A&P II Exam 1 2013 Name Russo Figure 14.1 Using Figure 14.1
advertisement
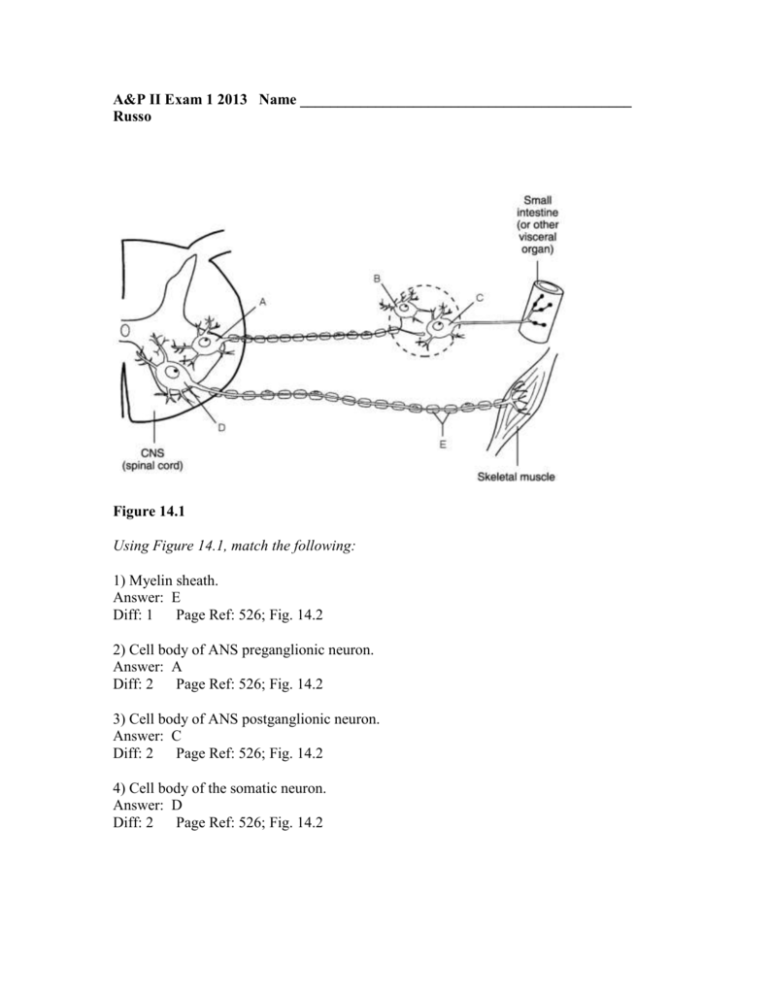
A&P II Exam 1 2013 Name ____________________________________________ Russo Figure 14.1 Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 526; Fig. 14.2 2) Cell body of ANS preganglionic neuron. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 526; Fig. 14.2 3) Cell body of ANS postganglionic neuron. Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 526; Fig. 14.2 4) Cell body of the somatic neuron. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 526; Fig. 14.2 T/F 5) The blood vessels of the skin are one of the few areas of the body where the vessels are innervated by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 537; Tbl. 14.4 6) The structures that specifically exhibit vasomotor tone are mostly under sympathetic control. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 536 7) The autonomic and somatic nervous systems are two separate systems that work totally independent of each other. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: 525 8) Albuteral is used by asthma patients to dilate the bronchioles of the lungs and ease breathing. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 535; Tbl. 14.3 Multiple Choice 9) Which of these effectors is not directly controlled by the autonomic nervous system? A) smooth muscle B) cardiac muscle C) skeletal muscle D) most glands Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 525 10) Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because ________. A) inactivation of ACh is fairly slow B) NE and epinephrine are secreted into the blood as part of the sympathetic response C) preganglionic fibers are short D) preganglionic fibers are long Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 537 11) Which of the following appears to exert the most direct influence over autonomic function? A) hypothalamus B) midbrain C) reticular formation D) medulla oblongata Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 535; Tbl. 14.2 12) Beta-blockers ________. A) increase a dangerously low heart rate B) decrease heart rate and blood pressure C) have widespread sympathetic effects D) are potent antidepressants Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 535; Tbl. 14.2 Figure 16.2 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 13) Growth hormone Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 602-4; Tbl 16.1 14) Follicle stimulating hormone Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 605; Tbl. 16.1 15) Prolactin Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 605-6; Tbl. 16.1 16) Adrenocorticotropic hormone Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 605; Tbl. 16.1 17) Thyroid stimulating hormone Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 605; Tbl. 16.1 Match the following: A) Hormonal stimulus B) Humoral stimulus C) Neural stimulus 18) Testosterone production Diff: 3 Page Ref: 603; Tbl.16.1 19) Epinephrine production Diff: 3 Page Ref: 597; Fig. 16.14 20) Aldosterone production Diff: 3 Page Ref: 605; Tbl. 16.1 21) Parathyroid hormone production Diff: 3 Page Ref: 596; Fig. 16.4 Answers: 18) A 19) C 20) A 21) B True/False Questions 22) The pineal gland is used as a brain orientation landmark for brain X rays. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 617 23) The antagonistic hormones that regulate the blood calcium level are calcitoninparathormone. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 610-611 24) The hormone that raises blood sugar levels is insulin. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 618 25) Addison's disease is due to a insufficient output of glucocorticoids only. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 615 26) Both "turn on" factors (hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli) and "turn off" factors (feedback inhibition and others) may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 597 27) ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 603; Tbl. 16.1 28) LH is also referred to as a gonadotropin. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 605 29) Oxytocin is a strong stimulant of uterine contractions. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 599 30) The prime metabolic effect of cortisol is gluconeogenesis. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 614 Multiple Choice 31) Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular ________. A) calcium B) deactivating ions C) nucleotides D) second messengers Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 593 32) Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus? A) enzyme B) humoral C) neural D) hormonal Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 596-7; Fig. 16.4 33) Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids and that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called ________. A) enzymes B) antibodies C) proteins D) hormones Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 592 34) The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract ________. A) connects the hypophysis to the pituitary gland B) is partly contained within the infundibulum C) conducts aldosterone to the hypophysis D) is the site of prolactin synthesis Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 599 35) Which of the choices below is not a factor required for target cell activation by hormone receptor interaction? A) blood levels of hormone B) type of hormone C) number of receptors for that hormone D) strength of the bond between the receptor and hormone Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 595 36) ADH ________. A) increases urine production B) promotes dehydration C) is produced in the adenohypophysis D) is inhibited by alcohol Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 599-601 37) Which of the following is not a type of hormone interaction? A) permissiveness B) synergism C) antagonism D) feedback Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 598 38) Which of the following is not a change typically produced by a hormonal stimulus? A) activates or deactivates enzymes B) stimulates production of an action potential C) alters plasma membrane permeability D) induces secretory activity Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 593 Match the following: A) Neutrophil B) Monocyte C) Basophil D) Erythrocyte E) Eosinophil 39) Nucleus has two lobes; contains granules of lysosomal enzymes; functions in attacking parasitic worms. