Wireless Technology
advertisement

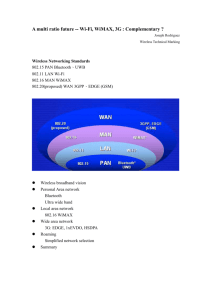
Chapter III Terrestrial Wireless Nyoman Suryadipta, ST, CCNA, CCNP Definition Terestrial (terrestrial) berarti terkait dengan tanah atau permukaan tanah (terra, tanah). (Wikipedia) Secara umum terestrial wireless mengacu pada sistem Transmisi nirkabel Gelombang elektromagnetik melalui jaringan transmisi berbasis darat (land-based transmitter) Wireless Terestrial = Wireless MAN (Metro Area Network) Global Wireless Standards WAN IEEE 802.16 WirelessMAN IEEE 802.11 WirelessLAN IEEE 802.15 Bluetooth MAN LAN 3GPP, EDGE (GSM) HiperMAN & HiperAccess ETSI BRAN HiperLAN/2 PAN ETSI BRAN : European Telecommunications Standards Institute – Broadband Radio Access Network GSC-9, Seoul IEEE 802 Standard Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers • • • • • • • 802.3 : CSMA/CD (Ehernet) 802.4 : Token Bus 802.5 : Token Ring 802.6 : MAN 802.11 : Wireless LAN 802.12 : Gigabit LAN 802.16 : Fixed Broadband Wireless Access System Electromagnetic Spectrum Very high frequency Ultra high frequency Super high frequency VHF UHF SHF 8 FM, television broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to30–300 aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications. Land MHz Mobile and Maritime Mobile communications, 10 m – 1 m amateur radio, weather radio 9 300–3000 MHz 1m– 100 mm Television broadcasts, microwave ovens, microwave devices/communications, radio astronomy, mobile phones, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee,GPS and two-way radios such as Land Mobile, FRS and GMRS radios, amateur radio 10 3–30 GHz 100 mm – 10 mm radio astronomy, microwave devices/communications, wireless LAN, most modern radars, communications satellites, satellite television broadcasting, DBS, amateur radio Fixed Terestrial Wireless (Fixed Broadband Wireless Access) • WLL • BWA • Radio Link (Backhaul) WLL (Wireless Local Loop) • • • • Konfigurasi Point to Point atau Point to Multipoint Frekuensi kerja 3,5 GHz Kapasitas sistem (Bandwidth) Base Station Kapasitas Base Station : Max. 64 x E-1 (Sektorial 180°) Interface to backhaul : N x E-1 Remote Kapasitas Remote Station : 64 Kbps s/d 256 Kbps Interface to user : 1 serial (V.35) & 1 Eth. 10/100 BaseT Misal : Merk AS 4000 (Serial) dan AS 4020 (IP Based) BWA (Broadband Wireless Access) • • • • • Misal : Walkair-SIEMENS Konfigurasi Point to Multipoint Frekuensi kerja 3,5 GHz dan 10,5 GHz Kapasitas sistem (Bandwidth) - Base Station 1 Sektor 1 IF-MUX (Maks. 8 BS-BU) (90°) Tiap BS-BU menempati kanal 1.75 MHz bandwidth per 1 Carrier: - 2 * E1 (4 Mbps) net payload - Max 16 Terminal Stations Jumlah kanal (carriers) per sector : - 3.5GHz: Max. 8 carriers per Sector (14 MHz) atau : 16xE1(32 Mbps) - 10.5GHz: Max. 8 carriers per Sector (14 MHz) atau : 16xE1(32 Mbps) Kapasitas sistem (Bandwidth) - Remote Kapasitas Remote Station : 64 Kbps s/d N x E-1 Maks. Bandwidth : 4 E1/BS-BU Interface to user : 1 E1, 1 serial (V.35) & 1 Eth. 10/100 BaseT Alvarion Aperto Airspan Redline Axxcelera SR Telecom Siemens Telsima BWA3 Redline Radio Link • • • • • • • • • • • • Frekuensi kerja 8 GHz dan 13 GHz Konfigurasi Point to Point Miniwave ODU 15/23/26/38GHz 1E1 2FSK Modulation 2E1 4-FSK Modulation Single “multiway” connector Indoor AC or DC supply G.703, or V.36 Interface Outdoor passive or active DC Only Misal : Nokia (4 x E1, Eth. 10/100 Base-T), Fresnel (4 x E1, Eth. 10/100 Base-T, E3), Harris Truepoint 5000 (STM-1), Ceragon (STM-1) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Architecture Base station (AP) serves up to 256 terminals (AT) per sector, using capacity sharing methods (multiplex gain) AP AP connected to public network AT SME custome r AT AT SOHO custome r Node B AT Multidwelling AT Residenti al custome r ATs access to the core network at high data rates with high QoS Mobile terminal AT HM or WLAN base station Other architectures: - Point-to-Point (PTP) - Multipoint-to-Multipoint (Mesh) GSC-9, Seoul HiperAccess Details (1 of 4) Network Topology Model AT AP (Access Terminal) Node B (Access Point) AT 1 ca rrier Node B - one APT per carrier - one APC per cell - several sectors per cell - several carriers per sector - overlapping cells (separated by frequency or polarization) APT AT n Core Network APC Node B Node B AT 1 ca rrier AT m se ctor UNI RNC APT AT APT = Access Point Transceiver APC = Access Point Con troller geogra phica l ce ll AP Sector SNI Air-Inte rfa ce HiperAccess Sy stem Cell with four sectors UMTS backhauling (HA AT is co-located with node B, HA AP is connected to RNC) GSC-9, Seoul PENGKANALAN PITA 10.5 GHz 10154 fc (DL) fc (UL) 10161 10185.5 10192.5 kanal 1 2 3 4 5 6 10507.5 10514.5 10521.5 10528.5 10535.5 10542.5 10511 10518 10525 10532 10210 10217 10574 10294 10238 10203 10199.5 10539 