan Selected Quality Management Procedures Architecture Artifacts Specifications Analyses/Trade Studies System Models/Simulations 18 WBS Cost Accounts, Work Packages, and Organizational Structure Cost/Control Account identifies: the portions of a WBS Element’s Work Packages that are allocated to each Organization/ Suborganization Cost/Control Accounts tie the (Product-Oriented) WBS to the Organizational Structure It enables Cost Reporting, Monitoring, & Control Note: Organizational Structures will be addressed next week. 19 WBS Summary [1] MIL-HDBK-881A provides guidance, definitions and examples Three types of WBSs (PWBS, CWBS, SWBS) They should be consistent to the extent possible WBSs should be product-oriented (not activity oriented) First Level 2 Element (PMPs) reflects System Architecture End Products Generally the structure of a Level 2 Element (PMP) will mirror the Level 1 structure Decompose to Work Package Level (Lowest Level WBS element) Large programs will have complex multi-layer WBSs. 20 WBS Summary [2] The WBS Defines the Program WBS reflects: System Structure Program Structure WBS (with Work Packages & WBS Dictionary) is used to: Organize/Define Work Organize Cost Provide framework to support: Risk Management Cost and Schedule Reporting/Monitoring Earned Value Management Life Cycle Costing 21 Notes on WBSs Level 2: Breakdown into “End Product” and “Enabling Product” Elements is generally adhered to There is a great deal of variation as to how that is done It is generally driven by customer It is generally influenced by contractor Project Management (and Systems Engineering input) Level 3: Parts are driven by Customer Parts are driven by Contractor Level 4+: Generally developed by Contractor Generally Product/Service Oriented (vs. Activity) Pre-verification development and unit testing are generally allocated to the CI There is generally pressure to organize the WBS by Organization Structure Customer Contractor => Conflict 22 Summary Points (9.4) The WBS is an essential tool for the organization and coordination of systems engineering processes, and is a product of the systems engineering process The importance of the WBS extends to business professionals and contracting officers. The needs of all stakeholders must be considered in its development The Program Office develops the Program WBS (and a high level contract WBS for each contract). Each contractor develops the lower levels of the Contract WBS for their contract The System (Physical) Architecture provides the basic structure for the “Product” part of the WBS SOW tasks should flow from the WBS The WBS provides a structure for organizing IPTs and tracking metrics 23 BACKUP 24 WBS-Backup Purpose Provides a coordinated, complete, and comprehensive view of program management Establishes a structure of organizing system development activities Provides a structure for budgets and cost estimates Provides a structure for to organize the collection of detailed costs Provides a structure for Identifying products, processes, and data Organizing risk management analysis and tracking Enabling configuration and data management Developing work packages Organizing technical reviews and audits Establishes the work that is required for a project Provides a framework for structuring a project’s work (work packages) Provides a method for organizing feedback Used to genera a cost structure Provides a framework for prioritizing work 25 Relationship between Physical Architecture and WBS 26