Microeconomics
advertisement

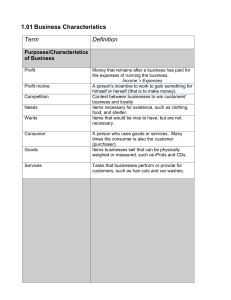
Microeconomics Business Operations Warm Up • What is microeconomics? • Microeconomics – Human behavior/choice – The individual/firm Why Does it Matter? • We interact with businesses on a daily basis • Some of us work for businesses • List 3 firms/stores you have done business with in the last month Types of Businesses • 3 forms of business ownership (free markets) – Sole proprietorships – Partnerships – Corporations Sole Proprietorships • Owned by 1 person – Makes all decisions – Receives all the profits/losses – Legally responsible for the debt • Ex. Family farms, carpet cleaning service, etc. • Name a business that is owned by one person Advantages • Easy to form and dissolve • All decision making power resides with owner – Decisions are made quickly • The profits of the firm is only taxed once – Profit you earn is considered income – Income tax Disadvantages • Unlimited liability – Personal assets may be used to pay of firm debt – Car/house may have to be sold to pay off debt if you go out of business • Can’t borrow funds easily; banks do not want to loan money to success depends on 1 person • When owner dies, business does too! Partnership • Business that is owned by two or more coowners • Share profits/debts • Examples: medical offices, law offices Advantages • Specialization – Each owner does what he/she is good at for the business • Only income tax applies to profits Disadvantages • General Partner – Share in debt of firm – Limited partner does not (doesn’t manage either) • Decision making can be complicated/frustrating Corporations • Legal entity that can – Conduct business in its own name and in the same way an individual does – Is owned by stockholders • Share of ownership • Examples: Disney, Google, Apple Advantages • Owners (stockholders) are not personally liable for the debt of the corporation – Limited liability • Can raise large sums of money by selling stock Disadvantages • Double Taxes – Corporate income tax on profits – Income on stockholders from dividends • Complicated to set up The Corporate Structure • Stockholders are the most important people • They elect the board of directors – Cast as many votes as you have shares of stock – Annual vote • Board of directors – Determine corporate policies and goals – What products to sell – What % of profits go to shareholders (dividends) – Appoints President, VP, Treasurer Financing Corporate Activity • Can borrow money from banks • Only corporations can – Sell bonds – Issue (sell) additional shares of stock • Bondholders must be paid back the debt The Franchise • Contract by a firm (usually a corporation) • Lets a person use its name and sell its products • Must make payments to them and agree to certain conditions • Examples: McDonald’s, Burger King, Wendy’s, Pizza Hut, Domino’s Pizza, Taco Bell How a Franchise Works • A franchisee (person) pays an initial fee – $45,000 for McDonald’s (excludes building/supplies) • Annual Payments to Franchiser – 12.5 % of annual profits • Meet requirements – Cook Big Mac for same length • In return, franchisee gets to use company name, sell products, financial assistance, assistance in training new employees, national advertising Advantages • National advertising • Successful business Disadvantages • Sometimes does not provide the financial and training support you expect • Occasionally does not meet the quality standards you expect Ethical/Social Responsibility • Do businesses have an ethical and social responsibility to the public? Yes – Ralph Nader • Provide customers with full information about their products • Treat employees well • Quality of life (flex time) • Donates funds to meet social needs in community No – Milton Friedman • Only 1 responsibility for businesses! • Use resources and activities designed to increase profits – Without deception/fraud • A business should not give away its profits and does not have any social responsibility to the community Where will they locate? • Similar firms have incentive to locate near each other (competition for customers) • Examples: – Gas stations – Car dealerships – restaurants Questions • The owners of which types of business organizations face unlimited liability? • Which type of business is the largest? • Do you think the initial fee for franchises is the same? Why or why not? • Do you agree or disagree with Milton Friedman’s position on ethical/social responsibility? Explain. Project • Open your own franchise • With 1 partner, choose a franchise • Answer questions – What do you need to qualify to open one? – Cost to open – Pros/Cons • Present your findings Stossel Quiz