DNA Structure
advertisement

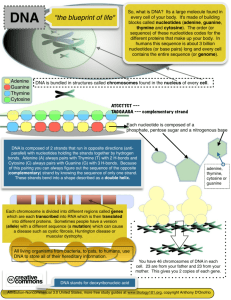
Hereditary material is found in the nucleus of each cell. Chromosomes are passed down from cell to cell during cell division. These chromosomes consist of protein and DNA Scientists knew that Chromosomes in cells were the Units of Heredity, but they did not know if it was the Protein component (Histones) of the Chromosomes or if it was the DNA component of a chromosome that was the important. Scientists also knew that Viruses consist of nothing more than DNA and Protein, so they radioactively labeled the DNA in some viruses. Then they let those viruses infect bacteria to see whether the radioactively labeled DNA was transferred into the bacteria. This resulted in the Radioactively labeled DNA being passed onto the bacteria During the second test, only the protein capsids of the viruses were radioactively labeled. When they let those viruses infect the bacteria, no radioactivity was found inside the bacteria. So they concluded that it must be the DNA, not the protein, that was the hereditary component that gets passed on. DNA STRUCTURE Recall that to build a nucleic acid, whether it be DNA or RNA, cells combine Nucleotides together to form long chains. As illustrated in the “Dehydration Synthesis” A.K.A. “Condensation Synthesis” reaction shown below. Also recall that DNA is built from four different DNA nucleotides. All four have the same pentose sugar (deoxyribose), the same phosphate group, but they differ in the type of Nitrogenous base that comes off of the Deoxyribose. This part will vary from one base to another It is at this carbon that an oxygen is missing, therefore it is called “Deoxyribose” sugar There are two categories of Nitrogenous bases. One category of nitrogenous base will have a double ringed structure. This group is called the PURINES, includes Adenine and Guanine. The other category which have a single-ringed structure. This group, called PYRIMIDINES include Cytosine and Thymine. Note the letter “Y” in Pyrimidine, Cytosine and Thymine – good memory device. To build a complete molecule of DNA, one strand of DNA will bond with a second strand, then both will form a spiral twist. This unique structure is known as a “DOUBLE HELIX” The two strands are held together by weak Hydrogen Bonds between each adjacent base. But the base pairing is very specific. A double ringed Purine will always hydrogen bond to a single ringed Pyrimidine. But it is even more specific than that. An Adenine will always pair and bond with a Thymine, while Cytosine will always pair and bond with a Guanine. One should also note that between each A and T there will be two H-Bonds, while between each C and G there will always be three H-Bonds. Good memory devices : “TA-Two” like “tatoo” and “C –G –Three” So you should be able to look at DNA and determine which base is a double-ringed Purine and which are a single-ringed Pyrimidine. Then you should observe how many H-bonds are found between the bases. From the above information you should then be able to identify each base. Try it. Try this pairing first, take note that there are only two H-bonds therefore; think “TA-Two”. It must be Adenine to Thymine. Then I need to recall that “Any Geek Can Teach”, in this mnemonic my first two words represent the two Double-Ringed Purines. So the double ringed base in this pairing has to be either adenine or guanine, but it can only be Adenine, because only adenine uses two H-bonds Try this pairing now, take note that there are three Hbonds therefore; think “c-g3”. It must be Cytosine to Guanine. Then I need to recall again that “Any Geek Can Teach”, in this mnemonic my first two words represent the DoubleRinged Purines. So the double ringed base in this pairing has to be either adenine or guanine, but it can only be GUANINE, because only guanine uses three H-bonds. The other base must be Cytosine. First noticeable difference is in the sugar found in RNA Nucleotides. The 5-carbon (pentose) sugar has all its oxygens. It is called “RIBOSE” sugar We will study RNA- Ribonucleic Acid in more detail later on this chapter. But for now we just need to know the basic differences between it and DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid The second noticeable difference is that one of the four nitrogenous bases is different than the DNA bases. Recall, “Any Geek Can Teach” – DNA. “Any Geek Can U” – RNA. The DNA base Thymine is replaced with the RNA base Uracil A third difference is that RNA is never double stranded RNA is not Helical either, it is just straight (linear)