File - About Ms. Sorensen
advertisement

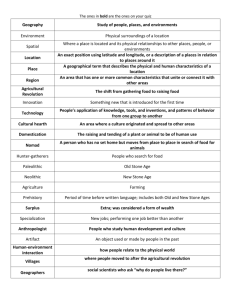
Earth Systems & Resources Essential Learning Questions / Objectives Define three major cultural and environmental changes that have occurred since humans were hunter-gatherers. Describe the environmental history of the United States in terms of the Tribal and Frontier Eras, the Early Conservation Era, and the Environmental Era. Compare slash-and-burn agricultural practices with the modern advanced forms of farming. State the advantages and disadvantages of each. List individuals who made major contributions to conservation/environmental movements in the United States and briefly describe these contributions. Define environmental backlash. Briefly describe the effects of this backlash. Summarize the key environmental events of the 1980s in the U.S. and the World Compare and contrast the environmental policies of the Clinton administration and the Bush administration. Early History • Earth has existed for an estimated 4.6 billion years • Homo sapiens have been on earth only about 60.000 years • Until about 12,000 years ago men were mostly hunter-gatherers. Cultural Changes & the Environment Hunter-Gatherers Humans (Homo sapiens) have been in existence for about 160,000 years, a mere blink of an eye in terms of biological life. (early humans lived off the land – nomadic) Agricultural (Neolithic) Revolution (10,000 to 12,000 years ago) Industrial-Medical Revolution (began in the 1700’s in England Progressed to United States in the 1800’s) Information and Globalization Revolution (since 1950 and especially since 1970) Hunter-Gatherers • Survived by eating edible wild plants, fishing, hunting, and scavenging meat killed by other animals • Lived in small bands • Were nomads • They discovered: o Which plants and animals could be eaten and used as medicine o Where to find water o How plant availability changed throughout the year o How game animals migrated Advanced Hunters-Gatherers • Used more advanced tools and fire • Contributed to the extinction of some animals (sabertoothed tiger) • Altered distribution of plants by carrying seeds • OVERALL IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT WAS LOW DUE TO: o Small population o Low resource use/person o Migration allowed ecosystem to repair itself o Lack of technology Agricultural Revolution • 10,000-12,000 years ago • Also called Neolithic revolution • Gradual shift from nomads to settling in agricultural communities • Domesticated animals and cultivated wild plants Slash-and-Burn Cultivation Slash and Burn did destroy local environment, but was usually very small and had a limited impact. Still a problem in some parts of developing World. (Amazon) 1 Clearing and burning vegetation 2 Allowing to revegetate 10 to 30 years 4 3 Planting Harvesting for 2 to 5 years The Agricultural Revolution: Trade offs The Agricultural Revolution • Most early farmers practiced SUSTAINABLE CULTIVATION • Had little impact on the environment because: o Depended on human muscle power and crude tools o Low population size and density o Land was available for movement to other areas The Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution • Began in England in the mid 1700’s and in America in the 1800’s • Based on dependence on coal (nonrenewable fossil fuel) rather than renewable wood • Invention of the steam engine • Switched from small-scale localized production to large-scale production of machine-made goods. • People began to live longer • Movement from rural to cities o Often very bad living and working conditions Resulted in: • Fossil-fuel powered farm machinery • New plant-breeding techniques increasing yield per acre • More reliable food supply • Longer life spans • Increase in population size Information & Globalization Revolution • • • • Many new technologies – telephone, computers, tv, etc Automated data bases Remote sensing satellites A shift took place where humans moved from relying on wood and flowing water to a dependence on machines run by nonrenewable fossil fuels (first coal, then later oil and natural gas)