Click To
advertisement

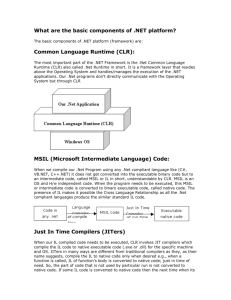
Unit -1 Chapter -1 REVIEW OF .NET FRAME WORK Topics to be covered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Introduction to .NET framework the Microsoft .NET strategy. Why is .NET? .NET product. .NET services. The origin of .NET technology. Brief history of .NET. The .NET framework application. The core feature of .NET framework. Benefits of the .NET approach: .NET framework 4.0 architecture(introduction and feature). Feature of .NET framework and asp.net 4.0 6. Execution environment of .NET framework application. (1). Common language runtime(CLR). Source code Compiler. Metadata. Microsoft Intermediate language(MSIL). Managed code. Class loader. Base class library or.net framework class library. Just in time compiler(JIT). Native machine code. Runtime manager. NET Assembly a. Kinds of assemblies-private and shared. b. Component of assemblies- manifest, module, type c. Function of assemblies. (2). Common language specification(CLS). (3). Common type system(CTS). (4). Garbage collector(GC). (5). How the garbage collector works. (6). Namespace The Microsoft .NET strategy. • Microsoft wanted to make the www more vibrant by enabling individual devices, computers and web services to work together intelligently to provide richer solution to the users. • By the intelligent ,integration of website on the internet, user can create a wide variety of value based applications such as unified banking services, electronic bill payment etc. • Microsoft calls this “web services” and the software strategy for implementing and delivering those services as “.NET” Contd…. • .NET is a software framework that includes everything required for developing software for web services. It integrates presentation technologies,componet technologies and data technologies on a single platform so as to enable users to develop internet application as easily as they do desktop system. Why .NET? • The world of computing till date has been chaotic. We have had various languages struggling to interoperate with each other, developers undergoing huge learning curves to shift from one language to another or from one application type to another, non-standard ways of modeling applications and designing solutions and huge syntactic differences between languages. The list goes on.... • Basically,microsoft introduce the .NET framework with the intention of bridging the gap in interoperability between application. Contd…. • This framework aim at integrating various programming languages and services. • It is designed to make significant improvement in code reuse, code specification, resource management,multilanguage development, security deployment and administration. • It consist of all the technologies that help in creating and running robust scalable and distributed applications. • The .NET offers a complete suite for developing and deploying applications. Contd…. The Microsoft .NET software solution strategy(suit) includes three key approaches: MS.NET STRATEGY MS .NET PLATFORM MS.NET PRODUCT AND SERVICES THIRD PARTY .NET SERVICES • Contd…. • MS .NET platform includes the following component that would help developing a new generation of smart internet services, and they are:.NET infrastructure and tools .NET framework. .NET user experience console application, windows application, libraries etc. .NET building blocks CLR,CTS,base class etc. .NET device software embedded system. • contd.. • Microsoft .NET product and services consist of the following:Windows .NET. MSN .NET. Office .NET. Visual studio .NET. Personal subscription services. bCentral for .NET. Contd… • Third-party .NET services: Third-party .NET services will provide opportunities to vast range of developers and users to produce corporate and vertical services using .NET platform. • The third-party languages are: COBAL Smalltalk Mercury Perl Python • Native languages are: VB C++ C# Brief history of .NET • The Microsoft .Net is a new internet technology or rather strategy introduced by Microsoft. .Net was originally known as the NGWS (Next Generation Windows Services) which was said to be an Internet based platform of Next Generation Windows Services. Before the official announcement of .Net, NGWS was the term used to describe the above phrase. • The .NET Framework was first released in in November 2000 and development continues today. Each version of the framework has betas, final versions, service packs, and patches associated with it. Version Version Number Release Date 1.0 1.0.3705.0 02/13/2002 1.1 1.1.4322.573 04/24/2003 2.0 2.0.50727.42 11/07/2005 Visual Studio Default in Windows VisualStudio.NET Visual Studio .NET 2003 Visual Studio 2005 3.0 3.0.4506.30 11/06/2006 3.5 3.5.21022.8 11/19/2007 Visual Studio 2008 4.0 4.0.30319.1 04/12/2010 Visual Studio 2010 Windows Server 2003 Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2 The origin of .NET technology Note: Before going into the detail of .NET feature further, we shall see how the concept of .NET was evolved over the past 10 years by Microsoft corp. • The current technology of .NET has gone through three significant phases of development. and they are:Interprocess communication Intermodule communication Intersite communication OLE TECHNOLOGY COM TECHNOLOGY .NET TECHNOLOGY Object linking and embedding (early phase-I 1990s) Component object module or model (phase-II 1995) Phase-III 1990’s later years • Contd… • Interprocess communication more than one independent process communicate with each other. Ex: crystal report with VB or VB.NET. • Intermodule communication integration of independent component or module developed in a particular language with each one is offering a particular service: VB 6.0 module ,java classes or packages etc. • Intersite communication cross language compatibility i.e. module developed in any language included in .NET package can be merged together to create an application. .NET Technology • .NET technology is a third generation