Polyatomic Puzzle
advertisement
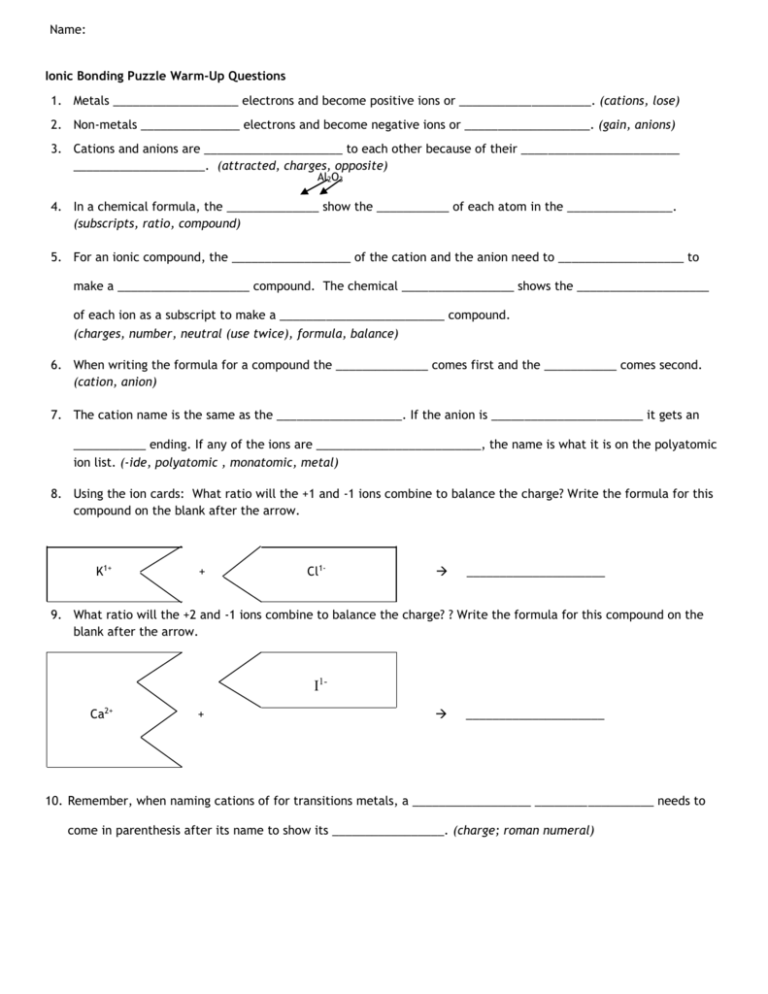
Name: Ionic Bonding Puzzle Warm-Up Questions 1. Metals ___________________ electrons and become positive ions or ____________________. (cations, lose) 2. Non-metals _______________ electrons and become negative ions or ___________________. (gain, anions) 3. Cations and anions are _____________________ to each other because of their ________________________ ____________________. (attracted, charges, opposite) Al2O3 4. In a chemical formula, the ______________ show the ___________ of each atom in the ________________. (subscripts, ratio, compound) 5. For an ionic compound, the __________________ of the cation and the anion need to ___________________ to make a ____________________ compound. The chemical _________________ shows the ____________________ of each ion as a subscript to make a _________________________ compound. (charges, number, neutral (use twice), formula, balance) 6. When writing the formula for a compound the ______________ comes first and the ___________ comes second. (cation, anion) 7. The cation name is the same as the ___________________. If the anion is _______________________ it gets an ___________ ending. If any of the ions are _________________________, the name is what it is on the polyatomic ion list. (-ide, polyatomic , monatomic, metal) 8. Using the ion cards: What ratio will the +1 and -1 ions combine to balance the charge? Write the formula for this compound on the blank after the arrow. K1+ + Cl1- _____________________ 9. What ratio will the +2 and -1 ions combine to balance the charge? ? Write the formula for this compound on the blank after the arrow. I1Ca2+ + _____________________ 10. Remember, when naming cations of for transitions metals, a __________________ __________________ needs to come in parenthesis after its name to show its _________________. (charge; roman numeral) Ionic Bonding Puzzle Activity Introduction When metals and non-metals chemically react, the atoms will tend to form ions or charged atoms. Ions form because electrons are either gained or lost. Metals will generally form cations or positive ions, since they tend to donate electrons Non-metals will form anions or negative ions, since they tend to accept electrons. Activity In this activity you will create models of ionic compounds and observe the chemical formula of the binary compounds you have created. Your data will be recorded in a data table. Follow the directions (A, B, C…) and answer the questions as you complete the data table using the puzzle pieces. A. Design a color code for your ions (e.g. Li+1: yellow, K+1: pink stripes) and color in the shapes. Once you’ve finished coloring, cut out the shapes. 1. Notice the shape and charge of each cation model. Why do you think there are slots in the cation models? (TIP: How do the atoms become ions?) 2. Notice the shape and charge of the anion models. Why do you think there are tabs in the anion models? 3. If you were to make a neutral atom following the model, what would the shape be? (a picture is fine) B. Group the ion models by charges (e.g. all of the +2’s together, all of the 1’s together an so on) 4. What do you notice about the number of tabs or slots? 5. What do you notice about the tabs or slots and charge of all ions? 6. Is there a pattern? 7. Why do you think the model is made that way? C. Use the puzzle pieces to build the ionic compounds listed in the data table. Fill in the data table as you complete each compound. 8. In the compounds you formed, what is the final charge of all the compounds? Make the following compounds with the puzzle pieces. Write their correct formulas and names. Combination: Titanium(IV) and carbonate Bromine and Yttrium(III) Calcium and Phosphorous Lithium and Phosphate Oxygen and Iron(III) Sodium and Hydroxide Iron (II) and Chlorine Hydroxide and Silver(I) Magnesium and Iodine Copper(II) and Oxygen Potassium and Sulfur Cation (+) symbol Anion () symbol Chemical Formula Compound Name Drawing of your puzzle pieces OH-1 H3O+1 Mg+2 Y+3 OH-1 K+1 Cl-1 K+1 P-3 Mg+2 Cl-1 Fe+3 Br-1 (Also use for I-1) K+1 P-3 Ag+1 Ca+2 Br-1 Ag+1 Br-1 Fe+2 Li+1 Sr+2 PO4-3 Ca+2 O-2 (Also use for CO3-2) Cu+2 Also use for Ca+2) H3O+1 Li+1 Li+1 S-2 NO3-1 Ti+4 O-2 Na+1 Na+1 Fe+3 CO3-2 (Also use for O-2) I-1






