Cell Organelles - BC Learning Network
advertisement

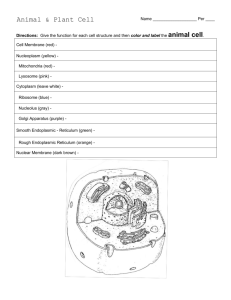
Just like our bodies have different organs that perform certain functions for our body, cells have different parts that perform certain functions for the cell. These are called organelles. An Animal Cell We will look at animal cells and plant cells. Many organelles are contained in both animal and plant cells, but some are present only in plant cells. We’ll (click) start by looking at animal cells. Cell Membrane A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in and out of the cell. Cell Membrane An Animal Cell An important part of all cells is the cell membrane. (click) The cell Membrane is A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in and out of the cell. Cell Membrane A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in and out of the cell. We’ll make a note this here. Cytoplasm A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The cytoplasm is a gel-like fluid inside the cell. It contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. We’ll make a note of this here. Nucleus Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The nucleus is a large structure inside the cell. (Click) It Controls activities in the cell and reproduction of the cell. It’s center contains deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, which determines traits that are passed on to new generations when a cell reproduces. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. We’ll make a note of this here. Nucleus Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Here the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Cell Membrane An Animal Cell A mitochondrion is an oval shaped organelle. The plural is mitochondria. (click) In this organelle, the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. We’ll make a note of this here. Mitochondrion The plural is mitochondria. Here the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Nucleus Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Ribosomes can either be floating freely in the cytoplasm, An Animal Cell Nucleus Free Ribosomes Ribosomes Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Or attached to an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum. Nucleus Ribosome Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Ribosomes These assemble or produce proteins in the cell. Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and some float freely in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Ribosomes are shown as small dots on the animal cell diagram. Here is (click) a closer look at a ribosome. (click) Ribosomes are organelles that assemble or produce molecules called proteins in the cell. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. Mitochondrion The plural is mitochondria. Here the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Ribosomes These assemble or produce proteins in the cell. Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and some float freely in the cytoplasm. We’ll make a note of this here. So far, we’ve looked at 5 different organelles in a cell. We still have more to see. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The next organelle we’ll look at is the endoplasmic reticulum. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The rough endoplasmic reticulum surrounds the nucleus and its surface is covered with ribosomes, shown as dots in this diagram. These ribosomes make the surface rough. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a smoother surface. It is connected to the outside of the nucleus and contains tubules that extend throughout the cell. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Taking a closer look at the endoplasmic reticulum, we see that both the rough and smooth forms consist of a complex network of small channels. Notice the ribosomes shown on the rough ER. Endoplasmic Reticulum Folded membranes that act as channels to transport proteins and other materials through the cytoplasm. The Endoplasmic Reticulum consists of folded membranes that act as channels to transport proteins and other materials through the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. Mitochondrion The plural is mitochondria. Here the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Endoplasmic Reticulum Folded membranes that act as channels Ribosomes to transport proteins and other These assemble or produce proteins in materials through the cytoplasm. the cell. Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and some float freely in the cytoplasm. We’ll make a note of this here. We’ll use this page later as a summary of organelles and their functions. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane The next organelle we’ll look at is called the Golgi body. An Animal Cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Taking a closer look, we see that it is surrounded by folded membranes. Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Mitochondrion Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. The golgi body, which is also called the golgi apparatus, receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, modifies some of them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called (click) vesicles, which (click) Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. We’ll make a note about this organelle and its functions on a second summary page. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell As we mentioned, vesicles are little structures that detach from the Golgi body and enter the cytoplasm. The type of vesicles produced by the Golgi body are called transport vesicles, because they transport materials, such as proteins Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the Mitochondrion cell. Vesicle Golgi Body Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cell Membrane An Animal Cell We can define vesicles as membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and even in and out of the cell. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. We’ll make a note of what vesicles are and what they do here, on our summary. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell The next organelle we’ll look at are vacuoles. Vacuoles are structures that can be found floating around anywhere in the cytoplasm. (click) here’s one in this diagram. