Chemistry - schultz915
advertisement

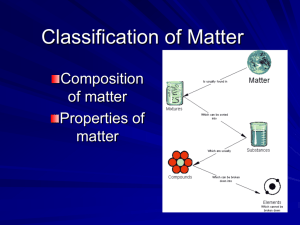
Mrs. Schultz Website: schultz915.pbworks.com Phone: e-mail: 741-3366 x2129 schultzc@manateeschools.net Means “to know” from Latin scientia *Gathering information through observation *Organizing information by looking for regularities *Wondering why the regularities exist *Communicating the findings to others Uses the senses to gather information (sight, sound, taste, touch, smell) 2 types: 1. Qualitative: general characteristics using senses Ex/ The wire is shiny and silver in color. 2.Quantitative: Makes a measurement using tools Ex/ruler for length, graduated cylinder for volume 1.Vague – having no point of reference Ex/ Obtain 5 hydrochloric acid. How much? 2.Defined – having a point of reference Ex/ Measure 5 mL HCl * ALL MEASUREMENTS need number, units, and label. The study of matter is chemistry. This course will study… structure, composition, properties, the changes that matter undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany these processes. Considered the central science because both living and nonliving matter consist of chemical structures. 1.volume is the amount of three dimensional space an object occupies. 2. mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. matter is anything that has mass and takes up space Any substance that has a definite composition. It is always made up of the same atoms no matter where it came from. Ex/ water, table sugar, carbon dioxide 1.Organic chemistry – study of carbon containing compounds 2.Inorganic chemistry – study of compounds that do not contain carbon 3.Physical chemistry – study of the properties and changes of matter and their relation to energy 4.Analytical chemistry – identification of the components and composition of materials 5.Biochemistry – study of substances and processes occurring in living things conducted for the sake of increasing knowledge only and not to meet practical goals. ex/ why a specific reaction occurs Conducted to meet goals defined by specific needs This research is driven by a desire to solve a certain problem. ex/ new refrigerants developed because of damage to ozone layer Employs existing knowledge to make life easier or more convenient ex/ computers and biodegradable materials A logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating hypotheses, testing hypotheses, and the formulation of theories that are supported by data. Experiments are proscribed procedures that collect data to support a hypothesis. Experiments have variables: independent variable – manipulated (variable you change in an experiment) dependent variable – responding (variable observed during experiment) A well-tested explanation for a broad set of observations. Ex/ Atomic theory is useful because it helps to form a mental picture of atoms. Note: Theories are not proven. They are supported by data. Model - An explanation of how phenomena occur and how data and events are related. Models are visual, verbal, & mathematical. Ex. Atomic Model shows structure & composition of atoms Statement that summarizes the results of many observations and experiments. 3 important chemical laws: Law of Conservation of energy Law of Conservation of mass Law of Conservation of matter *ALL LAWS FOLLOWED IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS Matter and Its Properties atom: simplest particle of matter, which keeps identity of element. element: made of only one type of atom ex/ oxygen is considered an element because it is only composed of oxygen atoms. compound: made of more than 1 type of atom linked together. ex/ water, sodium chloride (table salt) molecule: smallest particle of a substance retaining the properties of the substance. ex/ 2 H atoms and 1 O atom are bonded together in water to form a unit. Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter that is present. ex/ volume, mass, amount of energy in a substance. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter present. ex/ melting point, density, ability to conduct electricity Physical Property- can be observed without changing the identity of the substance. physical properties describe the substance itself examples: boiling point, melting point, density A change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance is called a physical change. (ex/ tearing, grinding, cutting) Chemical property: property of a substance related to a chemical change that the substance undergoes. ** CAN NOT BE OBSERVED WITHOUT CHANGING THE IDENTITY OF THE SUBSTANCE. *This means the substance has to go through a chemical reaction. A change in which one or more substances are converted into different substances is called a chemical change or chemical reaction. Ex. Rusting, corrosion, sour milk substances that react (enter) in a chemical change are called the reactants. substances that are formed by the chemical change are called the products. Mass, matter and energy are conserved in a chemical reaction (change). 