anatomy of the basal ganglia
advertisement

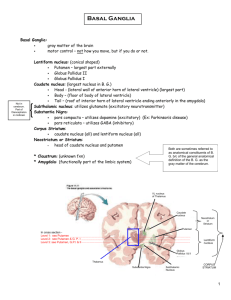
Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia Ahmad Hany Tatwany The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia are collections of neurons Found within the white matter of each cerebral hemisphere.Play an important role in the control of posture & initiation of voluntary movement. This would include the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the Globus pallidus,substabtia nigra, and the subthalamic The caudate and putamen are also called the neostriatum, histologically these are the same neurons but in the human brain they are partially separated from each other by projection fibers. The putamen and Globus pallidusare anatomically grouped together in the human brain and are called the lentiform or lenticular nucleus because of the lens-like configuration of the two nuclei. The striatum & pallidum (globus pallidus) are known as the corpus striatum Caudate nucleus Large C-shaped mass of gray mater. The caudate nucleus is anatomically associated with the lateral ventricle and follows its curvature. Anterolateral, superior, posterior and inferior to the thalamus. Medial to the anterior limb of the internal capsule. It is described as having three portions : • The head, located deep within the frontal lobe • The body, located deep in the parietal lobe • The tail, which goes in to the temporal lobe The head of the caudate nucleus is large and rounded and intrudes into the space of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle. The body of the caudate nucleus tapers and becomes considerably smaller and is found beside the body(floor)of the lateral ventricle. The tail is long and slender follows the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle into the temporal lobe . Terminates anteriorly in the amygdala. The lentiform The Putamen It is darker and lateral and closely intertwined with the caudate nucleus and globus pallidus, which are together known as the corpus striatum. Signals are transmitted through these structures to the motor thalamus, brain stem, and motor neocortex, which helps the body with all aspects of physical movement. The lentiform The globus pallidus, is lighter and immediately medial to the putamen and has a medial and lateral segment. There's a small rind of cells called the claustrum which is separated from the putamen by the external capsule and from the insular cortex by the extreme capsule. has two components, a medial (internal) and lateral (external) segment SUBSTANTIA NIGRA • The substantia nigra is a large pigmented cluster of neurons that consists of two parts, the pars reticulata and the pars compacta. Cells of the pars compacta contain the dark pigment melanin(neurmelanin)these cells synthesize dopamine and project to either the caudate nucleus or the putamen. Subthalamic nucleus Are small paired structures that are part of the functional basal ganglia. They are located inferior to the thalamus, dorsal to the substantia nigra and medial to the internal capsule. Made of the cranial ends of the red nucleus and substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamic nucleus has the shape of the biconvex and receives its main input from the lateral pallidum (external segment of the Globus pallidus). Medially The lentiform nucleus is now seen to be composed of its two portions, the putamen, laterally, and the globus pallidus, which is medially placed HORIZONTAL SECTION OF HEMISPHERES This brain section exposes the white matter of the hemispheres, the basal ganglia, and parts of the ventricular system. Understanding this particular depiction of the brain is vital to the study of the forebrain. The structures seen in this view are also of immeasurable importance clinically, and this view is most commonly used in neuroimaging studies, both CT and MRI Connections All part of the cortex send axons (glutamate secreting) to the specific part of the striatum(corticostriate) Fibers from intralaminar nuclei of thalamus to the striatum (thalamostriate) Dopamine-secreting inhibitory fibres from substantia nigra (nigrostriate) Serotonin-secreting ascending inhibitory fibres from the brain stem to striatum Lenticulostriate arteries Middle cerebral artery Blood supply Blood supply Basal ganglia pathways There are two described pathways for transmission of signals through the basal ganglia, a direct and an indirect pathway. These pathways have competing effects on movement and there is often thought to be a balance between these systems that is involved in establishing and regulating tone. In both the direct and indirect pathways, the caudate and putamen represent the first synapse in the system Direct pathway In the direct pathway excitatory input from the cerebral cortex project the striatal neurons in the caudate nucleus and putamen. Through disinhibition, activated inhibitory neurons in the striatum , which use GABA as their neurotransmitter , project to and inhibit additional GABA neurons in the internal segment of the Globus pallidus. Then the GABA axons of the internal segment of the globus pallidus to the thalamus. Because their input to the thalamus is disinhibited the thalamic input excites the motor cortex. The net effect of the disinhibition in the direct pathway result in increased level of cortical excitation and promotion of the movement. Indirect pathway In the indirect pathway , excitatory input from the cerebral cortex also projects to striatal neurons in the caudate nucleus and putamen. These inhibitory neurones in the striatum which also use GABA as their neurotransmitter project to and additional to GABA neurons in the external segment of the Globus pallidus The GABA axons of the external segment of the Globus pallidus project to the subthalamic nucleus. Through disinhibition the subthalamic nucleus excites inhibitory GABA neurones in internal segment of the Globus pallidus which inhibit the thalamus. This decrease the level of cortical excitation ,inhibitory movement .The net effect of the disinhibition of the indirect pathway result in DECREASED level of cortical excitation and suppression of the unwanted movement. Dopamine and cholinergic effects In addition to the GABA neurons, 2 other chemically significant neurons enhance the effect of the direct or indirect pathways. Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra in the mid brain project to the srtiatum.the effect of dopamine excites or drive the direct pathway increasing the cortical excitation. Dopamine excites the direct pathway through D1 receptors and inhibit the indirect pathway through D2 receptors Cholinergic neurons found within the striatum have the opposite effect . Acetylcholine drives the indirect pathway ,decreasing cortical excitation