Chapter 8 Volcanoes

Volcanoes and Plutons
Process that forma Magma
• Increasing Temperature
• Decreasing Pressure
• Addition of Water
Environments of Magma Formation
• Spreading Center
• Mantle Plume
• Subduction Zone
Mantle Plume: Hot Spots
Hawaii Island animation
Iris Hot Spot
Subduction Zone
Basalt and Granite
• Asthenosphere is “PERIDOTITE”
• PERIDOTITE =“OLIVINE+PYROXENE+ Ca-Feldspar”
Olivine 1,890°C, Pyroxene 1,390°C,
Calcium Feldspar 1,550°C
Peridotite 1,270°C the product of the first melt Rich In Silica
Partial Melting: A small amount of original peridotite melts to form basaltic magma
Plutons
• When a large granitic magma solidifies with in
Earth’s crust to form a large mass of Granite called a pluton
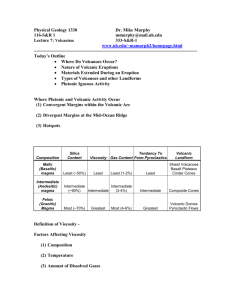
Types of Lava
• Pahoehoe Low Viscosity, as it cools stiffens forming smooth, glassy surfaced, wrinkled or ropy ridges
• Aa higher viscosity surface partially solidify as it flows
• Pillow lavas is a lava structure that typically when lava is emerged from an underwater volcanic vent.
• Pyroclastic rock rock fragments
• Volcanic Ash
Volcanoes
• When lava is too viscous to spread out as a flood it builds a hill or mountain call Volcano
Shield Volcanoes
• Basaltic Magma
• Gentle sloping mountain
• at angles 6° to 12°
Cinder Cones
• Small volcano composed of Pyroclastic fragments
• Large amount of gas accumulates in rising magma
Composite Volcanoes
• Stratovolcano
• form by longs periods of time by alternating lava flows and pyroclastic material
Calderas
Volcanic Eruptions and
Global Climate