8 10549.5 10546 10556.5 10553 10504 8 x 7 MHz (UpLink) 10252 10266 10280 10259 10273 10287 2 3 4 5 6 10581 10595 10609 10623 10637 10616 10630 10644 6 x 14 MHz (UpLink) 10650 GuardBand 6 MHz 10294 10245 10602 10560 10560 10231 10588 10210 10206.5 7 6 x 14 MHz (DownLink) 10224 10567 10560 10196 10178.5 kanal 1 fc (UL) 10189 10171.5 8 x 7 MHz (DownLink) 10210 fc (DL) 10182 10164.5 10154 GuardBand 4 MHz 10175 10157.5 10504 10150 10168 10644 16 Link Budget Tools REDLINE Parameter yang dimasukkan Parameter RSSI yang dilihat RF Signal Strength RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) Advantages of Fixed Wireless • • • • • • • • 21 High Speed High Reliability “Five 99999” Long Range Rapid Deployment Low Operating Cost No Cables to Trench / Maintain Minimal right of way issues Weather-proof (below 10 GHz) The Fixed Wireless Space • Above 11 GHz – – – LMDS Systems Limited Range (Rain equates to < 5 km) Although high speed, overall cost of ownership extremely high RADIOS ARE EXPENSIVE, MULTIPLE REPEATERS OFTEN REQUIRED, LICENSED BANDS • Below 11 GHz – – – – 22 Licensed-Exempt vs Licensed Lower Frequency = longer range 1st Gen (Spread Spectrum) vs 2nd Gen (OFDM etc) WLAN based versus BFW Designed Common Fixed Wireless Applications • Backhaul – – – – Telecom / Carriers Wireless Internet Service Providers Mobile Wireless Backhaul Hotspot • Public Access – – – Multi Tenant Units / Multi Dwelling Units Small, Medium, Large Enterprises Residential • Private Networks – – – – 23 Schools, Government, Utilities, Hospitals Manufacturing, Oil Rigs, SCADA Video Surveillance Business Continuity / Disaster Recovery Common Applications Business Continuity / Disaster Recovery 24 Common Applications: Mobility Backhaul 25 Common Applications: Multi Tenant / Multi Dwelling 26 Common Applications: Telephony 27 Common Applications Business Continuity / Disaster Recovery 28 Common Applications: Private Networks: Schools / Hospitals / Government 29 Common Applications: Oil Rigs 30 Radio Propagation Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves when they are transmitted, or propagated from one point on the Earth to another, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of : reflection, diffraction, absorption and scattering. Radio Propagation • Augustin-Jean Fresnel 1788– 1827), was a French engineer who contributed significantly to the establishment of the theory of wave optics. Fresnel studied the behaviour of light both theoretically and experimentally. • Fresnel zone: D is the distance between the transmitter and the receiver; r is the radius of the first Fresnel zone (n=1) at point P. P is d1 away from the transmitter, and d2 away from the receiver. The concept of Fresnel zone clearance may be used to analyze interference by obstacles near the path of a radio beam The general equation for calculating the Fresnel zone radius at any point P in between the endpoints of the link where, Fn = The Fresnel Zone radius in metres d1 = The distance of P from one end in metres d2 = The distance of P from the other end in metres = The wavelength of the transmitted signal in metres Where r = radius in metres D = total distance in kilometres f = frequency transmitted in gigahertz. Fresnel Zone … from buildings Direct …and trees Multipath … gives rise to multipath and diffractive effects creating inter-symbol interference (ISI) and severe signal fluctuations…. 38 Antenna Systems Omni Directional Antenna System Type: Mutually Coupled Dual Omni Antennas Construction: Stacked Dipoles • • Directional / Sectorised Antenna System Type: Dual Directional Antennas Construction: Microstrip Omni Directional Antenna Systems o Dual Omnis for Monopole Towers Directional / Sectorised Antenna Systems o Directional Antenna for wall and side-of-tower mounts o Sectored Antenna Configurations (constructed from 6 Antenna Systems) Rain Fade • Rain fade refers primarily to the absorption of a microwave radio frequency (RF) signal by atmospheric rain, snow or ice, and losses are especially prevalent at frequencies above 11 GHz. Throughput Path Profile BPSK 1/2 QPSK 1/2 QPSK 3/4 16 QAM 1/2 16 QAM 3/4 64 QAM 2/3 64 QAM 3/4 Line of Sight 45.77 km 37.78 km 30.72 km 13.72 km 10.90 km 6.13 km 4.87 km NLOS Rural 10.18 km 7.29 km 6.38 km 4.00 km 3.50 km 2.51 km 2.19 km NLOS Suburban 5.03 km 3.68 km 3.25 km 2.10 km 1.85 km 1.36 km 1.20 km NLOS Urban 3.25 km 2.46 km 2.20 km 1.50 km 1.34 km 1.01 km 0.91 km SNR Downlink 4.0 dB 6.5 dB 9.0 dB 12.0 dB 15.5 dB 19.50 dB 21 dB SNR Uplink 3.0 dB 7.0 dB 9.0 dB 14.0 dB 16.0 dB 19.0 dB 21 dB RSSI Downlink -99.0 dB -96.5 dB -94.0 dB -91.0 dB -83.5 dB -83.5 dB -82 dB RSSI Uplink -99.0 dB -95.0 dB -93.0 dB -88.0 dB -83 dB -83.0 dB -81 dB System Throughput 1.45 Mbps 2.91 Mbps 4.36 Mbps 5.82 Mbps 8.73 Mbps 11.64 Mbps 13 Mbps