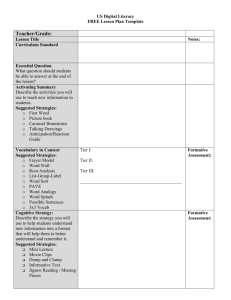
Formative Assessment - Michigan Association of Secondary School
advertisement

Wendy Zdeb-Roper Michigan Association of Secondary School Principals Executive Director wendyz@michiganprincipals.org Follow @massp on Twitter Find me on Linkedin Join #masspchat Monday nights from 8-9pm Three Sticky Notes… Do now…What do I already know about formative assessment? (Just a sentence or two) Do now…What do I hope to learn about formative assessment? Save till the end…What I did learn about formative assessment. Today’s Learning Targets To learn the what, when, who and why of formative assessment. To make the connection between clear learning targets and formative assessment. To learn a variety of ways to formatively assess student learning. To understand how formative assessment data drives the next steps of instruction. Success Criteria I can communicate in a 30 second "elevator speech" a working definition of what a formative assessment is and how it can be used to improve teaching and learning. I can write a student friendly learning target and select a formative assessment to monitor student progress. I will select five different formative assessment strategies that I will implement in the first month of school. I can use formative assessment data from my students to inform my practice. Quick Quiz…T or F? 1. Formative assessment is done at the end of the learning process. 2. Formative assessment is used only for the teacher to adjust instruction. 3. Students are graded on every formative assessment. 4. Formative instruction and instruction go hand-inhand. 5. Formative assessment can help teachers differentiate instruction. 6. Formative assessment can affect scores on summative assessments. Definition A formative assessment or assignment is a tool teachers use to give feedback to students and/or guide their instruction. It is not included in a student grade, nor should it be used to judge a teacher's performance. Both of these would be considered summative assessments. Turn & Talk A formative assessment or assignment is a tool teachers use to give feedback to students and/or guide their instruction. It is not included in a student grade, nor should it be used to judge a teacher's performance. Both of these would be considered summative assessments. Does the definition provided fit with your current practice? What is in agreement? What might be different? Formative Assessment gives teachers information that they can use to inform their teaching and improve learning while it is in progress and while the outcome of the race can still be influenced. - Laura Greenstein What Teachers Really Need to Know about Formative Assessment What is Formative Assessment? An Ongoing Process To: Evoke evidence about student learning Provide feedback about learning to teachers and to students Close the gap between the learner’s current state and desired goals Formative Assessment Must be… Clearly and directly linked to instructional goals Embedded in instruction A variety of methods and strategies Used to make changes Essential Principles Formative Assessment is Student Focused Instructionally Informative Outcomes Based Student Focused Formative Assessment helps teachers Consider each student’s learning needs and styles and adapt instruction Track individual student achievement Provide appropriately challenging instructional activities Design student assessments Offer all students opportunities for improvement through descriptive feedback Feedback: Students Clear and descriptive feedback to students that indicates: where they are in the learning progression how their response differed from that reflected in desired learning goal how they can move forward Instructionally Informative Formative Assessment - Provides a way to align standards, content, and assessment - Allows for purposeful selection of strategies - Embeds assessment in instruction - Guides instructional decisions Outcomes Based Formative Assessment Emphasizes learning outcomes Makes goals and objectives transparent to students Provides clear assessment criteria Closes the gap between what students know and desired outcomes Provides feedback that is relevant, comprehensible, actionable Provides valuable diagnostic information by generating informative data Formative Assessment focuses on achieving goals rather than determining if a goal was or was not met. A Typology of Formative Assessment Performance tasks (teacher observation of student(s) carrying out an investigation, oral presentation) Written tasks (teacher analysis science notebooks, history essay, literature response, explanation of mathematical strategy) Discussions (questions, teacher listens to group discussion, teacher/student conferences) Tests (quizzes , tests of discrete skills, diagnostic tests) Student self-assessment What does the Research Say? “Formative Assessment shows an effect size of between .4 and .7, the equivalent of going from the 50th percentile to the 65th percentile.” Paul Black & Dylan Wiliam, 1998 “Inside the Black Box: Raising Standards Through Classroom Assessment” Seven Strategies Where am I going? 1. Provide clear Learning Target 2. Use exemplars of strong and weak work Where am I now? 3. Provide descriptive feedback 4. Teach students to self-assess & set goals How can I close the gap? 5. Design lessons to focus on one aspect 6. Teach students focused revision 7. Engage students in self-reflection, let them keep track of and share their learning Stiggins, 2006 For formative assessment, teachers not only must be clear about what they want students to learn (the lesson objective or intended outcome for students who "get it"); they also must know typical student steps and missteps toward this goal (the typical learning progression). This knowledge is necessary because what the teacher is looking for in formative assessment is evidence of where students are on their journey toward mastery of the learning outcome. To interpret student work that is on the way toward mastery, teachers need to be able to recognize typical and not-so-typical progress. – Moss & Brookhart Think, Pair, Share… What is challenging about formative assessment? What support might you need from colleagues to be successful in your work? List Three Things… On the index card provided… List 3 Things that a fellow colleague may misunderstand about formative assessment. Three Sticky Notes… Do now…What do I already know about formative assessment? (Just a sentence or two) Do now…What do I hope to learn about formative assessment? Save till the end…What I did learn about formative assessment. For formative assessment, teachers not only must be clear about what they want students to learn (the lesson objective or intended outcome for students who "get it"); they also must know typical student steps and missteps toward this goal (the typical learning progression). This knowledge is necessary because what the teacher