Cell Theory
advertisement

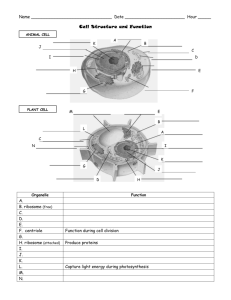
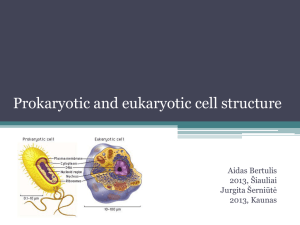
Cell Theory Section 7-1 CELL THEORY 1. Cells are the basic units of life 2. All living things have cells 3. All cells come from existing cells CELL THEORY 1. The basic unit of life is the cell. (Hooke) In 1665, an English scientist named Robert Hooke made an improved microscope and viewed thin slices of cork plant cell walls Hooke named what he saw "cells" CELL THEORY 2. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. Matthias Schleiden (botanist studying plants) Theodore Schwann (zoologist studying animals) stated that all living things were made of cells Schwann Schleiden CELL THEORY 3. All cells divide & come from old cells. (Virchow) Virchow Types of Cells Prokaryote – has no nucleus or organelles - usually unicellular (1 cell) - bacteria & viruses Eukaryote – has a nucleus and organelles - usually multicellular (more than 1 cell) - plants & animals Both have a cell membrane & cytoplasm PROKARYOTE & EUKARYOTE Section 7-1 Cell membrane Cytoplasm Prokaryotic Cell Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Go to Section: PROKARYOTE VS. EUKARYOTE Venn Diagram Section 7-2 Prokaryote Go to Section: Eukaryote Animal Cell Section 7-2 Ribosome (fixed) nucleolus nucleus Nuclear envelope Rough ER Cell membrane mitochondria Smooth ER Golgi Complex Go to Section: Ribosome (free) centriole Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome (free) Chloroplast Cell Membrane Ribosome (attached) Nuclear envelope Cell wall Nucleolus Golgi apparatus Mitochondrian Go to Section: Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum Venn Diagrams PLANT CELL VS. ANIMAL CELL Venn Diagram Section 7-2 Animal Cells Lysosomes centrioles Go to Section: Plant Cells Cell membrane Ribosomes Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Cytoskeleton Cell Wall Chloroplasts Vacuoles