Unit 14 The Law of Tort and Intellectual Property
advertisement

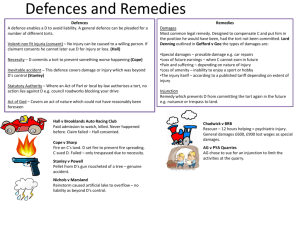
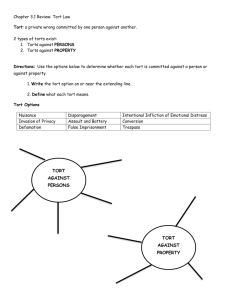
Unit 14 The Law of Tort and Intellectual Property TextⅠ The Law of Tort -To learn the definition, remedies and classification of tort and distinguish between tort and breach of contract and between tort and breach of trust Text Ⅱ Intellectual Property: the Nature - To learn about the nature and jurisprudential character of intellectual property Text III Case Reading -To read one case related to parental responsibilities and rights TextⅠ The Law of Tort Terms: tort, breach of contract, breach of trust, wrong, trespass, trespass on the case, nuisance, fraud, negligence, in personam cf. in rem, simple contract cf. contract under seal, assumpsit, chattel, conversion, duty of care, cause of action, damages (pl.), unliquidated / aggravated / exemplary / punitive damages, pleadings, trespass to land, Government servants, general warrant, remedy, injunction, abatement, ejectment from land, restitution (of goods), tortuous liability, assault and battery, false imprisonment, libel cf. slander, conspiracy, slander of title, deceit, malicious prosecution Proper names: Courts of Equity, Common Law Courts, Privy Council Outline of Text I Ⅰ. (para. 1-2) Origin and definition of “tort” Ⅱ. (para. 3-5) Differences between tort and breach of contract Ⅲ. (para. 6) Differences between tort and breach of trust IV. (para. 7-9) Remedies available in torts V. (para. 10-12) Classification of torts Questions based on Part I 1. How to understand the first sentence in para. 1? 2. In what languages do you find the origin of tort? 3. How is tort generally defined? What does the distinction refer to? Questions based on Part II and III 1. What are the differences between tort and 2. 3. 4. 5. breach of contract? What does “as they do in contract” in para. 3 mean? What does “the distinction” in para. 3 refer to? What are the 2 connecting points between tort and breach of contract given in para. 4? What are the differences between tort and breach of trust? Questions based on Part IV 1. What is the typical remedy in tort? 2. What are the other types of damages available in tort? 3. What is the view of the House of Lords as regards when to grant the injured party aggravated damages or punitive damages? 4. What are other remedies available in tort besides damages? Questions based on Part V 1. Why is the classification of torts difficult if not impossible? 2. How are torts classified in textbooks? 3. How does Winfield classify torts? Terms tort 民事侵权行为 -damage, injury, or a wrongful act done willfully, negligently, or in circumstances involving strict liability, but not involving breach of contract, for which a civil suit can be brought *tortfeasor n. 犯侵权行为者 tortious adj. 侵权行为的, 侵权行为性质的 breach of contract 违反契约 / 合同 breach of trust 违反信托 *trust 信托 -the confidence reposed in a trustee when giving the trustee legal title to property to administer for another, together with the trustee's obligation regarding that property and the beneficiary Terms wrong 过错 trespass 非法侵入, 非法侵害 trespass on the case 间接侵害诉讼,也称action on (the) case,与straight trespass action“直接侵害诉 讼”相对。间接侵害诉讼的创立就是适用于直接侵 害诉讼所不能处理的侵害。 nuisance 妨害行为、滋扰罪 *private nuisance 妨害个人安宁的行为 public/common nuisance 妨害公共秩序的行为 fraud 欺诈 Terms negligence 过失 -failure to exercise the degree of care considered reasonable under the circumstances, resulting in an unintended injury to another party *culpable/gross negligence 重大过失 ordinary negligence 一般过失 in personam (尤指诉讼或判决)对人地的(指专以 要求诉讼一方承担责任或履行债务为目标,而不以 财产为目标)与in rem相对,(字面意义against the person) in rem(尤指诉讼或判决)对物地的(指专以物,如 动产、不动产为目标)与in personam相对,(字 面意义against the matter) Terms simple contract 简式合同(指按口头诺言订立的但无 完备形式、未加盖印记的非正式合同 (informal contract);口头合同;无签名的合同 contract under seal盖印合同,属于正式合同 (formal contract) assumpsit 要求赔偿违约损失的诉讼 chattel [常用复数] 动产 conversion 对他人财产的非法挪用,是一种侵权行为 duty of care(英)注意义务(普通法上的概念)抚养 责任、保管责任 cause of action 原告的起诉缘由,诉因,案由 Terms damages (pl.) 