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Vesicle Vacuoles Golgi Body Structures that temporarily store water, other substances, and wastes in cells. Vacuoles in plant cells are usually Smooth much larger than those in animal cells. Endoplasmic Mitochondrion Reticulum Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Vacuoles are Structures that temporarily store water, other substances, and wastes in cells. Vacuoles in plant cells are usually much larger than those in animal cells, like the one shown here. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. Vacuoles Structures that temporarily store water, other substances, and wastes in cells. Vacuoles in plant cells are usually much larger than those in animal cells. We’ll make a note about vacuoles here in the summary. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Lysosomes are structures that are also found within the cytoplasm of cells. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Lysosomes Structures that contain digestive Golgi Body chemicals like enzymes, which break down and recycle worn-out organelles. Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Lysosomes contain digestive chemicals like enzymes, which break down and recycle worn-out organelles. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. Vacuoles Lysosomes Structures that temporarily store water, Structures that contain digestive other substances, and wastes in cells. chemicals like enzymes, which break Vacuoles in plant cells are usually down and recycle worn-out organelles. much larger than those in animal cells. We’ll add the information on lysosomes here Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cilia Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Many animal cells have little hair-like organelles on the outside, called cilia. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cilia Tiny hair-like structures attached to the body of some cells. They can move together in a wave-like fashion and help the cell move around. Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Cilia Vacuole Cell Membrane An Animal Cell Cilia are Tiny hair-like structures attached to the surface of some animal cells. They can (click) move together in a wave-like fashion and help the cell move around. Their movement can also be used to push materials past the cell. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. Vacuoles Lysosomes Structures that temporarily store water, Structures that contain digestive other substances, and wastes in cells. chemicals like enzymes, which break Vacuoles in plant cells are usually down and recycle worn-out organelles. much larger than those in animal cells. Cilia Tiny hair-like structures attached to the body of some cells. They can move together in a wave-like fashion and help the cell move around. We’ll add the information about cilia here. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cilia Cytoplasm Vacuole Flagellum Cell Membrane An Animal Cell A flagellum is a lash-like structure attached to the surface of some animal cells. Flagella are much larger than cilia, and there is usually a small number of these on one particular cell. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Flagellum A lash-like structure attached to the body of some cells. They can whip back and forth to help the cell swim though a liquid. Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Cilia Vacuole Flagellum Cell Membrane An Animal Cell They can whip back and forth to help the cell swim though a liquid. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. Vacuoles Lysosomes Structures that temporarily store water, Structures that contain digestive other substances, and wastes in cells. chemicals like enzymes, which break Vacuoles in plant cells are usually down and recycle worn-out organelles. much larger than those in animal cells. Flagellum Cilia Tiny hair-like structures attached to the A lash-like structure attached to the body of some cells. They can move body of some cells. They can whip back together in a wave-like fashion and help and forth to help the cell swim though a liquid. the cell move around. We’ll add the information about flagella on this summary. A Plant Cell So far, we’ve been looking at animal cells. Plant cells (click) can have most of the parts animal cells have, but they also have a couple more. Cell Membrane A Plant Cell Like animal cells, plant cells have a cell membrane surrounding them. The cell membrane is coloured yellow in this diagram. Cell Wall Cell Membrane A Plant Cell But plant cells also have a rigid cell wall outside their cell membrane. Cell Wall Cell Wall (in Plant Cells and Bacteria) A tough layer outside of the cell membrane. It can be rigid, which helps a plant cell hold its shape. It also protects the cell. Cell Membrane A Plant Cell Cell walls surround plant cells and bacteria. A cell wall is a tough layer outside the cell membrane. It can be rigid, which helps a plant hold its shape. It also protects the inside of the cell. Cell Wall (in Plant Cells and Bacteria) A tough layer outside of the cell membrane. It can be rigid, which helps a plant cell hold its shape. It also protects the cell. We’ll note the information about the cell wall in this summary. Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Membrane Vacuole A Plant Cell A green coloured organelle found in plant cells, but not in animal cells is called a chloroplast. Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Membrane Vacuole Chloroplasts (Only in Plant Cells) Carry out photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water + energy sugar + oxygen A Plant Cell Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells. In chloroplasts, the process of photosynthesis is carried out. Photosynthesis uses energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen. In this way, Cell Wall (in Plant Cells and Bacteria) A tough layer outside of the cell membrane. It can be rigid, which helps a plant cell hold its shape. It also protects the cell. Chloroplasts (Only in Plant Cells) Carry out photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water + energy sugar + oxygen We’ll add the information about chloroplasts here. Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Membrane Vacuole A Plant Cell You can see by the diagrams that vacuoles in plant cells are generally much larger than those in animal cells. Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Membrane Vacuole Vacuoles Structures that temporarily store water, other substances, and wastes in cells. Vacuoles in plant cells are usually much larger than those in animal cells. A Plant Cell Remember, vacuoles are structures that temporarily store water, wastes and other substances, and in cells. As we said, vacuoles in plant cells are usually much larger than those in animal cells. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Ribosomes Free Ribosomes Lysosome Vesicle Golgi Body Mitochondrion Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cilia Cytoplasm Vacuole Flagellum Cell Membrane An Animal Cell In summary, we’ll show you this diagram showing important organelles found in animal cells. With the exception of cilia and flagella, these organelles are also found in plant cells. You may want to pause the video, take a screen shot, Cytoplasm Cell Membrane A gel-like fluid inside the cell. It A layer that protects and surrounds cells. It controls substances that flow in contains water, other substances, and all the cell organelles. and out of the cell. Nucleus Controls activities in the cell and cell reproduction. It contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which determines traits that are passed on when a cell reproduces. Mitochondrion The plural is mitochondria. Here the cell produces energy using the process of cellular respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy Endoplasmic Reticulum Folded membranes that act as channels Ribosomes to transport proteins and other These assemble or produce proteins in materials through the cytoplasm. the cell. Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and some float freely in the cytoplasm. Here is the first page of a summary of these organelles. You may also want to pause the video here and make a copy of this. Golgi Body Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, sorts them, and packages them into little bag-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles Membrane covered structures that carry proteins, water, and nutrients around the cell and in and out of the cell. Vacuoles Lysosomes Structures that temporarily store water, Structures that contain digestive other substances, and wastes in cells. chemicals like enzymes, which break Vacuoles in plant cells are usually down and recycle worn-out organelles. much larger than those in animal cells. Flagellum Cilia Tiny hair-like structures attached to the A lash-like structure attached to the body of some cells. They can move body of some cells. They can whip back together in a wave-like fashion and help and forth to help the cell swim though a liquid. the cell move around. Here is the second page of the summary of organelles. Cell Wall Chloroplast Large Vacuole A Plant Cell Here’s a diagram showing that in addition to other organelles, plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts. Also, plants have larger vacuoles than animal cells. You could also make a copy of this. Cell Wall (in Plant Cells and Bacteria) A tough layer outside of the cell membrane. It can be rigid, which helps a plant cell hold its shape. It also protects the cell. Chloroplasts (Only in Plant Cells) Carry out photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water + energy sugar + oxygen And here is a summary of the cell wall and chloroplasts. A copy of this would also be useful to study from. Acknowledgements for Images Used "Animal cell structure en" by LadyofHats (Mariana Ruiz) - Own work using Adobe Illustrator. Image renamed from Image:Animal cell structure.svg. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Animal_cell_structure_en.svg#mediaviewer/File: Animal_cell_structure_en.svg_Slightly modified for this video. "Cell membrane detailed diagram 4" by derivative work: Dhatfield (talk)Cell_membrane_detailed_diagram_3.svg: *derivative work: Dhatfield(talk)Cell_membrane_ detailed_diagram.svg: LadyofHats MarianaRuizCell_membrane_detailed_diagram_3.svg. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons . Simplified for this video. "Blausen 0212 CellNucleus" by BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources it can be cited as:Blausen.com staff. "Blausen gallery 2014". Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 20018762. - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0212_ CellNucleus.png#mediaviewer/File:Blausen_0212_ CellNucleus.png Simplified for this video by removing text. Acknowledgements for Images Used "Mitochondrion mini" by Kelvinsong - Own work. Licensed under CC0 via Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Mitochondrion_mini.svg#mediaviewer/File: Mitochondrion_mini.svg_Text removed for this video. "Ribosome shape" by Vossman - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ribosome_shape.png#mediaviewer/File:Ribosome_ shape.png. Only part of the original image is used for this video. "Blausen 0350 EndoplasmicReticulum" by BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources it can be cited as:Blausen.com staff. "Blausen gallery 2014". Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 20018762. - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0350_ EndoplasmicReticulum.png#mediaviewer/File:Blausen_0350_ EndoplasmicReticulum.png Acknowledgements for Images Used "Golgi apparatus (borderless version)-en" by Kelvinsong - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Golgi_apparatus_(borderless_version)-en.svg#mediaviewer/File:Golgi_apparatus_ (borderless_version)-en.svg "Plant cell structure svg" by LadyofHats (Mariana Ruiz) - Self-made using Adobe Illustrator. (The original edited was also made by me, LadyofHats). Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plant_cell_structure_svg.svg#mediaviewer/File:Plant_cell_ structure_svg.svg . In this video, the image has been modified by decreasing the thickness of the cell wall. "Chloroplast II" by Kelvinsong - Own work. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chloroplast_II.svg#mediaviewer/File: Chloroplast_II.svg. Simplified for this video.