1. What is the reactant in the chemical reaction above? Ans. Copper(II) oxide 2. What are the products? Ans. Copper & oxygen A change of state is a physical change of a substance from one state to another. Most matter is found in one of the following 3 states: GAS: No fixed volume, no fixed shape, assumes shape of container, & particles weakly attracted to each other and move independently at high speed. LIQUID: Definite volume, no shape of its own, assumes shape of container, & particles slip past each other. SOLID: fixed volume, fixed shape (held tightly in a rigid structure), vibrate only slightly 4th State: PLASMA is a high temperature physical state of matter in which atoms lose their electrons. ex/ found in a fluorescent bulb 5th State: BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATES: matter has different properties at very low temperatures. Steps: 1. Put test tube in test tube rack. 2. Place a piece of copper in the test tube 3. Using the pipette, put nitric acid in the test tube. Put enough acid to cover the copper. 4. Return to your lab area & put the test tube rack on the high bench to observe until the reaction is complete. 5. Place the product of the reaction in the waste container. 6. Rinse out test tube with water, return materials, clean up Make a data table of observations that include before, during, and after the chemical reaction. Answer 4 questions (on the next slide) Copper + nitric acid copper(II) nitrate + nitrogen dioxide + water 1. What are the reactants? 2. What are the products? 3. List 3 observations that support that a chemical change occurred? 4. What chemical property of copper is demonstrated? All matter can be classified into two groups: pure substances or mixtures. A pure substance can be an element or compound. Its composition is the same throughout and does not vary from sample to sample. ex/ iron, carbon dioxide, sugar Mixture- a combination of 2 or more substances (each substance in mixture retains individual properties) ex/ air- mix of gases: O2, CO2, H2O, N2, H2 Heterogeneous mixture: (Greek heteros= different; genos= kind) A mixture that is not uniform in composition. ex/ Soil has clay, sand, silt, & decayed material. 2 Types of Heterogeneous Mixtures: Suspension- mixture containing relatively large particles; particles remain suspended for a while after stirring, but then settle out. ex/ Italian dressing Colloid- liquid mixture containing very small particles that do not settle out, even with time. ex/ milk- fat molecules are dispersed throughout the liquid Homogeneous Mixture (Greek: homos= same) A mixture that is completely uniform in composition. Chemists call homogeneous mixtures: SOLUTIONS Homogenous mixtures consists of a single phase (solid, liquid, or gas) ex/ tap water, energy drinks, brass key Periodic Table: table in which elements, arranged in order of atomic number, are placed so that those with similar properties are near each other. Period: horizontal rows of elements in periodic table. • 7 periods of elements on the Periodic Table Group (or family): vertical columns that each contain elements with similar properties • 18 groups on the periodic table Elements are symbolized by one or two letters What element is symbolized by W? Cu? Au? Ag? Metals -usually solid (except Hg) phase -shiny (luster) -malleable- flattened or shaped -ductile- drawn in wire -conductors of heat & electricity -react w/ acid + base -located on the left side of the periodic table Non Metals -can be any phase -dull -brittle -non conductors -don’t react w/ acid & base - located on the right side of the table Metalloids are elements that have some characteristics of metals and some characteristics of nonmetals. Located between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table (near the stair-step line) Differences in physical properties can be used to separate mixtures. To separate heterogeneous mixtures: Filtration – a process that separates solids from liquids by passing through filter paper. ex/ making coffee uses a paper filter to separate the coffee beans from the water. To separate homogeneous mixtures (solutions): Distillation – a process that uses differences in boiling points to separate a mixture Sketch a diagram of the distillation demo. Label the names of the lab equipment used in your drawing. Write a brief description of the process of distillation.