Food Chain Video
advertisement

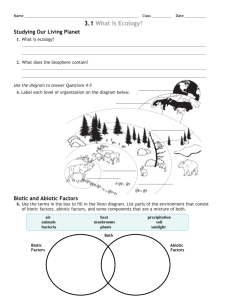
Food Chain Video 1. Why do we eat? 1. Why do we eat? To acquire energy 2. What is a food chain? 2. What is a food chain? A sequence of organisms that feed on each other. 3. Where does the food chain always start? 3. Where does the food chain always start? Abiotic source, usually the sun. 4. What is a producer? 4. What is a producer? An organism that gets it energy for an abiotic source. 5. How can we define a consumer? 5. How can we define a consumer? An organism that gets its energy from other organisms. 6. What are trophic levels? 6. What are trophic levels? The levels of a food chain where organisms obtain their energy. 7. Why is the antelope squirrel considered a “primary” consumer? 7. Why is the antelope squirrel considered a “primary” consumer? The squirrel is the first consumer in the food chain. 8. Distinguish between the secondary consumer and the tertiary consumer. 8. Distinguish between the secondary consumer and the tertiary consumer. The steps of the food chain in order after the primary consumer. 9. Where on the food chain is the “quaternary” consumer? 9. Where on the food chain is the “quaternary” consumer? At the top 10. What is a food web? 10. What is a food web? A combination of food chains that are interconnected to create a network of feeding relationships. 11. What is the detritivore trophic level? 11. What is the detritivore trophic level? An organism that feeds on waste products or dead organic material. Why is only about 90% of the energy is passed along at each trophic level? Why is about 10% of the energy is lost while being passed along at each trophic level? Due to the mobility and living conditions. Which of the following uses sun energy to make food? A. Heterotrophs B. Animals C. Plants D. Cells Which of the following uses sun energy to make food? A. Heterotrophs B. Animals C. Plants D. Cells All green plants, algae, and some bacteria are ___________. A. B. C. D. Heterotrophs Animals Consumers Producers All green plants, algae, and some bacteria are ___________. A. B. C. D. Heterotrophs Animals Consumers Producers A ___________ is an organism that eats other organisms. A. B. C. D. Trophic Omnivore Plants Herbivore A ___________ is an organism that eats other organisms. A. B. C. D. Trophic Omnivore Plants Herbivore A consumer that eats only plants is called an ___________. A. B. C. D. Herbivore Omnivore Carnivore Organism If an organism is eaten or decomposes, the consumer or decomposer takes in the _________stored in the original organism. A. B. C. D. Food Tissues Life Energy If an organism is eaten or decomposes, the consumer or decomposer takes in the _________stored in the original organism. A. B. C. D. Food Tissues Life Energy Trophic levels shows the _________ of energy transfer from one organism to another. A. B. C. D. Importance Need Levels Necessity Trophic levels shows the _________ of energy transfer from one organism to another. A. B. C. D. Importance Need Levels Necessity The arrows in a food chain represent the __________ of energy from the body of the consumed organism to the body of the consumer of that organism. A. Direction B. Power C. Importance D. Level The arrows in a food chain represent the __________ of energy from the body of the consumed organism to the body of the consumer of that organism. A. Direction B. Power C. Importance D. Level __________ form the base of food chains. A. B. C. D. Animals Heterotrophs Tertiary Autotrophs __________ form the base of food chains. A. B. C. D. Animals Heterotrophs Tertiary Autotrophs Producers transfer energy to the first, or ________ consumer in the food chain. A. B. C. D. Secondary Tertiary Primary Last Producers transfer energy to the first, or ________ consumer in the food chain. A. B. C. D. Secondary Tertiary Primary Last The secondary consumer _________ the primary consumer. A. Passes over B. Consumes C. Grows D. Energizes The secondary consumer _________ the primary consumer. A. Passes over B. Consumes C. Grows D. Energizes A _________ __________ is the combination of many food chains. A. B. C. D. Tertiary level Primary level Secondary level Food web A _________ __________ is the combination of many food chains. A. B. C. D. Tertiary level Primary level Secondary level Food web Many different ________ ________ lead from the producers to the top predators. A. B. C. D. Trophic levels Consumers levels Heterotrophic levels Autotrophic levels Many different ________ ________ lead from the producers to the top predators. A. B. C. D. Trophic levels Consumers levels Heterotrophic levels Autotrophic levels