Literacy Learning Adventure
advertisement

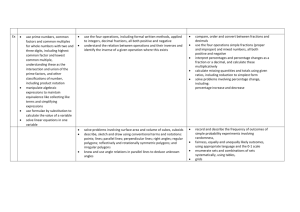
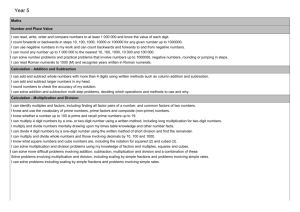
Literacy Learning Adventure TERM ONE NARRATIVE Suggested final written outcome NON-FICTION Suggested final written outcome Space Adventure Story (1 week) – Assessment Narrative Adventure story based on Space recount Recount (3 weeks) Persuasive Writing (4 weeks) Recount of a story linked to space. (Red Bull Space Dive) – Talk for Writing TERM TWO Greek Myths (4 weeks) Film Narrative (3 weeks) Stories from other cultures (3 weeks) Take One Book’ (1 or 2 weeks) One (or more) written outcomes, linked with fiction/nonfiction modules already covered during the term Instructions (3 weeks) Persuasive leaflet for saving our planet POETRY Suggested outcome TERM THREE Classic Poetry (2 weeks) Poetry of Interest (1 week) Listen to, read and respond to raps. Experiment with writing their own. Diary Entry (2 weeks) Stories by significant authors (4 weeks) Older Literature (3 weeks) Persuasion (3 weeks) Take One Book’ (1 or 2 weeks) One (or more) written outcomes, linked with fiction/nonfiction modules already covered during the term Limericks and Haikus (2 weeks) Take One Book’ (1 or 2 weeks) One (or more) written outcomes, linked with fiction/nonfiction modules already covered during the term Mathematical Learning Adventure Number Number Geometry Number and Place Value Fractions (including decimals and percentages) Properties of Shapes read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit compare and order fractions whose denominators are all multiples of the same number identify 3-D shapes, including cubes and other cuboids, from 2-D representations count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 1 000 000 identify, name and write equivalent fractions of a given fraction, represented visually, including tenths and hundredths know angles are measured in degrees: estimate and compare acute, obtuse and reflex angles interpret negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and convert from one form to the other and write mathematical statements > 1 as a mixed number [for example, 2/5 + 4/5 = 6/5 = 1 1/5 draw given angles, and measure them in degrees solve number problems and practical problems that involve all of the above add and subtract fractions with the same denominator and denominators that are multiples of the same number multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, supported by materials and diagrams angles at a point and one whole turn (total 360 degrees) read Roman numerals to 1000 (M) and recognise years written in Roman numerals. read and write decimal numbers as fractions [for example, 0.71 = 71/100 angles at a point on a straight line and 1/2 a turn (total 180 degrees) Addition and Subtraction recognise and use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents other multiples of 90 degrees add and subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using formal written methods (columnar addition and subtraction) round decimals with two decimal places to the nearest whole number and to one decimal place add and subtract numbers mentally with increasingly large numbers read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places use rounding to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, levels of accuracy solve problems involving number up to three decimal places Position and Direction solve addition and subtraction multi-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. recognise the per cent symbol (%) and understand that per cent relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’, and write percentages as a fraction with denominator 100, and as a decimal identify, describe and represent the position of a shape following a reflection or translation, using the appropriate language, and know that the shape has not changed. round any number up to 1 000 000 to the nearest 10, 100, 1000, 10 000 and 100 000 solve problems which require knowing percentage and decimal equivalents of 1/2, 1/4, 1/5, 2/5, 4/5 and those fractions with a denominator of a multiple of 10 or 25. Identify: use the properties of rectangles to deduce related facts and find missing lengths and angles distinguish between regular and irregular polygons based on reasoning about equal sides and angles. Multiplication and Division Measurement Statistics identify multiples and factors, including finding all factor pairs of a number, and common factors of two numbers convert between different units of metric measure (for example, kilometre and metre; centimetre and metre; centimetre and millimetre; gram and kilogram; litre and millilitre) solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph know and use the vocabulary of prime numbers, prime factors and composite (non-prime) numbers understand and use approximate equivalences between metric units and common imperial units such as inches, pounds and pints complete, read and interpret information in tables, including timetables. establish whether a number up to 100 is prime and recall prime numbers up to 19 measure and calculate the perimeter of composite rectilinear shapes in centimetres and metres multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers calculate and compare the area of rectangles (including squares), and including using standard units, square centimetres (cm2) and square metres (m2) and estimate the area of irregular shapes multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts estimate volume [for example, using 1 cm3 blocks to build cuboids (including cubes)] and capacity [for example, using water] divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the