Notes Intro to Charter
advertisement

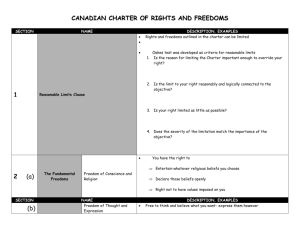
The Charter was significantly inspired by documents such as the 1948 United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights Passed by the United Nations Recognized inalienable rights and fundamental freedoms See Pages 38-43 Guaranteed the freedoms of: Thought Opinion Expression Conscience Religion Peaceful Assembly and Association It also declared: Equal rights for Men and Women Equality before the Law Innocent until Proven Guilty Education Rights Freedom from Torture or Inhumane Punishment Canada's original Constitution, the British North America Act, was passed in 1867 by British Parliament. This Act, also known as the Constitution Act, 1867, founded Canada as a nation. It made elected governments the highest political and legal institutions in the country. Canada's Constitution did not have a "Bill of Rights" that governments had to follow. The Canadian Parliament attempted to codify rights and freedoms across Canada A statute law enacted by Prime Minister John Diefenbaker, the Canadian Bill of Rights recognized: ◦ The right of individuals to life, liberty, personal security and enjoyment of property ◦ Freedom of religion, speech, assembly and association ◦ Freedom of the press ◦ The right to counsel and the right to a fair hearing The Bill of Rights had limitations: It was a federal statute and it applied only to matters under federal jurisdiction Had the same status as other statutes: ◦ It did not take precedence over any other statutes ◦ It could also be amended, or even eliminated by a majority vote in the House of Commons. People including PM Pierre Trudeau believed the Bill of rights did not offer Canadians sufficient protection Sought to entrench rights and freedoms into the Canadian Constitution Entrench – to protect and guarantee a right or freedom by ensuring that it can only be changed by an amendment to the Constitution When Canada's Constitution was patriated(brought home) in 1982, the Constitution Act included the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms: ◦ Ensures that people are protected, regardless of the government in power ◦ Also means that these rights and freedoms became constitutional law, which overrides all other laws ◦ Any federal or provincial law must be consistent with the terms of the Constitution Some of the rights and freedoms contained in the Charter are: freedom of expression the right to a democratic government the right to live and to seek employment anywhere in Canada legal rights of persons accused of crimes Aboriginal peoples' rights the right to equality, including the equality of men and women the right to use either of Canada's official languages the right of French and English linguistic minorities to an education in their language the protection of Canada's multicultural heritage. The Charter shifted the power from the supremacy of Parliament and legislatures towards supremacy of the Constitution Not all premiers agreed with entrenching rights and freedoms in the Constitution ◦ Some felt that entrenching certain rights and freedoms would reduce the law-making powers of Canadian governments Premiers only agreed to the Charter on the condition they had limited power to override (to prevail over) it Section 33 of the Charter grants the federal government and provincial governments limited power to pass laws that may violate freedoms or rights in the Charter (s 2 and s 7 to 15 of the Charter) When invoked (to put into effect), the particular law must specify what sections of the Charter are being overridden Expires every 5 years and rarely used Quebec Bill 101 Required all public signs to be in French only The Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Quebec's Bill 101 was invalid because it infringed on freedom of expression The Quebec government responded by bringing in another bill and invoking the notwithstanding clause to allow the "French only" law to stand. Section 1 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms is the section that confirms that the rights listed in the Charter are guaranteed. The section is also known as the reasonable limits clause or limitations clause, as it legally allows the government to limit an individual's Charter rights. This limitation on rights has been used in the last twenty years to prevent a variety of objectionable conduct such as hate speech (e.g., in R. v. Keegstra) and obscenity (e.g., in R. v. Butler). It has also been used to protect from the unreasonable interference of government in the lives of people in a free and democratic society by defining these limits. Any person in Canada, whether Canadian citizen, a permanent resident or a newcomer, has the rights and freedoms contained in the Charter. There are some exceptions: ◦ The right to vote( Section 3) ◦ The right to enter, remain in and leave Canada (Section 6) To make a change to the Charter, the federal Parliament and seven of the 10 provincial legislatures must agree to it. The population of those seven provinces must also make up at least 50 per cent of the total population of Canada. The Charter has been amended only twice since 1982 – HWK: find out the 2 amendments….