Mirrors Worksheet
advertisement

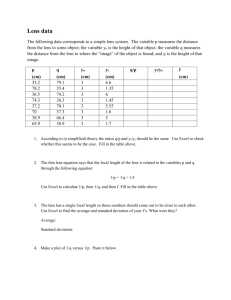
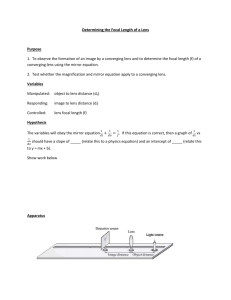
Optics Test Preparation Worksheet – SNC 2D 1. Calculate the distance from a converging lens to an object that is 3.5cm high, and whose image is 10cm high and 20 cm from the lens. 2. What are the Laws of Reflection? 3. Create a drawing with the following terms: incident ray, normal, angle of incidence, angle or reflection, reflected ray, point of incidence, angle of refraction, refracted ray. 4. What is the speed of light in diamond (2.42)? 5. Light travels slightly slower in ethanol than in methanol. a. Which medium has a higher index of refraction? b. When light strikes the boundary between the two media, it bends away from the normal. Which is the incident medium and which is the refractive medium? Answer with a labeled sketch. 6. Light travels from glass (1.52) into water (1.33). The angle of incidence in glass is 40.0 o. What is the angle of refraction in water? 7. Light incident in water (1.33) strikes a layer of ice (1.31) that has formed on top of the water. What is the critical angle in the water? 8. State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection. 9. Create a drawing with the following terms: optical centre, optical axis, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, focal plane. 10. What are the 4 ways to define characteristics of an image? 11. An object is placed at F` and then at 2F` in front of a converging mirror. Explain, using the 4 conventions discussed in question 10, what type of image will be formed. 12. At what distance must a postage stamp be placed behind a magnifying glass with a focal length of 10.0cm if a virtual image is to be formed 25.0cm behind the lens? a. What are the magnification and attitude of the image? 13. The focal length of a slide projector’s converging lens is 10.0cm. a. If a 35mm slide is positioned 10.2cm from the lens, how far away must the screen be placed to create a clear image? b. If the height of a dog on a slide film is 12.5mm, how tall will the dog’s image be on the screen? 14. Create a drawing with the following terms: principal focus, focal length, centre of curvature, principal axis, focal plane, vertex. 15. An object is placed at C and then at F in front of a converging mirror. Explain, using the 4 conventions discussed in question 10, what type of image will be formed. 16. A candle 20cm high is placed behind a converging lens. The distance from the lens to the object is 150cm. The image of the candle is formed 30cm from the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? What is the height of the image? 17. A piece of newspaper with print 2.0cm high is placed 20cm from a diverging lens. The distance to the image is -7.5cm. Calculate the focal length and the height of the image. 18. Create a drawing with the following terms: retina, cornea, lens, optic nerve, sclera, iris, pupil 19. Explain with diagrams how myopia differs from hyperopia? How are each corrected? 20. A pencil 8.0 cm high is placed 36.0 cm in front of a converging lens with a focal length 18.0 cm. Use the thin lens, and magnification equations to find. a. The distance to the image. [36.0 cm] b. The height of the image. [-8.0 cm] c. Describe the characteristics of the image. 21. A piece of newspaper with print 2.0 cm high is placed 20 cm from a diverging lens with a focal length of 12 cm. Calculate: a. The distance to the image. [-7.5 cm] b. The height of the image. [0.75 cm] c. Describe the characteristics of the image. 22. A candle 20 cm high is placed behind a converging lens with a focal length of 25 cm. If the image is of the candle is 30 cm from the lens calculate: a. The distance from the lens to the object [150 cm] b. The height of the image. [-4.0 cm] c. Describe the characteristics of the image. 23. A lens with a focal length of – 1.5 m is placed 2.0 m from a 20 cm tall candle. Calculate the height that the candle appears when it is viewed in the lens. [8.6 cm] 24. A slide projector has a lens with a focal length of 10.0 cm. A slide of a truck is placed 11.0 cm from the lens. Calculate the distance the screen should be away from the projector to ensure a clear image is projected. [1.10 m] 25. Which of the following two scenarios would work better have a larger amount of total internal reflection? Include a calculation for each. [6] Scenario A) Diamond and Water Scenario B) Glass and Air Useful data: Diamond n = 2.42 Glass n = 1.52 Water n = 1.33 Air n = 1.00 26. A converging lens is used to produce a real image of a light bulb filament. Explain using the diagram why there is still a dim image produced when 90% of the lens is covered with a thick black object. [4] Blac k Sc reen O I 27. A 2.0 cm tall headline in a newspaper is viewed through a lens with a focal length of 20 cm. If the lens is 10 cm from the paper how high is the image of the print? [5] 28. Explain how a diverging lens can help someone who is nearsighted? [4] 29. What is wrong with the following statement? The index of refraction of ethanol is 0.90. [3] Challenge Problem 30. An ant 1.0 cm tall is viewed through a magnifying glass with a focal length of 15 cm. If the image of the ant is 3.0 cm, how far away should the magnifying glass be from the ant? [10 cm] Variable do di ho hi F M Positive Always Real image (opposite object) When upright When upright Converging lens Upright image Negative Never Virtual image (same side as object) When inverted When inverted Diverging lens Inverted image Formulas of Interest 1 1 1 = + 𝑓 𝑑𝑜 𝑑𝑖 𝜂1 (𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃1 ) = 𝜂2 (𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃2 ) 𝒉𝒊 𝒅𝒊 𝑴= =− 𝒉𝒐 𝒅𝒐