EOC Flashcards NEW
advertisement
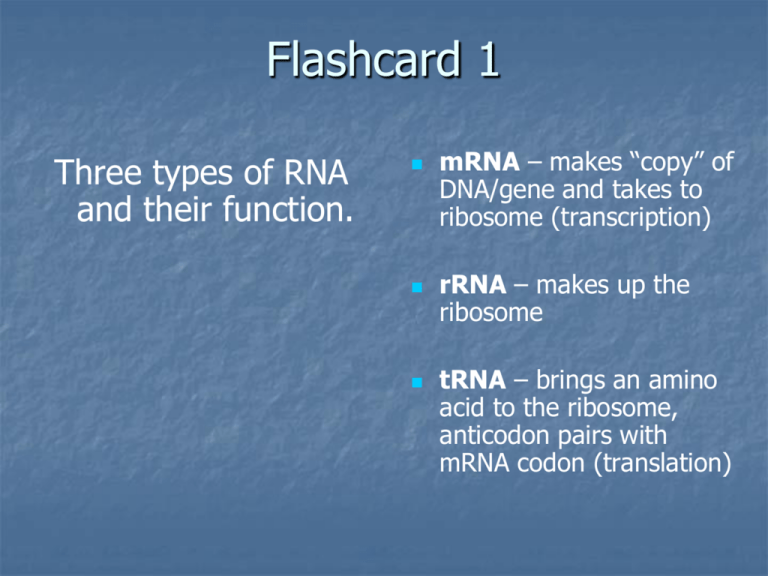
Flashcard 1 Three types of RNA and their function. mRNA – makes “copy” of DNA/gene and takes to ribosome (transcription) rRNA – makes up the ribosome tRNA – brings an amino acid to the ribosome, anticodon pairs with mRNA codon (translation) Flashcard 2 If DNA is…. CGAAGCATT What would be…. Complementary DNA mRNA DNA – A, T, C, G RNA – A, U, C, G COMPLEMENTARY DNA (orig.) CGA AGC ATT (new) GCT TCG TAA COMPLEMENTARY mRNA (DNA) CGA AGC ATT (mRNA) GCU UCG UAA Flashcard 3 Function of … Chloroplasts Chloroplasts – site of photosynthesis Mitochondria – site of cellular respiration Ribosome – site of protein synthesis ** Site means location!** Mitochondria Ribosome Flashcard 4 Organic Molecules are polymers, examples include: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Made of Examples C: Monosaccharide Sugar, starch P: Amino acids L: Fatty acids and glycerol N.A.: Nucleotides Meat, enzymes fats, oil, phosopholipids DNA and RNA Flashcard 5 Function of the Cell Membrane Selectively permeable (regulates materials coming in/out of the cell) Gives cytoplasm a boundary / shape HOMEOSTASIS (maintaining a constant internal environment) Flashcard 6 Differences between Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cells – have cell walls, chloroplasts, large vacuoles Animal Cells – have Centrioles (used for cell division) *BOTH ARE EUKARYOTIC! (have membrane bound organelles and a nucleus) Flashcard 7 OSMOSIS 9% NaCl 91% water 5% NaCl 95% water The cell will lose water!!!! Cells lose water in saltier environments because of osmosis!! The cell have more water and less solute! Osmosis – diffusion of water (water moving high to low) Flashcard 8 Functions Of Enzymes “Lock and Key” Acts as a “catalyst” (speed up reactions) Lowers activation energy Enzymes are proteins Works best at “Optimum” conditions! (this is different for each enzyme) Heat, pH can denature an enzyme Flashcard 9 *Opposites of each other* Photosynthesis Converts sunlight into chemical energy CO2 + H20 + light glucose + O2 Respiration Converts sugars into cell energy (ATP) C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 + ATP Used by ALL ORGANISMS!! Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Flashcard 10 What is a gene? Found on a chromosome Section of DNA Code to make a protein Controls traits! Flashcard 11 Mitosis Vs. Meiosis Mitosis (I-PMAT-C) Makes identical copy of cell Produces 2 daughter cells Used by somatic body cells Meiosis Reduces chromosome number by half Produces 4 daughter cells Makes haploid gametes Gametes = sex cells Crossing - Over Flashcard 12 Recombinant DNA also called Genetic Engineering How we make insulin for diabetics GMO = genetically modified organism DNA from two different species! Plasmid Human gene cleave splice together Gene+plasmid Recombinant DNA Flashcard 13 What happens in Protein Synthesis Every three letters (codon) codes for 1 amino acid. Making our bracelets! DNA transcription (mRNA) translation (mRNA to protein) protein made causes trait Flashcard 14 Gametes Sperm and eggs Made by meiosis Sex cells Haploid (contains only one copy of each chromosome/half of diploid) Fuse together in fertilization Flashcard 15 Karyotype Picture of chromosomes (should have a total of 46 (23 pairs) Shows chromosomal abnormalities (Ex. Down’s Syndrome = Trisomy 21) Down syndrome is caused by NONDISJUNCTION Usually follows an amniocentesis Flashcard 16 Asexual Vs. Sexual Reproduction Sexual is better – more diversity!!!! Asexual = one parent; makes IDENTICAL COPY!! (budding, binary fission, regeneration) Sexual = Two parents; genetic diversity; uses gametes (egg and sperm) Flashcard 17 Homozygous Dominant (AA) Heterozygous (Aa) Homozygous recessive (aa) * Recessive phenotype Dominant Phenotype Three Genotypes Flashcard 18 Paths of Inheritance (be able to do punnett squares) Dominant = one allele dominant Recessive = allele “hidden” by dominant Codominance= both alleles equal, both show up! Incomplete or Intermediate Dominance = Neither allele dominant, blending together (red and white make pink) Sex-linked = on X chromosome, no male carriers Flashcard 19 Gel Electrophoresis Separates DNA by size (smallest goes farthest) Identifies paternity and criminals Flashcard 20 Viruses Made of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat CAN NOT be killed by anitbiotics! Not living because they cannot reproduce outside a living organism (must have a host) Two reproductive cycles Lytic – fast, destroys cell Lysogenic – slower, viral genetic material hides in cell Flashcard 21 Plants, Flowers And Seeds Plants: Nonvascular – no xylem or phloem – ex. Moss Vascular – has xylem and phloem Gymnosperms – cones (conifers) Angiosperms – flowers and fruits Vascular plants have vessels, non-vascular(moss) do not Xylem- water up the plant Phloem- food(sugar) down Flowers – reproductive organ of angiosperm plants Male part = stamen/pollen Female part = carpel or pistil (produce egg) Pollination = transfer of pollen Seed = plant embryo + stored food (endosperm). Surrounded by fruit (forms ovary of plant.) Flashcard 22 Food Web D Secondary consumers E C Primary Consumers O M Producers P *Arrows follow transfer for energy O S *Producers have most energy E R *Energy is lost as it move up S (10%rule) Flashcard 23 Parts of the Cell Nucleus – control center Ribosome – makes protein Lysosome – digestive enzymes Vacuole – storage Rough ER – modifies protein Smooth ER – detoxifies alcohol Golgi – packages and ships Cell membrane – controls what enters and leaves Mitochondria – makes ATP cellular respiration Flashcard 24 Taxonomic Levels: From most general/inclusive to most specific/related Scientific names: Acer rubrum - red maple (genus – species) Lynx rufus - bobcat Domain (general / most number of species Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Scientific name Species * Most specific/ may interbreed Flashcard 25 Bacteria Prokaryotic cells (no nucleus; no membranebound organelles) unicellular Important for: decomposers, for Nitrogen cycle, for gene research (recombinant DNA with plasmids) First cells to evolve (prokaryotic and anaerobic) Flashcard 26 Evidence for Evolution DNA similarity is the best evidence that organisms have a COMMON ANCESTOR Biochemical analysis (DNA, amino acids, proteins) Fossil record Anatomy (if similar bone arrangement = homologous Development / embryology * More in common = more related* Flashcard 27 Natural Selection (Darwin) ADAPTATION – an inherited trait that helps an organism survive – they are born with it!!!!! Variation in populations Overpopulation of offspring Competition for survival/mates Survival/reproduction of best adapted / fittest. Flashcard 28 Levels of Organization in the BIOSPHERE Biotic – anything living Abiotic – non living factors – temp., soil, sun Biosphere (all of life on earth) Biome (ex. Desert, grassland) Ecosystem (all abiotic and biotic factors) Community (only biotic/living) Population (members of one species) Niche (total way of life for organism, its job) Flashcard 29 Life Processes Every living thing does these! Synthesis – to make (ex. protein synthesis) Transport – to move (ex. osmosis) Excretion – getting rid of wastes Respiration – to make ATP from sugar (aerobic or anaerobic) Nutrition – food getting (producer or consumer) Growth and Development Reproduction – to make more cells or organisms (mitosis/asexual or sexual) Regulation – to maintain homoestasis Flashcard 30 Innate Behaviors Inborn and genetic Genetic and Inborn Automatic (reflex and instinct) Courtship - mating Territoriality Aggression Dominance hierarchy Biological rhythms (migration, clocks) Some communication (need to sing in birds) Flashcard 31 Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Two species “living together” permanently Mutualism (+ ,+) both benefit Commensalism (+, 0) one isn’t helped or harmed Parasitism (+, -) One is harmed Flashcard 32 Biomagnification DDT in our bald eagles Mercury in our fish Pesticides and contaminants “move up the food chain” Chemical contaminants are stored and magnified in organisms higher up the food chain because predators accumulate pesticides in the bodies of their prey. Flashcard 33 Learned Behaviors Change with experience and practice. Classical conditioning (learning by association) Operant conditioning (trial and error learning) Insight / reasoning Language Flashcard 34 Carbon Cycle Carbon Cycle - Respiration releases carbon as CO2 (carbon dioxide) Photosynthesis removes carbon and makes sugar (C6H12O6) Human Impact Burning Fossil fuels releases CO2 Deforestation increases the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere Flashcard 35 Environmental Problems Overpopulation – cause of all environmental problems Global warming – too much CO2 in atmosphere increases average global temperature ->flooding, climate change Ozone depletion – CFC’s destroy ozone layer -> increase UV radiation exposure -> increases cancer and crop damage Flashcard 36 Behaviors as Adaptations Instinctive behaviors improve survival rates. Protective behaviors (spray, teeth bared) turn predators away and defends resources Parental behaviors (advanced in birds and mammals) increase survival of young. Communication and courtship allow mate recognition