Objective: Today we will identify structures in plants and animal cells
advertisement

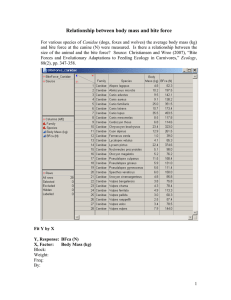
• • • • 01/08/15- No gum Please! • Materials • Pen/Pencil • Notebook • Packet book Objective: Today we will identify structures in plants and animal cells under microscopes Agenda Daily question Chapter 1-2 Packet lab Daily Question: Write down some structures that are found in plant cells but NOT animal cells. Ribosome's • Small structures in the cytoplasm that create proteins. • Ribosome's are either free floating in the cytoplasm of a cell or attached to endoplasmic reticulum in a cell. Vacuole • • • Fluid-filled, membranesurrounded cavities inside a cell Fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell Like your suitcase, a vacuole is a temporary storage space for the cell. Lysosome • Also called cell vesicles • Spherical organelles surrounded by a membrane • They contain digestive enzymes • Where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place Plant Vs. Animal Cell Lab Obtain materials from teacher Set magnification to 10x first (low power) Put Elodea slide under microscope observe what it looks like on low power –draw a picture Put Elodea slide on high power, observe and identify organelles-draw scientific picture in notebook Have one student come up to Ms. Mildebrath and swab cheek cell, Ms. Mildebrath will put dye on slide, return with animal cell to group Put animal cell under low power microscope, observe organelles and structures- draw scientific drawing in notebook Put animal cell under high power and observe changes, identify organelles and draw observations in notebook Scientific Drawing Example Cork cell Cell membrane Cork cell 100x Photosynthesis Is the process that plant cells use to change the energy from sunlight into chemical energy. Takes place in the chloroplasts. Chlorophyll- a light absorbing pigment, or colored substance, that traps the energy in sunlight. Chemical equation- 𝐻₂0 + 𝐶𝑂₂ ⟶ 𝐶₆𝐻₁₂𝑂₆ + 𝑂₂ Cellular Respiration Cells use oxygen to release energy stored in sugars such as glucose. Takes place in organelles called mitochondria. Chemical equation- 𝐶₆𝐻₁₂𝑂₆ + 𝑂₂ ⟶ 𝐻₂0 + 𝐶𝑂₂ Bite Mark Evidence Investigators can analyze bite marks for characteristics to help them identify victims or suspects as well as to exclude others. Marks can be left on a victim’s skin or other objects, such as Styrofoam cups, gum, or foods. Saliva or blood may be left behind that can be tested for DNA. Dental records including x-rays can also provide useful information, especially when attempting to identify a victim. Bite Mark Evidence Video Features to analyze: • Type of bite mark (human or animal) • Characteristics of the teeth (position, evidence of dental work, wear patterns, etc.) • Color of area to estimate how long ago the bite occurred (old or recent bite) • Swab for body fluids for DNA tests Did you know? The most famous incident where bite mark evidence led to a conviction, was in the case of the notorious serial killer, Ted Bundy. He was responsible for an undetermined number of murders between 1973 and 1978 and was finally tied to the murder of Lisa Levy through bites that he had inflicted on her body. Images: http://www.forensicdentistryonline.org/Forensic_pages_1/currentopic1.htm, http://www.trestonedental.co.uk/images/0303.jpg It’s time to investigate some “impressive” evidence! Image: http://www.sxc.hu/photo/442696 • • • • Bite Mark Lab Include your lab group members names Examine the candy in the bag, DO NOT TAKE OUT OF BAG Use your knowledge of bite marks, evidence, to figure out which suspect bit the candy On paper, write in complete sentences which suspect and why