Student Glossary - Springboro Community Schools

Student
Glossary
Simile
• A figure of speech in which a comparison is made between two unlike things using the words LIKE or AS
– Picturing something in your mind helps you to understand it better, it shows us the qualities of an object or person by comparing it to something else.
She’s as sly as a fox.
Samantha is as light on her feet as a ballet dancer.
She was sobbing like a baby with an empty bottle.
It’s as cold as a meat locker in here.
Metaphor
• A figure of speech in which an implied comparison is made between two unlike things. This is similar to a “simile” but the words LIKE and AS are not used.
When I was grounded for a week, my room was a prison of despair.
My room prison
My dad is a polar bear when it comes to swimming in cold water.
Dad polar bear
Foreshadowing
•
The technique of giving clues to coming events in a narrative.
– Encourages reader to read on
– Partially prepares reader for events to follow
Examples?
Theme
• A topic of discussion or writing; a
MAJOR idea broad enough to cover the whole literary work.
– A theme can be STATED or IMPLIED
Examples?
Credibility
• The quality or state of offering reasonable grounds for being believed.
– ask: is this source reliable?
– Is this source believable?
– Is this website “professional”?
Examples?
Open-ended Questions
• A type of question intended to produce a free response rather than a one or two word answer.
– Requires reader to “think” before they answer
– Requires reader to show support
– This type of question should be used while researching.
Examples?
Inference
• Inference is using facts, observations, and logic or reasoning to come to an assumption or conclusion.
• It is not stating the obvious
– Example: (stating the obvious) that girl is wearing a fancy dress and carrying a bouquet of flowers. (inference) that girl is a flower girl in a wedding.
– It is not prediction, though the two are definitely related.
• inference asks "What conclusions can you draw about what is happening now?"
• Prediction asks, "What will happen next?"
Connotation
• the attitudes or feelings associated with a word and not the word’s literal meaning.
– Feelings may be positive, negative, or neutral when associated with the word.
Positive
Laid-back: to have a relaxed attitude
Inactive; to do nothing
Lazy; does not want to work or do anything
Negative
Neutral
Denotation
• the literal meaning or “dictionary” definition of a word.
– D for denotation
– D for dictionary definition
Examples:
• Thrifty; tending to save money
Detonation
– “My thrifty aunt made unique picture frames for my graduation present.”
• Finds ways to save money
Connotation
• Cheap; contemptible because of lack of any fine, lofty, or redeeming qualities
Detonation
– “My cheap uncle bought me socks for graduation.”
• Doesn’t spend money
Connotation
Examples:
• Young; being in the first or an early stage of life, growth, or development Detonation
– “I was too young to join swim team this year.”
• wasn’t old enough(age)
Connotation
• Immature; lacking complete growth, differentiation, or development
Detonation
– “I was too immature to join swim team this year.”
• I couldn’t behave myself (attitude) Connotation
Examples:
• Thin; not well fleshed(lean)
Detonation
– “Runway models use to be thin and lean, now they are scrawny and gross.”
• Skinny
Connotation
• Scrawny; exceptionally thin and slight or meager in body or size
Detonation
– “My brother Matt is scrawny, he is a very picky eater.”
• Shrinking in size, very small Connotation
Plot Structure
Rising Action complication
Exposition
Climax
Falling action
Resolution
Copy screen wordfor-word
Exposition
• This is the introduction of the story
– Provides:
•
• Background information needed to understand story
• Characters such as protagonist & antagonist
– Who is your protagonist? Antagonist?
The setting of the story
– WHEN and WHERE does the story take place?
Copy screen wordfor-word
Exposition: Elli Friedman and her family live in Somorja. WWII era, Germany is invading surrounding countries. Elli is our main character and protagonist, Germany is our antagonist.
Complication
• When does the first conflict/problem arise and develop? What other problems start to arise and continue to develop?
• Ask yourself: what was it that put everything in motion?
Complication: Elli Friedman, her family, and other Jewish households are forced to move to Nagymagyar (The Jewish
Ghetto) and leave their homes, most of their possessions, and their old lifestyle behind.
Copy screen wordfor-word
Rising Action
• what occurs leading up to the climax.
Copy screen wordfor-word
• Ask yourself: what did the author do to set up the most exciting scene?
Rising Action: Elli, Mommy, and Bubi are on a train, there are rumors of allied forces and liberation. They have been on the train for days.
Climax
Copy screen wordfor-word
• considered the high point – the most exciting
part – of the story.
– This is where all the rising action and conflict building up in the story finally reaches the peak.
– It is usually the moment of greatest danger or decision-making for the protagonist.
Climax: Elli, Mommy, and Bubi have all been liberated. They are in terrible condition and Elli appears to be 62 years old. They have survived the Holocaust.