component model. • This provides a new level of interoperability compare to COM technology. • COM provides a standard binary mechanism for intermodal communication. This mechanism is replaced by an intermediate language called Microsoft Language (MSIL) or simple IL in the .NET technology. • Various .NET language compiler enforce interoperability by compiling code into ILs which is automatically compatible with other IL modules. • An inherent characteristics of IL code is metadata. Monolithic approach vs .NET platform compile Source code Object code linking execution .NET TECHNOLOGY csc Source code Manage code IL CLR (loading, running and checking Exe/dll code JIT Native code The .NET framework • The .NET framework is one of the tools provided by the .NET infrastructure and tool component of .NET platform. • .NET platform provides a new environment for creating and running robust, scalable and distributed applications over the web. • C# derives much of the power from the .NET framework on which it runs. • The .NET framework provides an environment for building, deploying and running web services(ASP.NET) and other application (windows application). • It is an important component that supports building and running the advanced application and XML services. .NET PLATFORM • .NET .NE BUILDING .NET DEVICE BLOCK SERVICES SOFTWARE .NET USER EXPERENCE .NET INFRASTRUCTURE AND TOOLS It consist of three distinct technologies: CLR, framework base class and the top layer consist contains a set of classes for developing web services and to deal with the user interface. .NET FRAMEWORK ARCHITECTURE. NET INFRASTRUCTURE AND TOOLS VISUAL STUDIO .NET WINDOWS .NET .NET EXPERINCE SERVICES .NET FRAMEWORK .NET FRAMEWORK WEB SERVICES WINDOWS FORM WEB FORMS DATA & XML CLASSES (ADO.NET,SQL) WINDOWA FRAMEWORK BASE CLASS (I/O, STRONG SECURITY, COLLECTION ETC) COMMON LANGUAGE RUNTIME (DEBUG,EXCEPTION HANDLING,TYPE CHECKING,JIT,COMPILEER) WINDOWS PLATFORM .NET Framework C# VB.NET C++.NET Other Common Language Specification Framework Class Library ASP.NET Web Services Windows Forms Web Forms ASP.NET Application Services Controls Drawing Windows Application Services ADO.NET XML Threading IO Network Security Diagnostics Etc. Common Language Runtime Memory Management Common Type System Operating System Lifecycle Monitoring Visual Studio .NET . The core feature/objectives of .NET framework Provide a better execution environment for reducing versioning conflicts and saving the deploying time. Provide a safe execution environment. Provide an object- oriented programming environment. Provide a consistent API as well as consistent experience to developer across widely varying types of applications such as windows-based applications and web based applications. Provide integrity with different type of code. Elimination of the performance problems of scripted or interpreted environment. it is a complete set of tools for building ASP web application,xml web services, desktop application and mobile application. VB .NET,VB C++ .NET, VB C#.NET and VB J# .NET all uses the same integrated development environment (IDE),which allows them to share tools and facilities in the creation of mixed-language or cross language solution. .NET framework 4.0 architecture (feature). Enhanced globalization. Garbage collector. Code contracts. Design-time-only interop(interoperability) assemblies. Memory –mapped files. Feature of .NET framework and asp.net 4.0 • The main feature are:Enhanced syntax for Html encode. Enhanced on Microsoft Ajax library. Session state compression. Output cache extensibility. View sate mode for individual controls. Auto start asp.net application. Jquery integration. Execution environment of .NET framework application. 1. ). Common language runtime(CLR). Source code Compiler. Metadata. Microsoft Intermediate language(MSIL). Managed code. Class loader. Base class library or.net framework class library. Just in time compiler(JIT). Native machine code. Runtime manager. NET Assembly a. Kinds of assemblies-private and shared. b. Component of assemblies- manifest, module, type c. Function of assemblies. Common language runtime(CLR). • The common language runtime(CLR) is one of the most essential component of the .NET framework. • CLR is a runtime environment in which all the programs using .NET technologies are executed. • It also support cross language compatibility. COMPONENTS OF COMMON LANGUAGE RUNTIME(CLR) COMMON TYPE SYSTEM(CTS) INTEMIDIATE LANGUAGE(IL) EXECUTION SUPPORT FUNCTION SECURITY GARBAGE COLLECTION CLASS LOADER MEMORY LAYOUT • Contd.. • The CLR provides services such as: Loading and execution of programs. Memory allocation and memory isolation for application. Verification of type safety. Compilation of IL into native executable code. Providing metadata. Memory management(automatic garbage collection) Enforcement of security. Interoperability with other systems. Managing exceptions and errors Support for tasks such as debugging and profiling. Source code Assembly Managed code compiler IL and Metadata Metadata Engine linkers Other native code Exe code Class loader Verifier test Basic class library For type safety JIT compiler Native machine code Runtime manager output Contd… Flowchart of CLR activities for executing a program Contd… • While executing the program CLR plays an important role: The source code is compiled to IL while the metadata engine creates metadata information. IL and Metadata are linked with other native code if required and the resultant IL code is saved. During execution, the IL code and any requirement from the base class library are brought together in the class loader. The combined code is tested for type-safety and then compiled by the JIT compiler to produce native machine code, which is sent to runtime manager for execution. • Contd… • Source code:• Initially, a programmer writes a program in a particular programming language. This form of the program is called the source code or source program. • Compiler: