“Typical” Plant Cell
advertisement

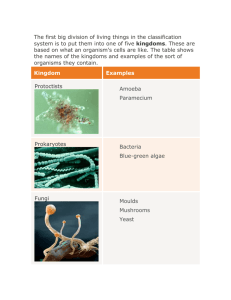
Section 2: Types of Cells Cell Theory (Review) 1. All organisms (living things) are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of (life) structure and organization of organisms. 3. All (new) cells come from preexisting cells. 4. Cell contain hereditary information (DNA) which is passed from cell to cell during cell division Two Types of Cells 1. Cells can be subdivided into the following subcategories: 2. Prokaryotes: Unicellular 3. Eukaryotes: Multicellular Prokaryotic 1. Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (contain ribosomes). 2. Few internal structures. 3. Bacteria are onecelled prokaryotes. Eukaryotic 1. Contain a nucleus and organelles surrounded by membranes (mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles, etc.) Plant Animal “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Hierarchy of Biological Order Kingdoms Contain ALL Organisms Macromolecule 5 Kingdoms each containing cells Bacteria (Kingdom Monera) Bacteria are made of cells 5 Kingdoms each containing cells Euglena are unicellular (Kingdom Protista) An Amoeba is unicellular (Kingdom Protista) Amoeba Spirogyra (Kingdom Protista) Volvox (Kingdom Protista) Kelp forest (Algae) (Kingdom Protista) 5 Kingdoms each containing cells Yeast Cells (Kingdom Fungi) 5 Kingdoms each containing cells All plants are made of cells Plant Cells Plants Cells 5 Kingdoms each containing cells All animals are made of cells Bones are made of cells Muscles are made of cells More Cell Types! Nerve cells Nerve Cells Red Blood Cells White Blood Cell Red and White Blood Cells Comparison of Cells