Falling Action
• The falling action deals with events which occur right after the climax. These events are usually the after-effects of the climax.
Copy screen wordfor-word
Falling Action: The Friedman family returns to their hometown.
Elli returns to school as does Bubi. Mommy makes a living by sewing dresses. Daddy passed away two weeks before
Liberation in Bergen-Belsen.
Resolution
• Here is the end of the falling action and the conclusion to the story.
• reveals the final outcome of the conflict
Items in
BOLD optional
– Keep in mind, that sometimes stories have endings with a lot of unanswered questions. It is up to your discretion on whether you want to identify a resolution, or argue that a resolution in the story was never fully developed.
Resolution: Elli, Mommy, and Bubi travel to America to begin a new life. The memoir ends as soon as they arrive. It was not fully developed.
Alliteration
• The repetition of a sound at the beginning of two or more neighboring words
The fluffy feline furrowed her fuzzy brow.
Babbling brook
Student Glossary Quiz
• Includes:
– Simile
– Metaphor
– Foreshadowing
– Theme
– Credibility
– Open-ended questions
– Inference
– Connotation
– Denotation
– Exposition
– Complication
– Rising action
– Climax
– Falling action
– Resolution
– alliteration
• Students should be able to define all of the words, show their comprehension through example
• Quiz will consist of fill in the blank, true/false, and short answers for your examples.
– 80 points
– 2 points for correct definition
– 3 points for providing correct example.
Quiz on 10/31/12
Symbol
• Symbols are objects, characters, figures, and colors used to represent abstract ideas or concepts
– A symbol may have more than one meaning. In fact, the most significant symbols do convey an indefinite range of meanings.
• What symbols do you see in your literature circle novels?
Oxymoron
• A two or three word phrase that contains
opposite words or ideas.
• Examples?
Suspense
That quality of a literary work that makes the reader or audience uncertain or tense about the outcome of events.
– Suspense makes the reader ask "What will happen next?".
– greatest when it focuses attention on a character you like.
– Examples:
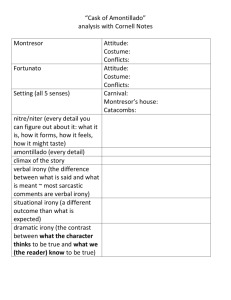
Irony
• Irony is the difference between the way things seem and the way they really are.
– Verbal
– Situational
– dramatic
Verbal irony
• Verbal irony is when a speaker or writer says one thing but actually means the opposite.
– “Is that really what is being said?”
– Example: Your parents give you about 2 hours of chores to do before you can leave and you reply,
“Wow, thanks mom and dad, I can’t wait to do all these wonderful chores!”
Situational Irony
• In situational irony the outcome of a situation is inconsistent with what we expect would normally occur.
– Ask yourself…“What were you expecting to happen?”
– Ask yourself…“What did you expect it to be?”
– Example: Your convertible top is stuck in the open position and you are on the way to the shop and it begins to pour.
Dramatic Irony
• Dramatic irony is when the audience or the reader is aware of something that a character does not know.
– Example: In Romeo and Juliet, Romeo believes
Juliet to be dead, but the audience knows she has only been given a potion to sleep.
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
If you had a phobia of long words, you must tell people that you are
Hippopotomonstrosesquipedali ophobic.
Situational
• It is ironic that people who have a fear of long words must say such a long word. It seems as if the people who made up the word did it on purpose!
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
A rat infestation at the
Department of Sanitation
Situational
You do not expect an agency that works to keep things clean having a rodent infestation.
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
• Mother: “I see you ironed your shirt.”
• Boy: “But I just dug it our of the bottom of the hamper.”
Verbal
The mother is being ironic in that she is pointing out that the boy’s shirt is terribly wrinkled. She is being sarcastic in order to make her point.
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
A person Tweets about how
Twitter is a waste of time and energy.
Situational
•
It is ironic that someone who hates Twitter so much would use the Twitter platform to share with others how useless Twitter is.
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
In Shakespeare's Hamlet, Hamlet stabs through a curtain thinking his traitorous murdering uncle is there, only to learn that he actually stabbed and killed the father of the women he loves, and a man for whom he had the utmost respect and admiration.
Dramatic
•
Hamlet expected to stab his uncle, who he hated, instead ended up stabbing and killing the one person he trusted and admired.
Practice: is this verbal, situational, or dramatic irony?
• You comment on the beautiful weather you have been having moments before a tornado rips through your house.
situational
• Hello, a tornado just destroyed your house right after you said the weather was wonderful!
What is ironic about this image?
Situational Irony
Situational Irony
Situational Irony
Situational Irony
Situational Irony
Situational Irony
Allusion
• A reference made to a famous person, place, or event.
