PPT slides 14-16
advertisement

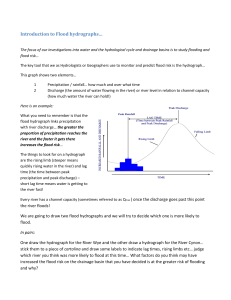
What affects a river’s discharge? 27th April 2015 U: how a flood hydrograph can show how a river responds to a rainstorm K: Revise the landforms of a river The 3 main processes in a river are: Erosion, transportation and deposition. Landforms are the features produced as a result of these processes. Landforms Interlocking Meanders, oxbow spurs, Waterfalls lakes, flood plain and gorges Levees and deltas You have 1 minute to…. 1. Write a definition of the term discharge 2. Write down the calculations – how do you work out the discharge of a river? What’s the connection? How? How? Factors affecting discharge How? How? How? What is a flood hydrograph? A flood or storm hydrograph is a graph showing how a river responds to a particular storm. It shows rainfall and discharge. Key Terms Check: Discharge - this is the amount of water in a river at any given point and time. Discharge is measured in cumecs (cubic metres per second) Velocity - speed of a river (measured in metres per second) Hydrograph - a graph showing changes in river discharge over time in response to a rainfall event. Lag time - the time taken between peak rainfall and peak discharge Rising Limb - shows the increase in discharge on a hydrograph Falling Limb - shows the return of discharge to normal / base flow on a hydrograph Peak Rainfall - maximum rainfall (mm) Peak Discharge - maximum discharge (cumecs Now have a go at the PPQ – June 2010 Mark scheme INSERT The 3 main processes in a river are: Erosion, transportation and deposition. Landforms are the features produced as a result of these processes. Landforms Interlocking spurs, Waterfalls and gorges Landforms of the upper course: Interlocking spurs are caused by erosion Meanders, oxbow lakes, flood plain Levees and deltas • In its upper stage the river erodes vertically rather than laterally. • Interlocking spurs are ridges produced when a river in the upper stage twists and turns round obstacles of hard rock along its downward pathway. Define and match up the four processes of erosion: Hydraulic action The force of the water hitting the bed and banks of the river. Corrasion (or abrasion) Attrition Corrosion The bedload pebbles and sand are carried along and rub against the bed and banks of the river wearing them away. The load collides and breaks itself up into smaller pieces. River water dissolves some types of rock e.g. chalk and limestone Match up the correct processes of transportation: 1.Saltation P. Large boulders are pushed along the river bed by the force of the water 2. Suspension K. Pebble sized particles are bounced along the river bed by the force of the water 3. Traction x. Soluble materials dissolve in water and are carried along 4. Solution a. Small particles like silt and clay are carried along in the water The formation of a Gorge Explain how a waterfall is formed (4) or Draw a diagram - INSERT & M/scheme Use an annotated diagram or diagrams in your answer Now mark your own answer: • A fault in the geology exposes layers of hard and soft rock (1). • Water pouring over the drop causes erosion of the softer underlying rock (1) by hydraulic action and corrasion (1). • This leads to the development of a plunge pool (1). • harder rock eventually collapses into plunge pool (1) • overtime the waterfall retreats towards the source forming a gorge (1). A = Floodplain (1), relatively flat area (1), in mid/lower course of rivers (1). B = Meander (1), sequence of bends on river (1), that move over time across/down the floodplain (1). Middle course - How do meanders form? A B Draw and label the x-section A – B. Use the revision book P.44 to help you. Key words: Erosion, deposition, Slip off slope, River Cliff, lateral erosion, Abrasion, slow velocity, friction, fast flowing, efficiency, deep, shallow Explain the formation of a meander ( 4 marks) Channel flow is directed towards one side of the river and erosion occurs forming river cliff (1) Slower flowing water passes around the inside of the channel (1) and deposition occurs forming a slip-off slope(1). Meander migrates in direction of outside bend (1) How do Oxbow lakes form? Now try a PPQ Mark scheme Lower course – Flood plains and Levees Use the revision book P.45 and AQA P.101 to complete activity 2 P.101 How can we manage river flooding? 29th April 2015 U: the causes and effects of flooding K: Learn the different types of hard and soft engineering strategies Review of homework PPQ: Explain how the demand for water is met within the UK. (8 marks) • The North and west have a high rainfall, so good supply of water. This is an area of water surplus (there’s a greater supply than demand) • The Southeast and midlands have high population densities, so high demand for water. This is an area of water deficit (there’s a greater demand than supply) Read the revision book P.51 ‘The UK needs to manage it’s water supply’. Number 1 -4. Now read your answer and the mark scheme. Which level would you award yourself? Mark /8 Why? How could you improve? You have 1 minute to answer the question: When does a river flood? What are the causes of flooding? Use the card sort and revision book P.48 to complete the table below: Physical causes of flooding Human causes of flooding Read the bottom of the revision book P.48 : Describe how flooding is happening more often in the UK What are the effects of flooding? 1. Effects can be classified into – Social, economic and environmental 2. Effects can also be classified: • Primary effects – caused directly by the flood e.g. house flooding • Secondary effects – as an indirect effect e.g. business closing down and people lose jobs Effects of flooding Social Economic Environmental Cumbria Pakistan How can we manage flooding? There are two types of strategies to deal with flooding: • Soft engineering is a method of river flood management which works or attempts to work with natural processes • Hard engineering is a method of river flood management which involves major construction work 1. Hard engineering – which type? Flood relief channel 2. Soft engineering – which type? Afforestation 3. Hard or Soft? Which type? Dam Landuse zoning 5. Hard or Soft? Which type? Channelisation 6. Hard or Soft? Which type? Flood warning 4. Hard or Soft? Which type? 7. Hard or Soft? Which type? 8. Hard or Soft? Which type? 9.. Hard or Soft? Which type?