is looking for in formative assessment is evidence of where students are on their journey toward mastery of the learning outcome. To interpret student work that is on the way toward mastery, teachers need to be able to recognize typical and not-so-typical progress. – Moss & Brookhart If we agree with Moss & Brookhart then our starting point for solid formative assessment practice has to be a clear learning target. What is a Learning Target? - Learning Targets guide learning. - They describe in language students understand. - Learning Targets are written from the students point of view. - They are shared through out the lesson so that students can use them to guide their own learning. What is a Learning Target? They convey to students the destination for the lesson—what to learn, how deeply to learn it, and exactly how to demonstrate their new learning. In our estimation (Moss & Brookhart, 2009) and that of others (Seidle, Rimmele, & Prenzel, 2005; Stiggins, Arter, Chappuis, & Chappuis, 2009), the intention for the lesson is one of the most important things students should learn. Without a precise description of where they are headed, too many students are "flying blind." Establishing Purpose Why use a learning target? Focuses attention Alerts learner to key ideas Prevents side trips and maximizes learning time Can be used in formative assessment What a Learning Target is NOT… An agenda A list of activities A section in the text book A hoop to jump through! Learning Targets = Shared Ownership Teachers and students have shared understanding and ownership of the learning goal Students become involved in self- assessment Students need to learn the strategies of self-assessment Students make “more knowledgeable decisions regarding their current learning tactics” (Popham, 2006) Writing Learning Targets in Student Language Guiding Question For Younger Students For Older Students What will I be able to do when I’ve finished this lesson? I can… Use question marks. I can… Explain the effect that Ross Perot, a third party candidate, had on the election of President Bill Clinton. Learning Targets: Moss and Brookhart Writing Learning Targets in Student Language Guiding Question For Younger Students For Older Students What idea, topic, or subject is important for me to learn and understand so that I can hit the target? To be able to do this, I must learn and understand that… To be able to do this, I must learn and understand… - Question marks come at the end of asking sentences. - The characteristics of a third-party candidate. - The economic - An asking conditions in the sentence usually US in 1992. begins with a word - The platform and that asks a financial question, like who, resources of Ross what, when, Perot. where, why and how. Writing Learning Targets in Student Language Guiding Question For Younger Students For Older Students What will I do to show that I understand the target, and how well will I have to do it? I will show I can do this by… - Changing telling sentences into asking sentences. I will show I can do this by… Writing an essay on the role Ross Perot played in 1992 election of Bill Clinton that includes three specific effects supported by documented facts from valid and reliable sources. Important to Note… What makes a statement a learning target is that it communicates, in student friendly language, what the student is expected to know by end of a bite size chunk of the lesson. Not all “I can” statements are learning targets or success criteria. They must be measurable. What do Learning Target’s Look Like? Partner Talk How do I check for understanding during a lesson? How often do you do this? Everybody got that? Any questions? Does that make sense? OK? Too often, we accept the answers of a few to serve as a check for understanding of all students. Checking for Understanding is… Formative Systematic Planned It is not… Left until the end of the unit Checking for Understanding involves… Oral language Questioning Written language Projects and performance Tests Common assessments and consensus scoring Fisher, D., & Frey, N. (2007). Checking for understanding: Formative assessment techniques for your classroom. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Checking for Understanding through Oral Language Involves speaking and listening Classrooms are often overwhelmed by teacher talk In high-achieving classrooms, teachers spoke 55% of the time, compared to low-achieving classrooms, where teachers spoke 80% of the time (Flanders, 1970) 56 different examples of formative assessment. https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1nzhdnyMQmio5lNT 75ITB45rHyLISHEEHZlHTWJRqLmQ/pub?start=false&loop=false& delayms=3000#slide=id.p Curated by David Wees, Formative assessment specialist, New Visions for Public Schools Digital Artifact Box! Review the 56 different examples of formative assessment Curated by David Wees. Select 5-8 different formative assessment strategies that you will implement in the first two weeks of school. Share with a partner… Why did you select these options? How will you involve students in the formative assessment process? Edutopia Dipsticks: Efficient Ways to Check for Understanding http://www.edutopia.org/blog/dipsticks-tocheck-for-understanding-todd-finley Student Self-Assessment Student Self-Assessment Learning Target, Formative Assessment…Now What? Once you have gathered evidence of student learning from your formative assessment how will it inform your next steps in instruction? My Favorite LT & Formative Assessment Resources Revisit Your Quiz… 1. Formative assessment is done at the end of the learning process. 2. Formative assessment is used only for the teacher to adjust instruction. 3. Students are graded on every formative assessment. 4. Formative instruction and instruction go hand-inhand. 5. Formative assessment can help teachers differentiate instruction. 6. Formative assessment can affect scores on summative assessments. Success Criteria I can communicate in a 30 second "elevator speech" a working definition of what a formative assessment is and how it can be used to improve teaching and learning. I can write a student friendly learning target and select a formative assessment to monitor student progress. I will select five different formative assessment strategies that I will implement in the first month of school. I can use formative assessment data from my students to inform my practice. Three Sticky Notes… Do now…What do I already know about formative assessment? (Just a sentence or two) Do now…What do I hope to learn about formative assessment? Save till the end…What I did learn about formative assessment. Our goal is not to determine how smart children are, but how children are smart. Wendy Zdeb-Roper Michigan Association of Secondary School Principals Executive Director wendyz@michiganprincipals.org Follow @massp on Twitter Find me on Linkedin Join #masspchat Monday nights from 8-9pm