A compiler is a special program that processes statements written in a particular programming language and turns them into machine language or "code" that a computer's processor uses. When we compile a program developed in a language that targeted the CLR instead of compiling the source code into machine-level code, at that time the compiler translates the source code into Microsoft intermediate language(MSIL) This ensure language interoperability. Microsoft intermediate language(MSIL) • MSIL or simple IL, is an instruction set into which all the .NET programs are compiled. • It contains instructions for loading,storing,initializing and calling methods. • It is low level language that the CLR understands. • When we compile any program written in a CLScompliant language, the source code is complied into MSIL. • In addition to IL,.NET includes a host of other technologies and tools that will enable us to develop and implement web-based application easily. Metadata • Metadata is data about data and it contains the description of code such as data types, classes and interface dependencies, location and the versions of the components used in the application. • It also defines the properites,methods and events associated with each member type. • It allows for true cross language integration. • It is always the job of the compiler not the programmer to produce the latest type metadata. • Metadata is used by the CLR complaint compilers to read many aspects of the application in .NET runtime environment. IL and metadata constitute as assembly. IL SOURCE CODE + METADATA COMPILER ASSEMBLY Assemblies contain metadata ,which describe the assembly’s internal version number and details of all the data and object type they contain. When we compile a an V.S complaint application, visual studio .NET create an assembly that is a single file with the extension .exe or .dll. • • • • • • .NET Assembly The net assembly is the standard for components developed with the Microsoft .NET . The .NET assemblies may or may not be excutable,i.e they might exist as the executable (.exe) file or dynamic link library (dll) file. All the .NET assemblies contain the definition of types, versioning information for the type,meta-deta and manifest. The assemblies can be used by single or multiple applications. An assembly can be a single file or it may consist of the multiple files. in case of multi file, there is one master module containing the manifest while other assemblies exist as non manifest modules. A module in .NET is a sub part of a multi file .NET assembly. Assembly is one of the most interesting and extremely useful areas of .NET architecture along with reflections and attributes. Component of assemblies- manifest, module, type Manifest module Metadata IL code type Properties , field, method • Manifest: describe the assembly ,it contains information like name and version number of the assembly, security permission required by the assembly. • Module: is either a dll or exe file. It contains IL and metadata. • Type : is a class that contains data and logic affecting the data. These class contains information like propreties,fields and methods. Kinds of assemblies-private and shared. • There are two kinds of assemblies in .NET described below; • 1. private assemblies: private assemblies are simple and normally used by a single application, and are stored in the application’s directory. These assemblies are often used to deploy language-specific assemblies work in side-by-side execution because the application has a separate product id for each language and installs satellite assemblies in a language specific subdirectory for each language. • 2. shared assemblies: a shared assembly is normally stored in the global assembly cache, which is a repository of assemblies maintained by the .NET runtime. for all calling assemblies within the application, the same copy of the shared assembly is used from its original location. Hence shared assemblies are not copied in the private folders of each calling assembly. Each shared assembly has a four part name including its face name, version ,public key token and culture information. the public key token and version information makes it almost impossible for two different assemblies with the same name or for two similar assemblies with different version to mix with each other. Function of assemblies. Supports execution. Provides security Support deployment. Provide unique identification. Tracks version. Managed code • As we know that CLR is responsible for managing the execution of code compiled for .NET platform. • The code that satisfies the CLR ,the foundation of the .NET Framework at runtime in order to execute is referred to as managed code. • Managed code supplies the metadata necessary for the CLR to provide services such as memory management, cross-language integration, code access security, and automatic lifetime control of objects. All code based on IL executes as managed code. • Compiler that are compatible to .NET platform generates managed code • The managed code generated by compiler is called IL code. Class loader • When we execute the .exe or .dll file, the code which is converted into IL and all the other relevant information from the base class library is sent to class loader. • The class loader loads the code into the memory. Base class library or.net framework class library. • The .NET framework class library is a collection of reusable types that tightly integrated with the CLR. • These are inbuilt classes which makes development very easy. • The .NET class library is unique for framework that means we have to study it once and we use it for any .NET language based application development. • These are object oriented class from which our own manage code can derived functionality. • It enable us to accomplished range of common programming task such as data collection,database connectivity, string management etc. • We can use class library for development of console