Interrelationships
advertisement

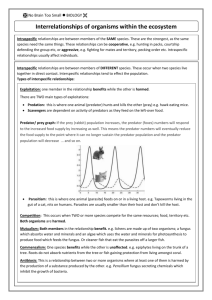
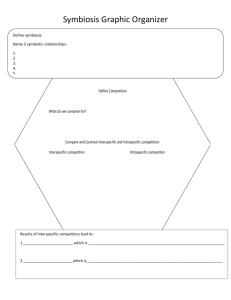
Learning outcomes • Describe the 5 interspecific relationships and the effect they have on each partner of the relationship • Explain what happens to the population and individual when intraspecific competition takes place Interrelationships Intraspecific relationships • Relationships between organisms of the same species • Very strong interactions – Co-operative • E.g. Courtship, looking after young, hunting in packs – Aggressive • E.g. Fighting for mates and territories Interspecific relationships • Relationships between organisms of different species • 5 main relationships Mutualism Both partners benefit from the relationship Commensalism • One partner benefits while the other partner is in-different Amensalism • The presence of one species has a harmful effect on the other, but is not affected by the association itself Antibiosis • One partner is harmed while the other partner is in-different Exploitation • One member of the partnership benefits while the other is harmed Overview Mutualism Commensalism A B Benefits Benefits A B Not affected Antibiosis Amensalism A B Benefits Harmed A B Not affected Exploitation Benefits Harmed A B Harmed Benefits Activity • Complete pg 309 in Biozone Intraspecific Competition • Members of the same population have the same resource requirements from the environment • What are these resources? • What happens when these resources are limited? When resources are limited • Populations - reduce their population growth rate (lower birth rates and/or higher mortality) • Individuals – reduce their growth rate and mature at a smaller size, some may not breed Intersepcific Competition • Competitive exclusion principle (Gause’s principle) “No two species with similar needs for the same limiting resources can coexist in the same place.” • Window and Notch caterpillars