national internal revenue code
advertisement

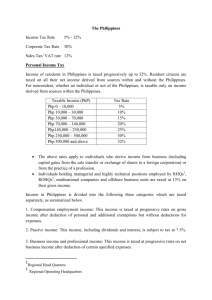
TAXATION, NATIONAL INTERNAL REVENUE CODE, BIR SARANGAYA, GAIL V. SEMFILA EA2 2015-2016 TAXATION TAXATION ⊸An INVOLUNTARY FEE levied on corporations or individuals that is enforced by a level of government in order TO FINANCE GOVERNMENT ACTIVITIES OBJECTIVES ⊸ SIMPLICITY – compliance by the taxpayer and enforcement by the revenue authorities should be as EASY as possible. ⊸ EFFICIENCY - taxation interferes as LITTLE as possible in the choices people make in the private marketplace OBJECTIVES ⊸ FAIRNESS - requires that equally situated taxpayers pay equal taxes and that better-off taxpayers pay more tax ⊸ REVENUE SUFFICIENCY - part of the reason for the deficit is that revenue sufficiency may conflict with efficiency and fairness NATIONAL INTERNAL REVENUE CODE 1. NIRC Outline I. TITLE I ORGANIZATION AND FUNCTION OF THE BUREAU OF INTERNAL REVENUE II. TITLE II TAX ON INCOME III.TITLE III ESTATE AND DONOR'S TAXES IV.TITLE IV VALUE- ADDED TAX V. TITLE V OTHER PERCENTAGE TAXES VI.TITLE VI EXCISE TAXES ON CERTAIN GOODS VII.TITLE VII DOCUMENTARY STAMP TAX VIII. TITLE VIII REMEDIES IX. TITLE IX COMPLIANCE REQUIREMENTS X. TITLE X STATUTORY OFFENSES AND PENALTIES XI. TITLE XI ALLOTMENT OF INTERNAL REVENUE XII. TITLE XII OVERSIGHT COMMITTEE XIII.TITLE XIII REPEALING PROVISIONS XIV. TITLE XIV FINAL PROVISIONS 2. National Internal Revenue Code State Policy ⊸It is hereby declared the policy of the State to PROMOTE SUSTAINABLE ECONOMIC GROWTH through the rationalization of the Philippine internal revenue tax system, including tax administration; TO PROVIDE, as much as possible, an equitable relief to a greater number of taxpayers in order to improve levels of disposable income and increase economic activity; and to create a robust environment for business to enable firms to compete better in the regional as well as the global market, at the same time that the State ensures that Government is able to provide for the needs of those under its jurisdiction and care. TITLE II: TAX ON INCOME CORPORATION ⊸ Include partnership, joint-stock companies, joint accounts, association, or insurance companies but does not include general professional partnerships and joint venture or consortium formed for the purpose of undertaking construction projects in energy operations pursuant to an operating consortium agreement under a service contract with the government DOMESTIC ⊸ Created or organized in the Philippines or under its laws RESIDENT ALIEN ⊸ An individual whose residence is within the Philippines and who is not a citizen thereof RESIDENT FOREIGN CORPORATION ⊸ A foreign corporation engaged in trade or business within the Philippines TAXPAYER ⊸ Any person subject to tax subject by this title POLL TAX ⊸ A tax of a uniform, fixed amount applied to an individual in accordance with the census INCOME TAX ⊸ Tax on a person's income, emoluments, profits arising from property, practice of profession, conduct of trade or business or on the pertinent items of gross income specified in the Tax Code of 1997 (Tax Code), as amended, less the deductions and/or personal and additional exemptions, if any, authorized for such types of income, by the Tax Code, as amended, or other special laws. INDIVIDUAL INCOME TAX ⊸ Resident citizens receiving income from sources within or outside the Philippines • Employees deriving purely compensation income from 2 or more employers, concurrently or successively at anytime during the taxable year • Employees deriving purely compensation income regardless of the amount, whether from a single or several employers during the calendar year, the income tax of which has not been withheld correctly (i.e. tax due is not equal to the tax withheld) resulting to collectible or refundable return INDIVIDUAL INCOME TAX • self-employed individuals receiving income from the conduct of trade or business and/or practice of profession • individuals deriving mixed income, i.e., compensation income and income from the conduct of trade or business and/or practice of profession • individuals deriving other non-business, nonprofessional related income in addition to compensation income not otherwise subject to a final tax INDIVIDUAL INCOME TAX • individuals receiving purely compensation income from a single employer, although the income of which has been correctly