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 644; Tbl. 17.2 40) Nucleus is multilobed; functions as a phagocyte; contains fine indistinct granules. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 644; Tbl. 17.2 41) Transports CO2 and oxygen. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 644; Tbl. 17.2 42) Contains a U- or an S-shaped nucleus; granules stain very dark; releases histamine and heparin. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 644; Tbl. 17.2 43) Largest of the WBCs; crucial in defense against viruses; associated with chronic infections. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 644; Tbl. 17.2 Answers: 39) E 40) A 41) D 42) C 43) B Match the following: A) Fibrinogen B) Alpha and beta globulins C) Albumin D) Gamma globulins 44) Main contributor to osmotic pressure. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 633; Tbl. 17.1 45) Antibodies released by plasma cells during immune response. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 633; Tbl. 17.1 46) Necessary for coagulation Diff: 1 Page Ref: 633; Tbl. 17.1 47) Transport proteins that bind to lipids, metal ions, and fat-soluble vitamins. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 633; Tbl. 17.1 Answers: 44) C 45) D 46) A 47) B T/F 48) Hemorrhagic anemias result from blood loss. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 638 49) White blood cells are produced through the action of colony-stimulating factors. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 642 50) Hemoglobin is made up of the protein heme and the red pigment globin. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 635 51) Myeloid stem cells give rise to all leukocytes. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 642 52) Each hemoglobin molecule can transport two molecules of oxygen. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 635 53) Diapedesis is the process by which red blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 640 Multiple Choice 54) Which of the following is not a functional characteristic of WBCs? A) granulosis B) diapedesis C) ameboid motion D) positive chemotaxis Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 640 55) What is the average normal pH range of blood? A) 8.35-8.45 B) 7.75-7.85 C) 7.35-7.45 D) 4.65-4.75 Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 632 56) Which of the choices below is the parent cell for all formed elements of blood? A) megakaryocyte B) normoblast C) hemocytoblast D) polymorphonuclear cell Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 636; Fig. 17.11 57) Which of the following is not a distribution function of blood? A) delivery of oxygen to body cells B) transport of metabolic wastes from cells C) transport of hormones to their target organs D) transport of salts to maintain blood volume Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 632 58) Which of the following is a protective function of blood? A) prevention of blood loss B) maintenance of adequate fluid volume C) maintenance of normal pH in body tissue D) maintenance of body temperature Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 633 59) Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis? A) hypoxia of EPO-producing cells B) decreased tissue demand for oxygen C) an increased number of RBCs D) moving to a lower altitude Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 636-637 60) Blood reticulocyte counts provide information regarding ________. A) rate of erythrocyte formation B) rate of platelet formation C) clotting ability of the blood D) WBC ability to defend the body against disease Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 636-637 Xtra Credit 1) Where would you not find a cholinergeric nicotinic receptor? A) all parasympathetic target organs B) all postganglionic neurons C) adrenal medulla hormone producing cells D) skeletal muscle motor end plates Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 533-534 Tbl 14.2 2) Which of the following adrenergic neurotransmitter receptors plays the major role in heart activity? A) beta 1 B) beta 2 C) beta 3 D) alpha 1 Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 534; Tbl. 14.2 3) One of the least complicated of the endocrine control systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. Which of the following describes this mechanism? A) carbohydrate oxidation B) catabolic inhibition C) protein synthesis D) humoral stimulation Answer: D Diff: 3 Page Ref: 596; Fig. 16.4 4) Which of the following would not be a possible cause of sickling of red blood cells in someone with sickle-cell anemia? A) travel at high altitude B) vigorous exercise C) malaria and travel at high altitude D) sleeping in a well-ventilated room Answer: D Diff: 3 Page Ref: 639-640 5) Platelets ________. A) stick to the damaged area of a blood vessel and help seal the break B) have a life span of about 120 days C) are the precursors of leukocytes D) have multiple nuclei Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 645-646





