Buprenorphine Group Treatment For Opioid Addiction
advertisement

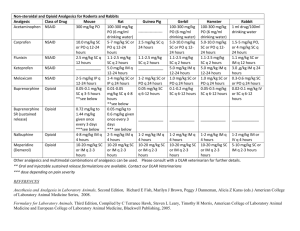
Ken Saffier, MD, Natasha Pinto, MD And Patients CCRMC/HC Noon Conference February 18, 2010 Drs. Pinto and Saffier have no financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturer of any commercial product discussed in this presentation. At the end of this presentation, participants will be able to: List at least 2 patient criteria needed for buprenorphine treatment. Explain why an opioid dependent patient must be in opioid withdrawal prior to taking their first dose of buprenorphine. Understand and experience aspects of what a buprenorphine treatment group is like. . Oxycodone and hydrocodone both registered substantial increases in emergency department mentions in the last 5 years Number of mentions 30,000 Hydrocodone Oxycodone 20,000 10,000 0 1995 2/2004 1996 1997 1998 Source: SAMHSA, Drug Abuse Warning Network. 1999 2000 2001 2002 Over 2 million are estimated to be dependent on or abusing prescription drugs in the past year. Past Year Dependent/Abusers, Ages 12 or Older (in Thousands) 4,294 Marijuana 2,018 Prescription Drugs 1,488 Cocaine 426 Hallucinogens Heroin 214 Inhalants 180 0 1,000 2,000 3,000 Source: SAMHSA, 2002 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 1/2004 4,000 5,000 Issues of Concern Percent of 12th Graders Reporting Nonmedical Use of OxyContin and Vicodin in the Past Year Remained High 12.0 10.5 9.6 Percent 10.0 9.3 8.0 6.0 4.0 5.0 4.5 4.0 2.0 0.0 OxyContin 2002 Vicodin 2003 2004 No year-to-year differences are statistically significant. Agonist Antagonist Naloxone, naltrexone Mixed agonist/antagonist Heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone, fentanyl Pentozacine, butorphanol (Stadol) Partial agonist Buprenorphine Intrinsic mu Activity: Full Agonist (Methadone), Partial Agonist (Buprenorphine), Antagonist (Naloxone) 100 90 Full Agonist (Methadone) 80 70 Intrinsic Activity 60 Partial Agonist (Buprenorphine) 50 40 30 20 10 Antagonist (Naloxone) 0 -10 -9 -8 -7 Log Dose of Opioid -6 -5 -4 High affinity for the mu opioid receptor Slow dissociation from the mu receptor Competes with other opioids and blocks their effects Can precipitate withdrawal in highly opioid dependent individuals Prolonged therapeutic effect for opioid dependence treatment “Ceiling effect” for stimulation of a given receptor Human Opioid Receptors , , and H2N extracellular fluid S S AA identical in 3 receptors AA identical in 2 receptors AA different in 3 receptors cell membrane cell interior HOOC LaForge, Yuferov and Kreek, 2000 Zubieta et al., 2000 Poor oral bioavailability Fair sublingual bioavailability Takes about 10 minutes to dissolve Schedule III drug With naloxone (4:1) (Suboxone) or without (Subutex) Analgesic dose for mild to moderate pain is 0.3 – 0.6 mg. (0.4 mg = ~10 mg morphine) Opioid dependent Wants to stop using Psychiatrically stable Interested in office-based care Reliable – can keep appointments Agrees to urine tox screens Has social support Went to the ED in withdrawal. Longstanding use of OxyContin. $100/day “habit”. Snorts q day for months, then stops. Moves back to the Bay Area and within days, he’s back to using. I’m snorting 5 oxies per day – it’s an insane amount to be putting into my body. My palms are sweaty in the morning. Then I have intense pain in my thighs. I feel fidgety to an extreme. So much physical and mental anguish. I don’t want to waste money on this. It’s destroying my life. Dysphoric mood Craving Irritability Tearing, rhinorrhea Fever, chills Sweating Gooseflesh (cold turkey) Dilated pupils Muscle aches Back pain Tremor Yawning Restless sleep, then Insomnia Anorexia N/V, diarrhea, cramps Buprenorphine maintenance Short acting opioids Long acting opioids Buprenorphine detox Buprenorphine taper (As an analgesic (buprenex)) Remaining in treatment (nr) 20 15 4 Subjects in Control Group Died 10 Detoxification 5 Maintenance 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 Treatment duration (days) 300 350 Our patients, especially Ryan. Drs. Michael Saxon and Mary Jeanne Kreek Chris Verdugo, CCTV Gary Larson Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration Center for Substance Abuse Treatment Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine in the Treatment of Opioid Addiction # 40 National Clearinghouse for Alcohol and Drug Information (800) 729 – 6686 or (301) 468 – 2600 www.buppractice.com (discounted for residents) Buprenorphine at CCRMC & HC’s: 925 370 5868 (leave message) or 925 370 5859 (leave message) Call Ken Saffier, MD, pager 334 http://buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/about.h tml#top www.csam-asam.org