Pyramid of energy
advertisement

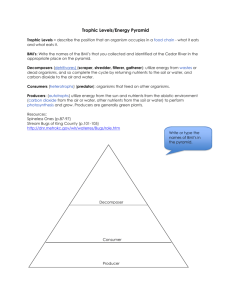
Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Biology 12(C) Energy • Originates from sun • Transferred between organisms • Leaves ecosystem as motion and heat Biotic & Abiotic Factors • Biotic factors – the living components of the environment EX: • Abiotic factors – the nonliving components of the environ EX: Autotrophs & Heterotrophs • Heterotroph – organism that must acquire energy by consuming other organisms • Autotroph – organism that is able to capture energy from the sun to make it’s own food ATP (Adenine Tri Phospate) • Organisms use chemical energy from food • Breaking down carbohydrate bonds releases energy • Stored in Bonds of (ATP) • Draw in notebook ATP Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Organisms survive by: • Producing food or feeding on other organisms Flow of matter and energy: • Organisms eat each other to get energy (except plants) • Instead of saying “bear eats fish” we say “the energy in the fish is transferred to the bear” Trophic Levels Trophic level – distinct level of feeding within ecosystem • Species at each level vary in different communities Trophic levels: • Producer • Consumer – Primary – Secondary – Tertiary (or top) • Decomposer Trophic Levels Producer – produce own food, first or lowest trophic level • Example: plants Primary consumer – firstorder consumer, eats a producer • Example: grasshopper Trophic Levels Primary consumer – first-order consumer, eats a producer • Example: grasshopper Secondary consumer – second-order consumer, eats primary consumer • Example: lizard Trophic Levels Secondary consumer – second-order consumer, eats primary consumer • Example: lizard Tertiary consumer – thirdorder consumer, eats secondary consumer • Example: snake Trophic Levels Decomposer (saprobe) – breaks down dead plant and animal matter and returns nutrients to soil – Examples: bacteria and fungi You will have a quiz in 5 minutes….STUDY! Trophic Energy Quiz 1 (10pts) • On a separate sheet of paper answer the following: 1. What are biotic factors and list 2 2. What are abiotic factors and list 2 3. What does this picture show? 4. Make a pyramid and divide it into half (a top half and a bottom half). Places the words “producer” and “consumer” into the part of the pyramid where they apply to and define each next to the word in the pyramid. Trophic Levels Sometimes consumers are referred to by type of food they eat rather than trophic level: • Herbivore – eats only plants – Examples: deer, rabbit • Carnivore – eats only animals – Examples: lion, shark • Omnivore – eats plants and animals – Examples: bear, human • Scavenger – feed only on dead organisms – Examples: vulture, hyena Food Chains Food chain – sequence of organisms feeding on one another at a lower trophic level Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer • In this food chain, which is the … Producer1* Primary Consumer2* Primary Consumer3* Primary Consumer4* Primary Consumer- Food Webs Food web – network of interacting food chains • Most organisms eat more than one food type • Ecosystems usually contain more than one food chain • Complex relationships between trophic levels • • Highlight 4 different food chains and put them in order of Producer, 1 C, 2 C, 3 C, 4 C , …. What do they have in common, different, are any organisms on two different trophic levels? You will have a quiz in 5 minutes….STUDY! Trophic Energy Quiz 2 (20pts) • On a separate sheet of paper answer the following: 1. Define and give an example for: - producer - herbivore - carnivore - omnivore - scavenger - decomposer 2. Copy the food web at right and label each organism as one of the above based only on the data in the food web. Food Webs • Which organisms are the producers? – Pond weed and algae • Which organisms are the secondary consumers? – Perch, minnow, and dragonfly • Which organisms do frogs eat? – Minnow and dragonfly Complex Food Web Food Webs • • Which consumers feed on bivalves? – Sea ducks, tundra swans, and herbivorous ducks Which consumers feed on zooplankton? – Small fish, bivalves Ecological Pyramids Ecological pyramid – used to visualize food chains • Pyramid of energy – amount of energy in bodies of organisms at each trophic level • Pyramid of numbers – number of organisms feeding at each trophic level • Pyramid of biomass – total mass of dry, organic matter at each trophic level Matter and Energy Matter cycles through the ecosystem when one organismwhen is passed to another when and Energy cycles through the ecosystem eaten one organism is passed to another when eaten Pyramid of Energy Energy decreases up the pyramid: • Grass captures sun’s energy • Rabbit obtains 10% of stored energy in grass • Snake obtains 10% of stored energy in rabbit • Eagle receives 10% of stored energy snake Pyramid of Energy 1 kcal 10 kcal 100 kcal 1000 kcal Pyramid of Numbers Numbers decrease up the pyramid: • More individual organisms at lower trophic levels • Fewer individuals at higher trophic levels Pyramid of Numbers Pyramid of Biomass Biomass decreases up the pyramid: • Greatest biomass at producer level • Least biomass at tertiary consumer level Pyramid of Biomass Tertiary Consumer (1.5 grams/square meter) Secondary Consumer (11 grams/square meter) Decomposer 5 grams/square meter Primary Consumer (37 grams/square meter) Producers 807 grams/square meter Use the 10% rule to see how much energy will get transferred! Q: If the plants start with 100J of energy how much is in all the rest of the levels? Q: If the heron received 3J of energy how much did the plant start with? Use the 10% rule to see how much energy will get transferred! Q: If the primary consumers have 676J of energy how much is in all the rest of the levels? Q: If the bass received 1 J of energy how much did the plant start with? You will have a quiz in 5 minutes….STUDY! Trophic Energy Quiz 3 (10pts) Draw a trophic pyramid to solve each question: 1. If the secondary consumers have 2 J how much is in all the rest of the levels? 2. If the bass received 100 J of energy how much did the plant start with? 3. Plants start with 1005 J of energy how much is in all of the levels? 4. The heron received 3,500 J how much did the plant start with? 5. Plants started with 500 J how much did the tertiary consumer get?