Endocrine Unit Test Study Guide 1
advertisement

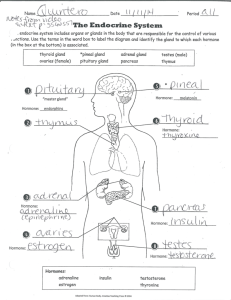
Name _________________________________________ Period __________________ Study Guide for the Endocrine System ___________ is also called adrenaline and it is secreted by the adrenal medulla. The hypothalamus, a neuroendocrine gland, is in the __________. The pituitary gland or __________ is attached to the base of the brain and has anterior lobe and posterior lobe. The _______________ System is slow and longer lasting than the Nervous System. The __________ gland is controlled by the hypothalamus. Cells have special protein receptors. Cells that have more affinity for receptors than other cells are called ______________________. The kidney is not a major _____________ gland. _____________ affect target cells by diffusing into cells from the bloodstream and the study of these chemical is called endrocrinology. The more ___________ produced by the adrenal medulla is likely to produce increased metabolism. The pineal gland produces ________________ which sets sleep cycles. FSH and LH control the gonads and are called __________________. The thyroid hormone that moves calcium from the blood to storage in the bone is ____________. ____________ is the process of forming new sugar from non-carbohydrate molecules (glucose from proteins and fats; occurs in the liver ). The ___________ is a mixed gland composed of both endocrine and exocrine gland cells. Hormonal stimuli is where the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to release TSH; TSH then stimulates the ____________ gland to release thyroxine. The _____________ pituitary gland secretes ADH and oxytocin. ___________ gland produces calcitonin. ___________ is from the adrenal cortex and released during stress; it causes glucose to be made from proteins and fats. Islets of Langerhans are scattered across the __________________. The ______________ cortex makes small amounts of female hormones. Hyposecretion of the parathyroid hormone is called _______________________. The __________ cells of the pancreas produce insulin which moves glucose from the bloodstream into cells. The __________________ consist of ovaries and testes. _______________ feedback is where too much thyroxine in the blood shuts off the hypothalamus production of TSH. FSH is the ____________-stimulating hormone. Too much _____________ hormone in childhood can make a giant. _____________ is where too much growth hormone is produced in adulthood and large hands and feet result. The hormone _______________ is responsible for the increase in the body’s metabolism. Match the hormone with its endocrine gland. Thyroxin Pancreas Oxytocin Parathyroid gland Cortisol Posterior pituitary gland Insulin Adrenal cortex Parathyroid hormone Thyroid gland Match the endocrine gland with the hormone it secretes. Adrenal medulla Melatonin Pancreas Androgens Adrenal cortex Glucagon Anterior pituitary gland Epinephrine Pineal gland Growth Hormone WORD BANK for Fill in the Blank (Words may be more than once or not at all) brain thyroid pancreas negative hypothalamus melatonin thyroxine parathyroid gland gonadotropins hormones posterior cortisol hypophysis gluconeogenesis abnormal follicle glucose adrenal acromegaly homeostasis pituitary hypoparathyroidism beta gonads epinephrine calcitonin endocrine follicle growth up-regulation