• Allusion’s in The Outsiders
– Paul Newman
– Robert Frost
– Great Expectations
– Gone With the Wind
– The Beatles
– Elvis Extra credit to those who show Allusions found in their independent novel until end of this quarter. Max TWO entries.
Idiom
• the language peculiar to a people or to a district, community, or class
– An expression that means something different from what it says. (The meaning cannot be decided on by looking up all the words in the phrase)
“Sam is a real cool cat. He never blows his stack and hardly ever flies off the handle. What’s more, he knows how to get away with things…well, of course, he is getting on, too. His hair is pepper and salt, but he knows how to make up for lost time and take it easy. He gets up early, works out, and turns in early.
He takes care of the hot dog stand like a breeze until he gets time off. Sam’s got it made, this is it for him.”
“Sam is a real cool cat. He never blows his stack and
(loses control)
(Sam is a really calm person) hardly ever flies off the handle. What’s more, he knows
(becomes too angry) (Also) how to get away with things…well, of course, he is getting
(getting older) on, too. His hair is pepper and salt, but he knows how to
(beginning to turn gray) make up for lost time and take it easy. He gets up early,
(knows how to compensate for lost time by relaxing) works out, and turns in early. He takes care of the hot dog
(goes to bed early) stand like a breeze until he gets time off. Sam’s got it
(without visible effort) (successful) made, this is it for him.”
(reached his life goal)
“Sam is a real cool cat. He never blows his stack and hardly
(not very warm domestic animal) (exhales his pile of material objects) ever flies off the handle. What’s more, he knows how to get
(propel oneself into air using part of an object designed to hold by hand) away with things…well, of course, he is getting on, too. His hair is pepper and salt, but he knows how to make up for lost time and take it easy. He gets up early, works out, and turns in early. He takes care of the hot dog stand like a breeze until he gets time off. Sam’s got it made, this is it for him.”
Examples
Blow my mind: to become wildly enthusiastic about something as if understanding it for the first time in a new light
Blue in the face: very angry, upset
Coast is clear no danger or enemy in sight
Curiosity killed the cat: getting too nosey may lead a person into trouble
In your glossary: Write a sentence using one or two of the idioms correctly.
Conflict
• A struggle between two opposing forces in a novel, short story, or play.
• A Story’s plot is developed around one or more of the five basic conflicts.
– Character vs. character
– Character vs. nature
– Character vs. society
– Character vs. fate
– Character vs. self
Conflict
Character vs. Nature
• Examples:
– In Life as We Knew It the characters had to survive after the moon is knocked closer to the earth and the natural disasters that occur as a consequence.
– In The Cay, Timothy and Philip must survive the wrath of the hurricane while stranded on an island in the Caribbean.
Conflict
Character vs. Self
• Examples:
conflict
Character vs. Character
• Examples:
• Harry Potter Vs. He Who
Must Not Be Named
• Percy Jackson Vs. Whoever he is up against at the moment…(Luke?)
Conflict
Character Vs. Society
• Examples:
– In The House of the Scorpion,
Matteo has to endure the cruelties of the world as life as a clone. Society looks down on clones and believes them to be animals.
– The Hunger Games?
– Any others?
Conflict
Character vs. Fate
• Example:
– In HP and the Order of the
Phoenix our main character is learns of a prophecy in which is needs to fight against to survive.
Tone
Tone is the author’s attitude toward the writing.
– can have more than one tone
– set by the setting, choice of vocabulary and other details.
Words That Describe Tone
Amused Simplistic Humorous Pessimistic Angry Informal
Playful Youthful Cheerful Ironic Pompous Melodramatic
Horror Light Sad Clear Matter-of-fact Serious Slangy
Formal Resigned Suspicious Gloomy Optimistic Witty
Example: tones in The Outsiders?
“witty” “matter-of-fact” “Youthful”; “melodramatic”;
“slangy”; “simplistic”
Mood
Mood the feeling the reader gets from reading those words.
Words That Describe Mood
Fanciful Melancholy Frightening Mysterious Frustrating
Romantic Gloomy Sentimental Happy Sorrowful Joyful
Suspenseful
Example? What feeling do you get as you read The
Outsiders?
Frustrating, sentimental
Student Glossary Quiz (2)
• Includes:
– Symbol
– Oxymoron
– Suspense
– Irony (all 3)
– Allusion
– Idiom
– Conflict (all 5)
– Tone
– Mood
• Students should be able to define all of the words and show their comprehension through example, some of which will relate to The
Outsiders
• Quiz will consist of fill in the blank, true/false, and short answers.
• 75 points
Quiz on Tuesday, Jan.
29 th