Statistics - Sage Middle School
advertisement

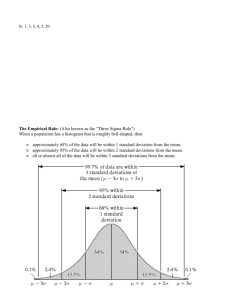
Statistics A statistic: is any number that describes a characteristic of a sample’s scores on a measure. Examples are but not limited to average (arithmetic mean), median and mode, and mean absolute deviation. Mean • The mean is referred to often as the average or as the arithmetic mean. • You may already be familiar with the procedure for finding mean. Given a set of numbers you total them using addition and then divide by the number of numbers in the set. • • • • • • • • For example give the following test scores 80,90,70 (out of 100) The total of 80 + 90 + 70 = 240 240 is out of a possible 300 Divide 240 by 300 and you get an average of .8 .8 is equal to 8 tenths or 80 one hundredths In other words the average test score is 80% On the next slide however we are going to look into where mean comes from. Mean continued • Below are the test scores from the previous slide on a number line. With out using the procedure find the average. X X X • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Mean continued • Now mentally move the X’s toward the middle. • X • X X X X • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Mean continued • All of the scores are now averaged or we have found the mean! This is why mean is referred to as a measure of central tendency. We are literally moving two points by half the distance from either side of the mean until we achieve the mean by using the procedure of algorithm. X X X • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Mean Challenge • Can you find the average of the following scores with out using the algorithm? X X X X X X X • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Mean Challenge • How about this one? What do you begin to encounter? X X X X X X • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Median • The median in a set of data is the number or value that is in the middle of the data and is not always the same as the mean. If you have an even amount of values in your data set you must split the difference between the two values. If there are an odd amount of values in the data set you find the value in the middle. • Given:10 20 50 60 70 (odd number set) • Given 50 60 70 80 (Even number so the median is 65. • Visualize the data set on a number line Mode • The mode is the number or value in a data set that occurs the most. It is possible to have bimodal and multimodal sets of data. • Given: 10 20 30 30 30 100 (30 is the mode) • Given: 10 20 50 50 60 70 70 (Bimodal data set) • Given: 10 10 20 20 3030 (Multimodal data set) Mean Absolute Deviation • The absolute deviation is essentially the average distance of each data point from the mean. • To calculate it add up the distance of each data point in the set from the mean then divide by the number of data points to come up with the standard deviation of the mean. Mean absolute deviation X Average • 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 X • First find the average of the data set which in this case is 50. • Now what is the distance between the average and each data point? • In this case the score of zero is 50 points from the average and so is 100 • Therefore 50 +50 = 100 and there are 2 data points therefore the Mean absolute deviation is 100 divided by 2 or 50. Mean absolute deviation • Why is it useful to find the absolute deviation? • The answer is it tells us about the distribution of the data. A mean absolute deviation that is very small could indicate a picture that might look like this on the left versus the one right X XX X X X X X X X X X X X 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Standard Deviation • Standard Deviation allows one to look at where scores fall in relation to the data. This is related to many times but not always to the standard bell curve distribution. Standard Deviation • To calculate standard deviation • 1) Find the mean of your data • 2) Find the distance between each data point and the mean. • 3) Square the differences • 4)find the sum of the squares • 5) Divide the sum of the squares by the data points. Penny example with the bell curve • Using excel in class students will flip a coin 10 times and record the results. The data points will be entered into excel and graphed. Watch what happens!