withheld, but whose spouse is not entitled to substituted filing • marginal income earners ⊸ Non-resident citizens receiving income from sources within the Philippines ⊸ Aliens, whether resident or not, receiving income from sources within the Philippines ⊸ Corporation shall include partnerships, no matter how created or organized. INDIVIDUAL INCOME TAX ⊸ Domestic corporations receiving income from sources within and outside the Philippines ⊸ Foreign corporations receiving income from sources within the Philippines ⊸ Estates and trusts engaged in trade or business CORPORATE AND PARTNERSHIP TAX ⊸ Many countries impose corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, on the income or capital of some types of legal entities ⊸ Similar tax may be imposed at state or lower levels ⊸ May also be referred to as INCOME TAX OR CAPITAL TAX INCOME TAX ON CORPORATE AND PARTNERSHIP INCOME ⊸ Corporations may be taxed on their incomes, property, or existence by various jurisdictions. Many jurisdictions impose a tax based on the existence or equity structure of the corporation. For example, Manila imposes a tax on corporations organized in that state based on the number of shares of capital stock issued and outstanding. Many jurisdictions instead impose a tax based on stated or computed capital, often including retained profits PHILIPPINE CORPORATE AND PARTNERSHIP TAX ⊸ Corporate income tax rate both for domestic and resident foreign corporations in Philippines is 30%, based on net taxable income. ⊸ Company tax is payable by domestic companies on all income derived from sources within and outside the Philippines. Foreign corporations, whether resident or nonresident, are taxable only on income derived from sources within the Philippines. PHILIPPINE CORPORATE AND PARTNERSHIP TAX ⊸ The corporate income tax rate both for domestic and resident foreign corporations is 30%. Excluded from the income tax are dividends received from domestic corporations; interest on Philippine currency bank deposit and yield or any other monetary benefit from deposit substitutes and from trust funds and similar arrangements; and other passive income previously subject to final taxes. ⊸ Regional operating headquarters are taxed at 10% on taxable income. PHILIPPINE CORPORATE AND PARTNERSHIP TAX ⊸ Special economic zone enterprises duly registered with the Philippines Economic Zone Authority are taxed at the rate of 5% on gross income in lieu of national and local taxes, except real property tax. The term 'gross income' refers to gross sales or gross revenue derived from the business activity within the Ecozone, net of sales discount, sales returns and allowances, less the cost of sales or direct costs but before deduction is made for administrative expenses and incidental losses during the taxable period. TAX DEDUCTION ⊸ Reduction of the income subject to tax, for various items, especially expenses incurred to produce income. ⊸ Subject to limitations or conditions ⊸ Allowed only for expenses incurred that produce current benefits, and capitalization of items producing future benefit is required, sometimes with exceptions INCOME TAX DEDUCTIONS ⊸ Except for taxpayers earning compensation income arising from personal services rendered under an employer-employee relationships where the only deduction provided that the gross family income does not exceed P250,000 per family is the premium payment on health and/or hospitalization insurance, a taxpayer may opt to avail any of the following allowable deductions from gross income: ▫Optional Standard Deduction - an amount not exceeding 40% of the net sales for individuals and gross income for corporations INCOME TAX DEDUCTIONS ▫ Itemized Deductions which include the following: ⋅Expenses ⋅Interest ⋅Taxes ⋅Losses ⋅Bad Debts ⋅Depreciation ⋅Depletion of Oil and Gas Wells and Mines ⋅Charitable Contributions and Other Contributions ⋅Research and Development ⋅Pension Trusts TAX EXEMPTIONS ⊸ Various tax systems grant a tax exemption to certain organizations, persons, income, property or other items taxable under the system. ⊸ may also refer to a personal allowance or specific monetary exemption which may be claimed by an individual to reduce taxable income under some systems ⊸ Tax exempt status may provide a potential taxpayer complete relief from tax, tax at a reduced rate, or tax on only a portion of the items subject to