formal written method of short division and interpret remainders appropriately for the context solve problems involving converting between units of time multiply and divide whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 use all four operations to solve problems involving measure [for example, length, mass, volume, money] using decimal notation, including scaling. recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared (2) and cubed (3) solve problems involving multiplication and division including using their knowledge of factors and multiples, squares and cubes solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division and a combination of these, including understanding the meaning of the equals sign solve problems involving multiplication and division, including scaling by simple fractions and problems involving simple rates. Connected Curriculum Learning Adventure Term1 The Blue Planet and Space Primary Focus: Exploring our World Secondary Focus: Mathematical Understanding Outline of unit content Earth and Space, planet sizes, distances from sun, data problem solving, large numbers, place value. Sun rise/sun set data. Sizes of Earth, Sun and Moon. Shadows – changes during the day and during the year. Seasons- reasons for them due to rotation of earth on its axis. Day and night, tilt of earth, effect on daylight/weather. Phases of the moon and understand why its appearance changes. Space travel. D and T project making and launching a rocket. Visits/Visitors: Planetarium Global Dimension: The Space Race. Exploration of space. Science Earth and Space- see outline of unit content Term 2 Great Greeks Primary Focus: Understanding our World Secondary Focus: Expressing Ourselves Outline of unit content Research Greek pot designs – design own pots using appropriate colours Making pots from clay, transferring designs Dress in Ancient Greece. Compare climate with England. Olympicscompare with modern Olympics. Where is Greece? – mapwork. Timeline of events during Ancient Greek times and Battle of Marathon – warfare. Greek Triremes ships. Worship in Ancient Greece – gods and goddess’s. Sparta/Athens comparisons. Term 3 Vile Vikings Primary Focus: Mathematical Understanding Secondary Focus: Understanding our World Outline of unit content Viking maths – maps, coordinates, compass points, data, years/dates, word problems. Viking raids and invasion. Alfred the Great and Athelstan, first King of England. Anglo-Saxon laws and justice. Edward the Confessor. Visits/Visitors: Greek Day Global Dimension: When did the Ancient Greeks live? Compare on a timeline. Contributions to modern life and language. Science Forces-Archimedes theory. Gravity acting on an object. Friction/air resistance. Levers/pulleys/gears. Visits/Visitors: Jorvik Viking Centre Global Dimension: Contribution to History and modern times and to exploration of the seas and mapwork. Viking ships, trade, settlements Viking towns/family life Viking beliefs and customs. Term 4 Inspirational India Primary Focus: Understanding our World Secondary Focus: Mathematical Understanding Outline of unit content Data, money, temperature graphs/rainfall charts. Where is India and what is it like to live there? Study people local to the area. Homes. Trade, tea etc. Clothing and homes and their way of life. Food- crops etc. Viking Gods. Science Properties and changes in materials. Group materials according to properties. Knowledge of Solids, Liquids and Gases to separate them. Reversible changes. Visits/Visitors: Wolseley Centre Global Dimension: Compare climate in India to local climate. Trade links with the rest of the world. Science Life cycles. Lifecycle of plants and insects. Study each phase of the cycle. Term 5 Amazing Art Primary Focus: Expressing Ourselves Secondary Focus: Exploring our World Outline of unit content Design Indian patterns for Batik. Transfer patterns onto paper and wax designs Creating clay models of elephants. Peacock feather drawing and pastel work. Study our local area and make comparisons to a village in India. Fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area. Visits/Visitors: India Day Global Dimension: Contrast different ways of life to our way of life. Importance of Indian food worldwide. Science Animals including humans. Describe the changes as humans develop to old age. Gestation. Stages of growth and development in humans. Cooking R.E. Taking part in worship Literacy and Numeracy Genre Links Recounts eg. Planetarium/ Red Bull space dive taking/research/reports/designin g and describing a new planet/space creature. Earth and Space, planet sizes, distances from sun, data problem solving, large numbers, place value. Sun rise/sun set data. Persuasive writing-looking after our planet. Cooking Bread making R.E. Christmas Literacy and Numeracy Genre Links Greek myths-studying Greek Myths and creating their own including designing their own Mythical Beast and/or hero. Film narrative (The Snowman). Diaries linked to Ancient Greek life. Cooking Chocolate links R.E. Lord’s Prayer, Easter Literacy and Numeracy Genre Links Links to Science topictemperatures/graphs etc. Instruction writing. Classic Poetry (The Highwayman). Poetry of Interest inc. Chocolate Cake(Michael Rosen). Cooking Indian food R.E. Hinduism Literacy and Numeracy Genre Links Stories from other cultures-Tigers’ Secret novel. Reports, role-play, characterisation, descriptions. Data, money, temperature graphs/rainfall charts. Diaries linked to Indian life. Cooking Indian food R.E. Journeys with a purpose Literacy and Numeracy Genre Links Stories by significant authors/illustrator(Michael Foreman). Limericks, Haikus Numeracy links to Art