EXAM REVIEW - CLN4U
advertisement

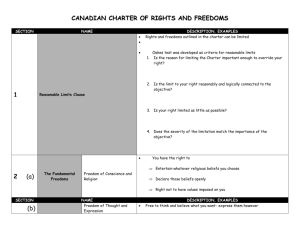
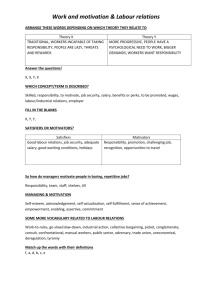
Philosophers • Aquinas – Believed in law leading men to virtue – Believed there needs to be an authoritative body • Aristotle – Justice should aspire to equality – Believed in an egalitarian society where justice could be exercised in distribution of wealth (distributive justice) • Plato – – – – Natural Law (law with moral authority) Believed an ideal society run by a philosopher king Initially believed justice could be levied without law Lost faith in idea of philosopher king (unrealistic) • Cicero • Bentham Sources Of Law • Primary – Customs and conventions – Religion – Social and Political Influences • Secondary – Constitutions – Statute Law – Judicial decisions (case law) Terms/Concepts • Justinian Code- the basis of the legal systems in most European countries – Corpus Juris Civilis – Ensured laws would be coded (recorded) – Made slavery against the law • Code Of Hammurabi- established the concept of an eye for an eye • Ratio Decidendi – A Latin term meaning reason for the decision referring to that part of the judges decision that provides the legal reasoning for the judgment Terms/Concepts • Case Law – extracting legal principles from past judgments • Tort Law – Branch of civil law – Deals with personal damages – Negligence issues Rights and Freedoms • Charter of Rights and Freedoms – Equality rights means that every individual is free and equal before the law – Section 1 Reasonable Limits Clause – Section 24 Exclusion of Evidence Case Study • R. v. Keegstra – Case dealt with freedom of expression in regards to hate laws. Criminal Law • Defenses – Mental Disorder • Not responsible because they cannot form mens rea – Automatism • A defense for unconscious or involuntary behaviour – Alibi • is a defense that places the accused at the relevant time in a different place than the scene of the crime. Cases • R v. Manninen – Result was the exclusion of illegally gathered statements • R. v Hufsky – Alberta Random Spot police checks – Charged with failing to provide breath analyzer sample – Dealt with detention to protect right of society Criminal Law Concepts • Resolution discussion = plea bargaining – Negotiation between crown and defense for a lighter sentence in exchange for a guilty plea • Leading question- questions that suggest the answer • Hearsay- testimony that comes from a third party and is not within the knowledge or personal experience of a person • Direct Examination – Questioning your own witness Criminal Law Concepts • • • • • • Indictable Summary Hybrid Mens Rea/ Actus Reus Non Culpable Manslaugher – The causing of death by an unlawful act where there was no intention to cause death is called • Infanticide – Charge which can be used when a mother kills her infant. • Non culpable homicide – Death by which the accused cannot be held legally responsible • Double Jeopardy – Prevents a person from being tried for a crime twice • Denunciation – Objective of sentencing – Considers society’s revulsion for a particular crime of the character of actions of a particular accused • Motive – Reason why a person acts – Necessary to convict in a murder case Criminal Law Concepts • Cross Examination – Questioning of opposing side’s witness International Law • Hugo Grotius – known as the father of international law • Geneva Conventions – agreements stipulates that prisoners of war must be treated in a humane manner • Extradition treaties – Double criminality rule – Principle of reciprocity – Principle of specialty LABOUR LAW CONCEPTS • • Compensation package = employees contract Trade Unions Act – made it fully legal to organize and form unions • Act for the Prevention of Cruelty to and Better Protection of Children – Major impact was creating Canada’s first Childrens’ Aid Society • Master And Servant Act – A servant must remain with his or her master regardless of the working conditions • Industrial Disputes Investigation – responded to increasing strikes by passing an act that allowed them to form a conciliation board • Wartime Labour Relations Regulations – Made it fully legal for workers to organize and join a union • Closed shop – Means that new employees have to already be members of a union • Individual bargaining – individual negotiation with the employer to set out the terms of the contract – Terms must be valid under federal and provincial legislation and contract law LABOUR LAW CONCEPTS • Collective Bargaining – bargaining through a representative or association • Employment Standards Act – – – – Minimum wage and OT Pregnancy and emergency leave Holidays and vacations Ontario Act amended to allow employers to have employees work a 60-hour workweek without receiving overtime. • Labour Day created to celebrate worker’s rights LABOUR LAW CONCEPTS • Certification – Union is certified when the majority of workers approve its status • Decertification – a majority of members vote to remove the union. Environmental Law • Kyoto Accord – International agreement dealing with climate change – Primary reason for refusal to sign is impact on economic growth – Aim to cut worldwide emissions by 5% – Canada agreed to cut 6% – Key problem was the United States did not sign ESSAY • Write an essay on one of the major legal issues studied throughout the course related to Rights and Freedoms. Your paper should attempt to address the issue of whether the rights related to this particular issue are acceptable or should change in the future. You may choose from one of the following topic areas: • • • • Prostitution Law Marijuana Law Right To Strike Abortion • Your paper should attempt to address the specific Charter right, and whether the rights and freedoms should or should not protect this particular right. Your essay paper should provide background/ historical information regarding the issue, examine the Charter right, include relevant Supreme Court decisions, and discuss future direction of law in regards to this right(s).