tax. EXEMPTION FROM INCOME TAX ⊸ An individual who is a minimum wage earner ⊸ An individual whose gross income does not exceed his total personal and additional exemptions ⊸ An individual whose compensation income derived from one employer does not exceed P 60,000 and the income tax on which has been correctly withheld EXEMPTION FROM INCOME TAX ⊸ An individual whose income has been subjected to final withholding tax (alien employee as well as Filipino employee occupying the same position as that of the alien employee of regional headquarters and regional operating headquarters of multinational companies, petroleum service contractors and sub-contractors and offshore-banking units, non-resident aliens not engaged in trade or business) EXEMPTION FROM INCOME TAX ⊸ Those who are qualified under “substituted filing”. However, substituted filing applies only if all of the following requirements are present : ▫ the employee received purely compensation income (regardless of amount) during the taxable year ▫ the employee received the income from only one employer in the Philippines during the taxable year ▫ the amount of tax due from the employee at the end of the year equals the amount of tax withheld by the employer ▫ the employee’s spouse also complies with all 3 conditions stated above EXEMPTION FROM INCOME TAX ⊸ Non-resident ▫ A citizen of the Philippines who establishes to the satisfaction of the Commissioner the fact of his physical presence abroad with a definite intention to reside therein ▫ A citizen of the Philippines who leaves the Philippines during the taxable year to reside abroad, either as an immigrant or for employment on a permanent basis ▫ A citizen of the Philippines who works and derives income from abroad and whose employment thereat requires him to be physically present abroad most of the time during the taxable year EXEMPTION FROM INCOME TAX ⊸ Overseas Filipino Worker, including overseas seaman ⊸ Charitable organizations ⊸ Religious groups ⊸ Duty Free shopping also termed as “Taxfree shopping” ⊸ Veteran workers ⊸ Under poverty PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTION (TAX REFORM ACT OF 1997) PROHIBITIONS ⊸ Section 20, Article III, Bill of Rights -Prohibition against imprisonment for non-payment of poll tax ⊸Section 28, Article VI, Legislative Department -Requirement of uniformity and equity in taxation ⊸Section 29, Article VI, Legislative Department -Prohibition against taxation appropriation for religious purposes PROHIBITIONS ⊸ Section 28, Article VI, Legislative Department -Prohibition against taxation of religious, charitable and educational entities(Religious and charitable institutions exempt from property taxes) ⊸Section 4, Article XVI, Education -Prohibition against taxation of non-stock , non-profit educational institutions and proprietary educational institutions (exempt from property and income taxes as well as customs duties except income derived from business activity not related to its educational purpose) TITLE III: VALUE ADDED TAX VALUE-ADDED TAX (VAT) OR GOODS AND SERVICES TAX (GST) ⊸ Form of consumption tax ⊸ From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price ⊸ From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the value added to a product, material, or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its manufacture or distribution ⊸ The manufacturer remits to the government the difference between these two amounts, and retains the rest for themselves to offset the taxes they had previously paid on the inputs. AMENDMENTS REPUBLIC ACTS National Internal Revenue Code of 1997 (NIRC) R.A. 8424 Tax Reform Act December 11, 1997 Starts: January 1, 1998 R.A. 8761 Act imposing Value-Added Tax (VAT) on certain services Section 5 February 16, 2000 Starts: January 1, 2001 R.A. 9010 Act to further defer the imposition of VAT Starts: January 1, 2003 February 27, 2001 REPUBLIC ACTS R.A. 9224 Act rationalizing Excise Tax on automobiles Section 149 August 29, 2003 Starts: October 4, 2003 Act to exclude several services from the coverage of VAT R.A. 9238 Act to reimpose Gross Receipt Tax (GRT) on banks and non-bank financial intermediaries performing or not performing Quasi-Banking functions Section 108, 109, 121, 122 Starts: January 1, 2004 February 5, 2004 REPUBLIC ACTS Act rationalizing provisions on Documentary Stamp Tax (DST) R.A. 9243 Section 174, 175, 176, 