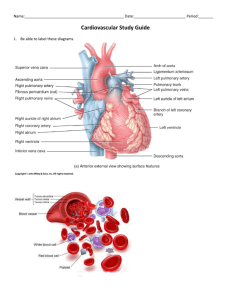
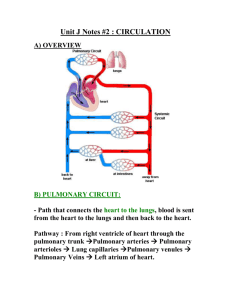
Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement
advertisement

Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Issued May 2004 1 Lecture Content Patient Positioning Identify Phelbostatic Axis Leveling Square Wave Test Obtain PA Reading Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 2 Patient Positioning Angels 45º Supine Head of bed: 0-60° 30º 0º Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 3 Leveling Eliminates effects of hydrostatic forces on the observed hemodynamic pressures Ensure air-fluid interface of the transducer is leveled before zeroing and/or obtaining pressure readings Phlebostatic axis: Level of left atrium 4th ICS & ½ AP diameter Mark the chest with washable felt pen Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 4 Identify Phlebostatic Axis Intersection of the 4th ICS and ½ the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest McHale DL, Carlson KK. AACN Procedure Manual for Critical Care 4th ed WB Saunders: Philadelphia, Pa 2001 (479) With permission from Elsevier Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 5 Mark location chest wall with washable felt pen Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 6 Level Transducer System Ensure air-fluid interface of the transducer is level to phelbostatic axis. Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 7 Level Transducer System Relevel the transducer with any change in the patient’s position Angels 30º 45º Referencing the system 1 cm above the left atrium decreases the pressure by 0.73 mm Hg Referencing the system 1 cm below the left atrium increases the pressure by 0.73 mm Hg 0º Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 8 Square Wave Test Determines the ability of the transducer to correctly reflect pressures Perform at the beginning of each shift Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 9 Square Wave Test Figure A: Expected square wave test Figure B: Over damped Figure C: Under damped Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert Reprinted from Darovic GO. Hemodynamic Monitoring: Invasive and Noninvasive Clinical Application 2nd ed. Philadelphia,Pa: WB Saunders Co;1995;161-162 Used with permission from Elsevier 10 Under Damped System Over responsive, exaggerated, artificially spiked waveform SBP erroneously high; DBP erroneously low Reprinted from Darovic GO. Hemodynamic Monitoring: Invasive and Noninvasive Clinical Application 2nd ed. Philadelphia,Pa: WB Saunders Co;1995;161-162 Used with permission from Elsevier Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert Causes: small air bubbles, too long of tubing, defective transducer 11 Over Damped System Sluggish, artificially rounded & blunted appearance SBP erroneously low; DBP erroneously high Causes: large air bubbles in system, compliant tubing, loose/open connections, low fluid level in flush bag Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert Reprinted from Darovic GO. Hemodynamic Monitoring: Invasive and Noninvasive Clinical Application 2nd ed. Philadelphia,Pa: WB Saunders Co;1995;161-162 Used with permission from Elsevier 12 PAP Documentation Measure at end expiration Measure pressures from a graphic tracing Measure pulmonary capillary wedge pressure at end-expiration using the mean of the a wave a wave indicates atrial contraction and falls within the P – QRS interval of the corresponding ECG complex Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 13 Respiratory Component Changes in intrathoracic pressure during respiration change PAP readings Record and trend pressure readings at end expiration Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 14 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 15 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 16 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 17 Respiratory Variation Spontaneous ventilation Mechanical ventilation Aherns TS, Taylor LK. Hemodynamic Waveform Analysis. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders; 1992 27 Used with permission from Elsevier Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 18 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 19 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 20 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 21 Used with permission of PACEP Collaborative Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 22 Need Further Assistance? For more information or further assistance, please contact a clinical practice specialist with the AACN Practice Resource Network. Email: practice@aacn.org Phone: (800) 394-5995, x217 Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement Alert 23