Ecology Bingo Review Sheet 2
advertisement

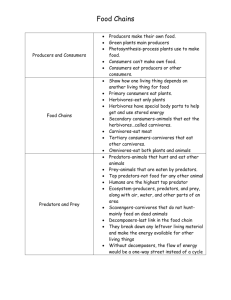
What is a food web? What is bioaccumulation? List 3 types of Natural Disturbances that could be limiting factors for population of species. What is biodiversity? What is Carrying Capacity? What is a producer (in a food chain)? What is the definition of Limiting Factors? Explain the Carbon Cycle. What is precipitation? What are its forms? What is the definition of pollution? What is the cyclical order of the Water Cycle? Explain why top consumers have the most pollutants in them. What is a Primary Consumer? In the Carbon Cycle, not all carbon is put back into the cycle immediately. Why is this so? Where does it go? Give 3 possible examples of limiting factors. When water falls back to Earth in the water cycle, what are the two things that could happen to it after it hits the ground? If a top consumer was removed from a food chain, explain the effects it would have on that food chain. Why is it important for farmers to have a buffer of trees and vegetation between their fields and a water source? In a food chain diagram, what do the arrows the arrows represent? Hint: What is flowing up through the food chain? What is a Secondary Consumer? Using the example of a forest fire, explain what Ecological Succession is. What is Transpiration? What is a Tertiary Consumer? What is a Quaternary Consumer? What is Condensation? What is Evaporation? How many food chains are in this food web? What is a food web? What is bioaccumulation? List 3 types of Natural Disturbances that could be limiting factors for population of species. A series of interconnected food chains. Food chains represent the flow of energy from producers through to varying levels of consumers. The buildup of pollutants in organisms. As pollutants move through the food chain, pollutants remain in the organism’s tissues. What is a producer (in a food chain)? What is the definition of Limiting Factors? An organism that is able to make its own food through the process of photosynthesis. Any abiotic (non-living) or biotic (living) factor that controls the number of individuals in a population. Carbon-containing materials are passed along from organism to organism through the food chain. When organisms use food for energy, the carbon is converted back into carbon dioxide and is available for plants to use again. What is the cyclical order of the Water Cycle? Explain why top consumers have the most pollutants in them. What is a Primary Consumer? -Avalanche -Tsunami -Landslide -Earthquake -Fire/Lightning -Drought -Flood -Extreme Weather Explain the Carbon Cycle. An animal that eats a producer. Evaporation ---> Transpiration ---> Condensation ---> Precipitation ---> Ground Water/Run Off As pollutants enter the food chain, they are stored in the tissues of organisms. As other animals consume these polluted animals, the pollutant is passed on and becomes more concentrated. Top consumers end up getting the most pollutants. What is a Secondary Consumer? An animal that eats a primary consumer (can also eat producers) What is Transpiration? What is a Tertiary Consumer? A forest fire would drastically change an ecosystem. Over time, since there is no forest canopy, rain and sunlight can reach the ground. Small grasses, plants and shrubs will start to grow. Consequently, small insects and rodents would move back into the ecosystem. As more vegetation grew, and primary consumers increased, secondary consumers would start to move back. As more species start to inhabit the ecosystem, it is revived again. This is a very SLOW process and involves gradual change. When water is absorbed through plants’ roots and evaporates through the leaves, stem and flowers. An animal that eats a secondary consumer (can also eat primary consumers and producers) What is a Quaternary Consumer? An animal that eats a tertiary consumer (can also eat secondary/primary consumers and producers) Evaporated water in the form of gas collects and cools in clouds. The cooled gas is condensed and turns back into water in the form of precipitation. What is Evaporation? How many food chains are in this food web? There are 18 food chains What is Carrying Capacity? The measure of the variety of species in an ecosystem. The maximum number of individual organisms that an ecosystem can support. What is precipitation? What are its forms? What is the definition of pollution? When water falls from clouds back to the surface of the Earth in the form of rain, hail, sleet or snow. Any substance that is added to an environment that cannot be broken down, stored or converted into a form that is not harmful. Pollutants cause pollution. In the Carbon Cycle, not all carbon is put Give 3 possible examples of limiting factors. back into the cycle immediately. Why is this so? Where does it go? -Temperature -Predation When organisms die, they become part of the thick -Predator/prey cycles carbon containing material at the bottom of -Diseases/parasites lakes/oceans. After millions of years and pressure, the -Competition for resources materials are converted to coal, oil & gas. When -Natural disturbances people use this fuel, or burn coal/oil, the energy is released and carbon is converted into carbon dioxide. Using the example of a forest fire, explain what Ecological Succession is. What is Condensation? What is biodiversity? When water lakes, oceans, rivers, etc. is heated from the sun and turned into water vapor. When water falls back to Earth in the water cycle, what are the two things that could happen to it after it hits the ground? If a top consumer was removed from a food chain, explain the effects it would have on that food chain. It will either soak into the ground (ground water) or be stored in the water table, or it will run off the land into lakes, ponds, rivers, streams and oceans. It would have negative effects on the food chain. Top consumers are predators and keep populations of species under control. If species are no longer prey for predators, there population will increase. This in turn, will put stresses on the amount of food available for the growing population. This will lead to competition for resources and could eventually wipe out the producers. Why is it important for farmers to have a buffer of trees and vegetation between their fields and a water source? The buffer of trees and vegetation will help to absorb any pollutants that might be on the farmer’s field (pesticides or animal feces) and limit the chances of it getting into the water (which could affect that ecosystem) In a food chain diagram, what do the arrows the arrows represent? Hint: What is flowing up through the food chain? The arrows represent the flow of energy.