177, 178, 179, 180, 183, 186, 199 February 17, 2004 Starts: March 20, 2004 R.A. 9294 Act restoring tax exemption of Offshore Banking Units (OBUs) and Foreign Currency Deposit Units (FCDUs) Section 27, 28 Starts: May 21, 2004 April 28, 2004 REPUBLIC ACTS Act rationalizing provisions on Documentary Stamp Tax (DST) R.A. 9243 Section 174, 175, 176, 177, 178, 179, 180, 183, 186, 199 February 17, 2004 Starts: March 20, 2004 R.A. 9294 Act restoring tax exemption of Offshore Banking Units (OBUs) and Foreign Currency Deposit Units (FCDUs) Section 27, 28 Starts: May 21, 2004 April 28, 2004 REPUBLIC ACTS R.A. 9334 Act increasing Excise Tax Rates (ERT) imposed on alcohol and tobacco products Section 131, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 288 December 31, 2004 Starts: January 1, 2005 Act amending the sections of NIRC R.A. 9337 Section 27, 28, 34, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 116, 117, 119, 121, 148, 151, 236, 237, 288 Starts: July 1, 2005 November 1, 2005 May 24, 2005 REPUBLIC ACTS Act amending the sections of NIRC R.A. 9361 Section 110(B) November 21, 2006 Starts: December 13, 2006 Act amending the sections of NIRC R.A. 9504 Section 22, 24, 34, 35, 51, 79 June 17, 2008 Starts: July 6, 2008 R.A. 10001 Act reducing taxes on life insurance policies Section 123, 183 Starts: March 5, 2010 February 23, 2010 REPUBLIC ACTS R.A. 10021 Act to allow exchange of information by the BIR of tax matters pursuant to internationally-agreed tax standards Exchange of Information on Tax Matters Act of 2009 March 8, 2010 Section 6, 71, 270 R.A. 10026 Act granting income tax exemption to local water districts Section 27(C), 289-A March 11, 2010 ROLES OF BIR BUREAU OF INTERNAL REVENUE ⊸attached agency of Department of Finance ⊸COLLECTS more than one-half of the TOTAL REVENUES OF THE GOVERNMENT ⊸Main office: BIR National Office Bldg., BIR Road, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines INCUMBENT BIR OFFICIALS Commissioner of Internal Revenues Kim S. Jacinto-Henares Deputy Commissioner Information Systems Group Lilia C. Guillermo Deputy Commissioner Resource Management Group Celia C. King Deputy Commissioner Legal and Inspection Group Estela V. Sales Deputy Commissioner Operations Group Nelson M. Aspe ROLES AND FUNCTIONS SECTION 2: POWERS AND DUTIES OF THE BIR ⊸ Under supervision and control of Department of Finance ⊸Power and duty to comprehend assessment and collection of all national internal revenue ⊸Give effect to and administer the supervisory and police powers of the Code and other tax laws SECTION 3: CHIEF OFFICIALS OF THE BIR ⊸Chief to be known as “Commissioner of Internal Revenue” or Commissioner ⊸Along with 4 Deputy Commissioners SECTION 4-8: POWERS AND DUTIES OF THE COMMISSIONER ⊸Interpret provisions of the code and other tax laws ⊸Decisional power over matters relating to BIR and the code ⊸Power to obtain information, summon and examine testimonies ⊸Make assessments and prescribe additional requirements ⊸Delegate power ⊸Ensure provision and distribution of forms, receipts, and certificates SECTION 9-18: POWERS AND DUTIES OF REVENUE DISTRICT OFFICERS ⊸ Supervision of its districts; implement, administer, enforce the law; coordinate with regional offices and local governments ⊸ Examine efficiency of employees ⊸ Authorities to administer oaths, take testimony, make arrest and seizures ⊸ Reports violation GAME TIME!! WHO IS THE CURRENT COMMISSIONER OF INTERNAL REVENUES? Kim S. JacintoHenares The Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) is an attached agency of the . Department of Finance Corporate income tax rate both for domestic and resident foreign corporations in Philippines is is . 30 % What is a tax on a person's income, emoluments, profits arising from property, practice of profession, conduct of trade or business or on the pertinent items of gross income specified in the Tax Code of 1997? Income Tax •http://www.bir.gov.ph/index.php/tax-information/income-tax.html#it0015 •http://www.bir.gov.ph/index.php/tax-code.html •http://www.chanrobles.com/legal6nationalinternalrevenuecodeof1997.ht ml REFERENCES •http://quezoncity.gov.ph/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&i d=226&Itemid=347 •http://www.tradingeconomics.com/philippines/corporate-tax-rate http://www.gov.ph/section/republic-acts/ http://www.lawphil.net/statutes/repacts.html Thanks! HOPE YOU LISTENED!