赔偿金 unliquidated damages 未确定的/等待法庭裁定的损害赔偿 aggravated damages 严重损害他人(财产)赔偿 exemplary / punitive damages 惩罚 / 惩戒性赔偿 other types of damages *nominal damages(象征性 / 名义赔偿): when the nonbreaching party suffers no compensable loss or fails to prove the amount of loss *compensatory / general damages(补偿性 / 一般性赔偿): make the injured party “whole”, meaning bring the injured party to the position it would have enjoyed if the contract had not been breached *consequential / special damages(间接 / 特殊赔偿): not normally foreseeable, in addition to compensatory damages; the injured party suffers additional loss Terms pleadings 诉讼文件 trespass to land 对土地的侵犯行为 government servants 政府公职人员 general warrant(英)一般扣押令 remedy 法律救济 injunction] 禁令(法院强制被告从事或不得从事某项 行为的正式命令) abatement 减轻债务 ejectment from land 收回地产之诉; 收回产权诉讼 restitution (of goods)归还原物 tortuous liability 侵权责任 Terms assault and battery 殴打,侵犯他人人身 false imprisonment 非法禁锢 libel 书面诽谤 slander 口头诽谤 slander of title 权利诽谤;诋毁(他人的财产)所有 权(指一种恶意诽谤他人的物业或权利,使其蒙受 损失,例如说人家的住宅闹鬼,以致租不出去) conspiracy 同谋,共谋。两个或多个人之间进行犯罪 或通过非法行为实现一个合法目标的一种协定。 deceit 欺诈 malicious prosecution (and defamation) 诬告和诽谤 Proper names Courts of Equity 衡平法院 Common Law Courts 普通法法院 Privy Council 枢密院 -a council of the British sovereign that until the 17th century was the supreme legislative body, that now consists of cabinet ministers ex officio and others appointed for life, and that has no important function except through its Judicial Committee, which in certain cases acts as a supreme appellate court in the Commonwealth Partial translation 1. international agreements other than treaties 2. frown upon parents using the children or money as leverage 3. the plaintiff is not entitled to Translation • 1. 法庭寻求对于原告名誉损失的赔偿,特别是当 • • 原告的尊严受到影响,遭受信誉和友情的损失时。 2. 诽谤是指发布虚假陈述损毁受害人的名誉。 (尽管对于犯罪性诽谤的控告可以继续)由于诽 谤是人身伤害行为,因此它随着被害人的死亡而 解除。 3. 从历史上看,口头诽谤被看作是可听到的口头 的诽谤,而文字诽谤是可看到的或是书面的诽谤。 因此,文字诽谤是诽谤最明显的例子,但侵权也 包括了其他视觉形式的诽谤。 Translation • 4.In some lawsuits, the problems still exist that • concern who should be the plaintiff, who should be the defendant, and how the court should deal with the decision of the government when there is a conflict between the investigation result of the court and the decision of the government. 5.(Patent Law of the People’s Republic of China) Article 1 This law is formulated in order to protect patent rights of invention-creations, encourage invention-creations and facilitate their popularization and application, promote the development of science and technology and meet the needs of the socialist modernization. Text Ⅱ Intellectual Property: the Nature words: assign, mortgage, license, anomaly, aggrieved, conversely, instructive, correlative (n.), proviso, curtail, dictate, vehement, proprietor, confidential phrases: give rise to (prep.), classification scheme, enforce a right, as regards, express notice, an exception to, without purpose or consequence, in relation to, sheet music, make copies of, pertain to, spring to life, come into existence, establish a goodwill, be concerned with, in terms of, owe a duty, infringe a right, know of cf. know, exploit a work, to the effect that…, reach a balance between, by way of, provide for cf. provide, fall outside / within, be opposed to (prep.), a rule of thumb, be limited to, of… (adj.) duration terms: intellectual property rights (IPRs): copyright, patent and trademark right, real cf. personal property, tangible cf. intangible property, easement, profit a prendre (French), chose in possession cf. chose in action, consideration, subject matter, negative right, passing off, fair dealing, compulsory license, monopoly right, breach of confidence proper names: Law of Property Act 1925, Patents Act 1977 Outline of Text II Ⅰ. (para. 1-4) Nature of intellectual property: intangible personal property Ⅱ. (para. 5-9) jurisprudential character of intellectual property intellectual property rights (IPRs)的分类 • 基本分为copyright, patent and trademark right • 另分为: (1)artistic property: artistic, literary and musical work protected by copyrights and neighboring rights (2)industrial property: -inventions: patents, petty patents, inventors’ certificate -trademarks: true trademarks, trade names, service marks, collective marks, and certification marks Questions based on Part I 1. What are the similarities between intellectual 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. property and other forms of property? According to the classification scheme on P315, what is the nature of intellectual property? How do you understand “chose in action” as opposed to “chose in possession”? How does the text describe the assignment of intellectual property? What does the exception in the middle part of para. 4 refer to? Try to figure out what is meant by easement and profit a prendre based on the notes. Questions based on Part II 1. What are the rights of the copyright owner? 2. When does copyright come into being? And what 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. about patent and trade mark right? How does the tort of passing off relate to intellectual property right? Para. 6 and 7 discuss figure 14.1. Try to explain the relationship between the rights and duties in intellectual property in your own words. Why are there some provisos on IPRs? How many examples are given as regards provisos on IPRs? What are they? What does the rule of thumb refer to in para. 9? Terms intellectual property rights (IPRs) 知识产权 copyright 版权、著作权 patent and trademark right 专利和商标权 real cf. personal property不动产/动产 tangible cf. intangible property有形财产/无形财产 easement 地役权 profit a prendre (French) 取利权 chose in possession 实际占有动产 chose in action 权利动产 consideration 约因、对价 subject matter 标的物 negative right 消极权利 Terms passing off 冒充、假冒 fair dealing 合理使用(原则 ) compulsory license(专利)强制许可证 monopoly right 垄断权、专利权、专用权 breach of confidence 背信、破坏信用;泄密 Proper names Law of Property Act 1925 1925年财产法 Patents Act 1977 1977年专利法 Text III Case Reading • words: interlocutor, repel, remit, lodge, • • • unopposed, paramount, anomalous, material (adj.), minute, contradictor, supra phrases: in respect of, on…occasion, grant leave to, be in a position to do sth., be open to (prep.), in principle, give effect to, to that end legal and semi-legal terms: plea-in-law, residence order, motion, submission proper names: QC, Sheriff Principal, the Children (Scotland) Act 1995, the Ordinary Cause Rules Terms plea-in-law 法律提述(指原告据此作为提起诉讼之 依据);法律上的抗辩 residence order 居住命令 -A Residence Order states where and with whom a child should live. It also gives the named person/people parental responsibility for the child. A Residence Order may be granted to more than one person and may specify the period the child is to spend in each of the households. motion 动议 submission 向法官或陪审团提出的意见;辩护词 *submission to arbitration 提交仲裁 proper names QC (Queen’s Counsel) 皇室顾问 Sheriff Principal 州長官, 郡保安官, 保安官 the Children (Scotland) Act 1995 《 1995 年蘇格蘭兒童法令》 the Ordinary Cause Rules -the First Schedule to the Sheriff Courts (Scotland) Act 1907