Factors Governing the Success or Failure of Technology Transfer
advertisement

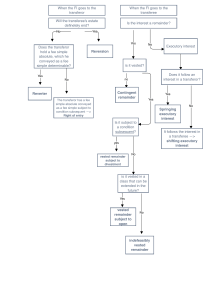
Factors Governing the Success or Failure of Technology Transfer: State Sector Experience of Sri Lanka Muditha P Liyanagedara, Kushani Jayaweera, Ranil D Guneratne National Science and Technology Commission, Sri Lanka Nastec@sltnet.lk Purpose The purpose of this exercise is to identify the factors governing the success or failure of technologies developed and transferred by the government sector R&D institutions. Because identifying factors affecting the destiny of technologies transferred is a vital requirement for a successful commercialization of technologies. NASTEC 2 The Approach A survey was conducted to test out the existence of predetermined factors that may affect the fate of the technologies transferred Institutions surveyed Arthur C Clarke Institute for modern technologies, Atomic Energy Authority, Coconut research institute, Tea Research Institute, National Engineering Research and Development Centre, Department of Agriculture, National Building Research Organization, Rubber Research Institute, Veterinary Research Institute, Industrial Technology Institute, Universities Mainly considered technology Fields Agriculture/Plantation, Engineering, Food and Herbal NASTEC 3 Predetermined Factors Surveyed Transfer mandate Technology type Transfer fee Transfer mode Barriers at institutions’ end and receivers’ end Transfer methods Financial support for receiver Post-transfer involvement NASTEC 4 Direct Outcomes of the Survey Transfer mandate - yes for all institutions Technology type Transfer fee Improvement to the existing technologies - 69.3% New technologies 36.7% Free of charge - 69.5% For a nominal fee - 21.7% Market value - 8.8% Transfer mode Know-how only - 79.5% Know-how & Financial support - 8.1% NASTEC 5 Direct Outcomes of the Survey ( contd.) Main Barriers at institutions’ end Main barriers at receivers’ end Inadequate human resources - 51.7% Inadequate financial resources - 38.7% Lack of organizational infrastructure – 18.4% Inflexible regulations – 18.4% Lack of management support – 10.2% Poor communication - 34.6% Lack of Interest - 18.3% Transfer methods Training Programmes - 85.7% Field trials/proto type pilot plant demonstrations – 71.4% Workshops/Seminars - 61.2% Personal contacts with individual receivers – 61.2% NASTEC 6 Direct Outcomes of the Survey ( contd.) The common order of the transfer methods that worked well for many transferors The common order of the transfer methods that many transferors preferred to follow training programmes>workshops/seminars = field trials/prototype pilot plant demos>handouts>…>websites Financial support to receiver workshops = field trials>training programmes>brochures>handouts>news letters>websites Did not assist - 63.2% Post-transfer involvement Only when a problem is referred to - 57.1% Continuous monitoring - 48.9% NASTEC 7 Inferences Factors increasing success rate Transferring for a nominal fee Transferring technical know-how with financial support Using brochures,newsletters & TV programmes for dissemination Monitoring continuously Factors decreasing success rate Inadequacy of institutional finance resources Inflexible institutional regulations Lack of interest of transferee Monitoring only when a problem is referred to NASTEC 8 Mainly highlighted reasons for success or failure Success Cost effectiveness Fulfills receiver’s urgent need Interest of transferor and transferee Easy to adapt Failure Poor communication between transferor and transferee Inadequacy of financial and human resources Later invasion of the market by cheaper alternatives Practical difficulties inherent to the technology itself Lack of producers NASTEC 9 Other Reasons Success Existence of technology transfer centres Effectiveness of a technology as a new approach to a traditional method Failure High cost Lack of media publicity Low purchasing power of the producers/end users Small domestic market (difficult to achieve economy of scale) NASTEC 10 Conclusions & Recommendations To transfer a technology to producers having potential to commercialize, it should be provided at least for a nominal fee The difference in the order of the transfer methods that worked well for transferors and that of they preferred may negatively affect the success of the transfer Transferor should identify the most effective transfer methodology for each technology Continuous monitoring is a key to a successful transfer Transferor should get involved in Continuous improvements of the technology to face the market competition by smart alternatives NASTEC 11 Conclusions & Recommendations (Contd.) There should be an effective technology advertising mechanism Establishing a repository of Government developed technologies It is better to do a market study before developing a technology Supply push approach preferred The country should have a proper transfer policy and mechanism NASTEC 12 Technology to Improve Kithul Sap Yield: Factors Governed the Success Effectiveness of the technology as a new approach to a traditional method Interest of transferor and transferee Easy adoptability Cost effectiveness Assistance (both financial & technical) provided to increase production capacity and to find the market for produces Personal contact with individual receivers NASTEC 13 Thank You NASTEC 14 NASTEC 15 NASTEC 16