Linnaean System of Classification Class Notes
advertisement

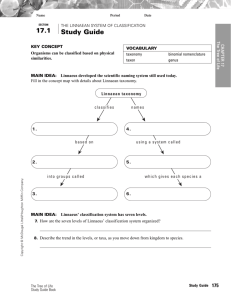
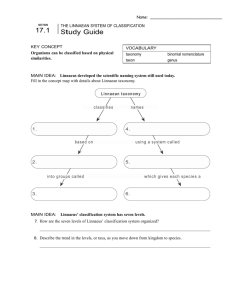
17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification Class Notes 2: Classification 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification I. Classification A. Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. B. Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today. Taxonomy is the science of naming and classifying organisms. White oak: Quercus alba 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification C. Binomial nomenclature is a two-part scientific naming system. 1. uses Latin words 2. scientific names always written in italics 3. two parts are the genus name and species descriptor 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification D. A genus includes one or more physically similar species. 1. Species in the same genus are thought to be closely related. 2. Genus name is always capitalized. E. A species descriptor is the second part of a scientific name. 1. always lowercase 2. always follows genus name; never written alone Tyto alba 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification II. Linnaeus’ classification system has seven levels. A. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species. B. Levels get increasingly specific from kingdom to species. 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification III. Cladistics A. The Linneaen system of classification only uses physical similarites. B. Modern classification is called cladistics and is based on evolutionary evidence: 1. Fossil Records 2. DNA similarities 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification IV. Cladograms A. B. A cladogram is an evolutionary tree that groups organisms together by common ancestry. A clade is a group of species that shares a common ancestor. 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification V. Kingdoms A. Classification has changed over time. B. Until 1866, only two kingdoms- animalia and plantae existed. C. Over time, the kingdoms protista, fungi, archae, and bacteria were added. 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification IV. Domains A. Domains are above (more general than) the kingdom level. 1. Proposed by Carl Woese based on rRNA studies of prokaryotes 2. The three domains are Bacteria, Archae, and Eukarya 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification B. Domain Bacteria includes prokaryotes in the kingdom Bacteria. 1. one of largest groups on Earth 2. classified by shape, need for oxygen, and diseases caused 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification C. Domain Archaea includes prokaryotes in the kingdom Archaea. 1. cell walls chemically different from bacteria 2. differences discovered by studying RNA 3. known for living in extreme environments 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification D. Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. 1. kingdom Protista 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification D. Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. 1. kingdom Protista 2. kingdom Plantae 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification D. Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. 1. kingdom Protista 2. kingdom Plantae 3. kingdom Fungi 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification D. Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. 1. kingdom Protista 2. kingdom Plantae 3. kingdom Fungi 4. kingdom Animalia 17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification Summary What are the 2 parts in binomial nomenclature? What are the 7 levels of Linnaean nomenclature? What is the most general? What is the most specific?