application,windows application,ASP.NET application,XML web services etc. JIT-manage code execution • Before the code can be executed, the .NET framework needs to convert the IL into native or CPU-specific code. • The just-in-time complier translates the code from IL into managed native code. • During the process of compliation,the JIT compiler compiles the code that is required during execution instead of compiling the complete IL code. • When an uncompiled method is invoked during execution, the JIT compiler converts the IL for that method into native code. • During JIT compilation, the code is also checked for type safe. Type-safe • This feature ensures that the objects are always accessed in compatible way. Therefore, the CLR will prohibit a code from assigning a 10-byte value to an object that occupies 8byte. • Type safety also ensures that objects are safely isolated from each other and therefore safe from any malicious corruption. Native machine code • Native code is computer programming (code) that is compiled to run with a particular processor and its set of instructions. Runtime manager • After translating the IL into native code,the converted code is sent to the .NET runtime manager. • The .NET runtime manager executes the code. • While executing the code, a security check is performed to ensure that the code has the appropriate permission for accessing the available resources. .NET platform-Security management • In case of .NET platform, security is achieved through the code access security(CAS) model. • In this model, the CLR enforces restriction on managed code through the use of object called permission. • The CLR allow the code to perform only those tasks for which it has permission. • In other words, the CAS model specifies what the code can access instead of specifying who can access resources. 6. Execution environment of .NET framework application…CONTD… (2). Common language specification(CLS). (3). Common type system(CTS). (4). Garbage collector(GC). (5). How the garbage collector works. (6). Namespace Common type system(CTS) • The .NET framework provides multiple language support using the features known as common type system(CTS) that is built into CLR. • CTS support a variety of type and operation found in most programming languages and therefore does not required type conversion. • CTS defines how data types are declared, used and managed in the code at runtime. • The CTS also defines the rules that ensure that the data types of objects written in various languages are able to interact with each other. Common language specification(CLS) • CLR consists of a set of common rules followed by all the languages of the .NET framework. This set of rules is known as common language specification(CLS). • CLs defines a set of rules that enables interoperability on the .NET platform. • These rules serves as a guide to the third-party compiler, designers and library builders. • CLS enable an object or application to interact with the object or application of other language. • The class that follow the rules specified by CLS are termed as CLS compliant class. • The classes defined in the .NET framework class library are CLS compliant. Garbage collector(GC). • The garbage collector is a tool for memory management provided by .NET framework. • The garbage collector(GC) runs in a low-priority thread and checks for un-reference dynamically allocated memory space. • If it finds some data that is no more referenced by any variable/reference, it re-claims it and returns the occupied memory back to the operating system so that it can be used by other programs as necessary. • The presence of standard garbage collector free the programmer from keeping track of slack data. How the garbage collector works. • The garbage collector examines how objects are arranged in memory and identify all those objects that can be used by the running programme by using some references. When a garbage collection starts ,it looks at a set of references called the ‘gc roots’. These are memory locations that are designated to be always reachable for some reason, and which contain references to objects created by the program. It marks these objects as ‘live’ and then looks at any objects that they refrence;it marks these as being ‘live’ too. It continues in this manner, iterating through all of the object it knows are ‘live'. it marks anything that they reference are also being used until it can find no other objects. • An object is identified, by the garbage collector, as referencing another object if it, or one of its super classes that contains the other object. once all of these live objects are known, any remaining objects can be discarded and the space can be re-used for new objects. the net reduces memory so that there will be no gap which means that free memory is always located at the end of a heap and makes allocating new objects very fast. If an object has a finalizer,it is not immediately removed when the garbage collector decides it is no longer ‘live'. these objects usually require more than one garbage collection to be removed from memory, as they will survive the first time they are found to be unused. Benefits of the .NET approach: • Microsoft has advanced the .NET strategy in order to provide a number of benefits to developer and user. • Some of the benefits are: Simple and faster system development. Rice object model. Enhanced builting-in functionality. Many different ways to communicate with the outside world. Integration of different languages into one platform. Easy deployment and execution. Wide range of scalability. Interoperability with existing applications. Simple and easy-to-build sophisticated development tools. Fewer bugs. Potentially better performance. Application that are supported by the .NET platform • • • • • • • Console application. Windows application. Developing windows control. Developing ASP.NET project. Creating web controls. Providing web services. Developing .NET component library.