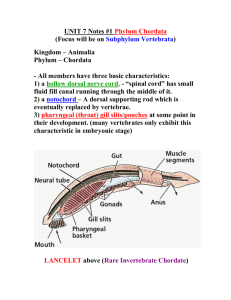
Phylum Annelida
advertisement

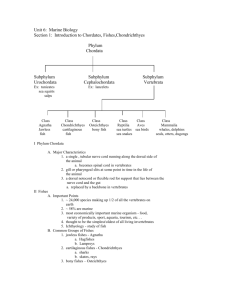
Class Chondricthyes chimaeras, sharks, rays • The cartilaginous fishes • Most primitive living vertebrates that have: – complete vertebra – movable jaws – paired appendages Chondricthyes • Most are predacious, some such as the whale shark is a filter feeder. • None have a swim bladder – adapted to bottom dwelling – Or predators in water column Chondricthyes characteristics • Placoid scales- scales with spiny points – are modified anterior to form replaceable rows of teeth- resemble teeth of higher vertebrates – originate from same tissues as teeth • Other types of scales include: – primitive bony fishes- Ganoid Scales – more advanced bony fishes • Ctenoid scales• Cycloid scales Chondricthyes characteristics • Paired pectoral and pelvic fins; • - pelvic fins in males modified as "claspers" • two median dorsal fins Chondricthyes characteristics • Types of tails in fishes: – heterocercal tail- most primitive form; spinal column turns up (dorsad) in fin – diphycercal tail- spinal column goes straight into fin – homocercal tail- fin located behind spinal column Chondricthyes • Nostrils (nares)• - not connected to mouth cavity; • - have two nasal sacs. • Spiral valve in intestine; • - increases surface area & efficiency of digestion. • Notochord persists • Heart is two chambered; • - atrium & ventricle characteristics Chondricthyes characteristics • respiration done by 5-7 pairs of gills • No swim bladder or lung. • Fairly well developed brain; – with 10 pairs of cranial nerves; – well developed olfactory bulbs Chondricthyes characteristics • • • • Sexes separate; gonads paired; have a cloaca; development one of three types: – oviparous - i.e., lay eggs – ovoviviparous- eggs retained in uterus without attachment to female – viviparous- eggs attach and get nutrients directly from female. • Some sharks possess uteri with very primitive placentas Chondricthyes characteristics • Three types of kidneys in vertebrates: – pronephritic kidney: functional kidney of adult hagfishes, • and the embryos of some higher vertebrates – mesonephritic kidney: functional kidney of sharks and bony fishes; • collecting duct is the Wolffian Duct, also carry sperm. – metanephritic kidney: functional kidney of birds reptiles and mammals; • is drained by a ureter. Chondricthyes characteristics • Lateral line system; – vibrations and currents in water • Ampullae of Lorenzini – Electromagnetic forces Chondricthyes characteristics • Digestive tract well developed: • - mouth - pharynx - esophagus - stomach - liver - pancreas - intestine - spiral valve • rectal gland– functions in regulating salt content of blood Chondricthyes • Ancestor of these fishes evolved in freshwater – Sea water is hyperosmotic (i.e., salt conc. of blood less than that of seawater) • so they have a problem of losing water from there tissues. • to prevent water loss they retain nitrogenous wastes in blood; – this elevates salt conc. in blood to be slightly higher than sea water, – and therefore they will not lose water passively; – rectal gland helps keep this balance characteristics Chondricthyes characteristics • Features that are more advanced than Agnathans (Cyclostomates) – – – – – – Scales 2 pairs of lateral fins moveable jaws enamel covered teeth 3 semicircular canals (inner ear)- agnathans had two paired reproductive organs and ducts Chondricthyes characteristics • Features that make them more primitive than boney fishes: – – – – – Cartilage placoid scales separate gill clefts spiracle to pharynx no air bladder Chondricthyes characteristics • Interesting trivia about sharks – Have very large livers • 20% of body weight can be liver oil- called squalene; – use as fuel for long term swimming or cruising. – Squalene important commercially in Japan as a cosmetic and aphrodisiac.